Methods for detoxifying a lignocellulosic hydrolysate
A technology for lignocellulose and hydrolyzate, which is applied in the field of detoxification of lignocellulose hydrolyzate, and can solve problems such as raising maintenance cost and pipeline blockage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1: Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass (Section 5.1)
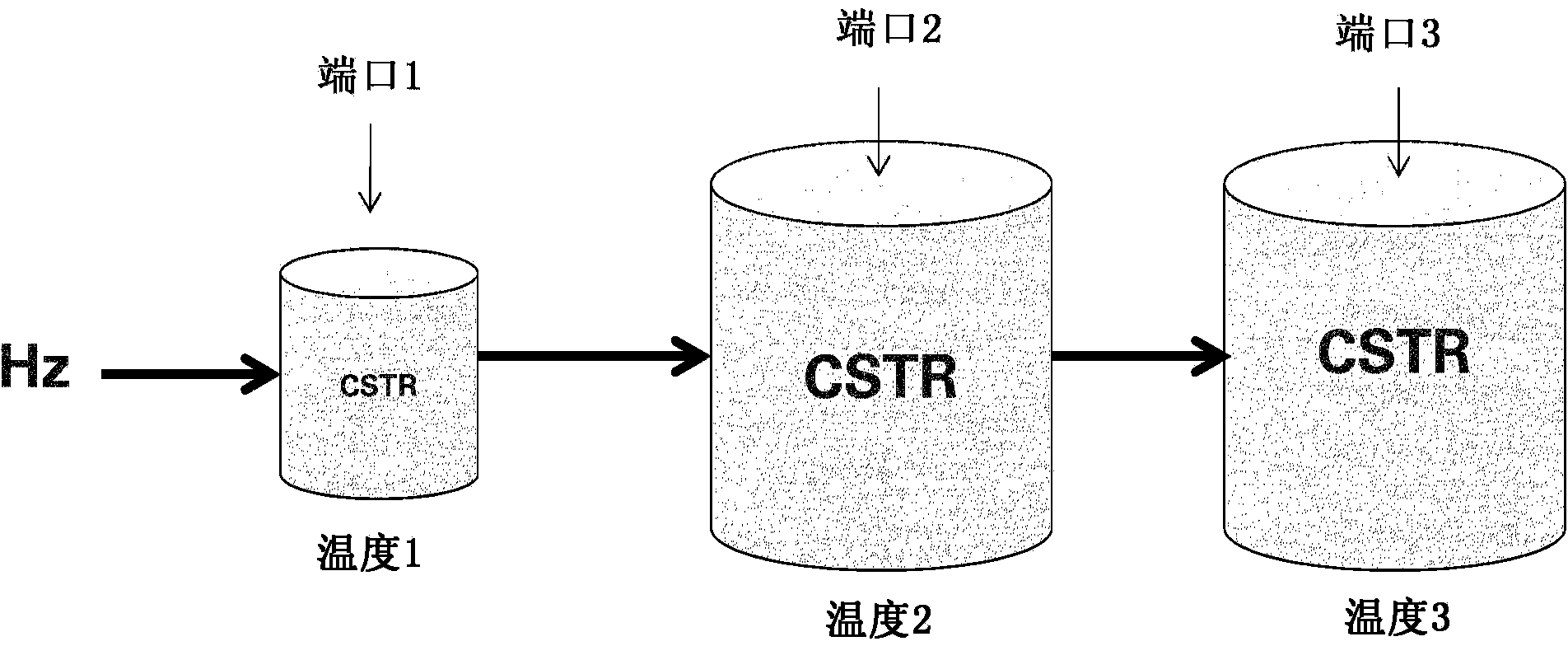
[0091] Lignocellulosic biomass (such as energy cane or sugarcane) is harvested and cut to size using a feed chopper, inoculated with a Lactobacillus bacterial preparation and stored in agricultural bags until use. Prior to dilute acid hydrolysis, lignocellulosic biomass was removed from the bags and washed with process water to remove organic acids, then dehydrated using a screw press. The biomass is then sent to a pressurized reaction chamber (ie hydrolyzer) along with water and sulfuric acid (0.2% to 3%). The liquid / solid ratio of the slurry is minimized to maximize the concentration of dissolved sugars in the hydrolyzate after hydrolysis. The residence time in the hydrolyzer and the temperature of the hydrolyzer depend on the parameters of the biomass (such as humidity and dextran level). Generally, the temperature of the hydrolyzer is in the range of 120°C to 180°C, and the residence time is in the r...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2: Two-step detoxification of sugarcane hydrolyzate using magnesium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide - batch process (Section 5.2)
[0097] Materials and methods (Section 5.2.1)
[0098] Sugarcane DP 110105 (section 5.2.1.1)
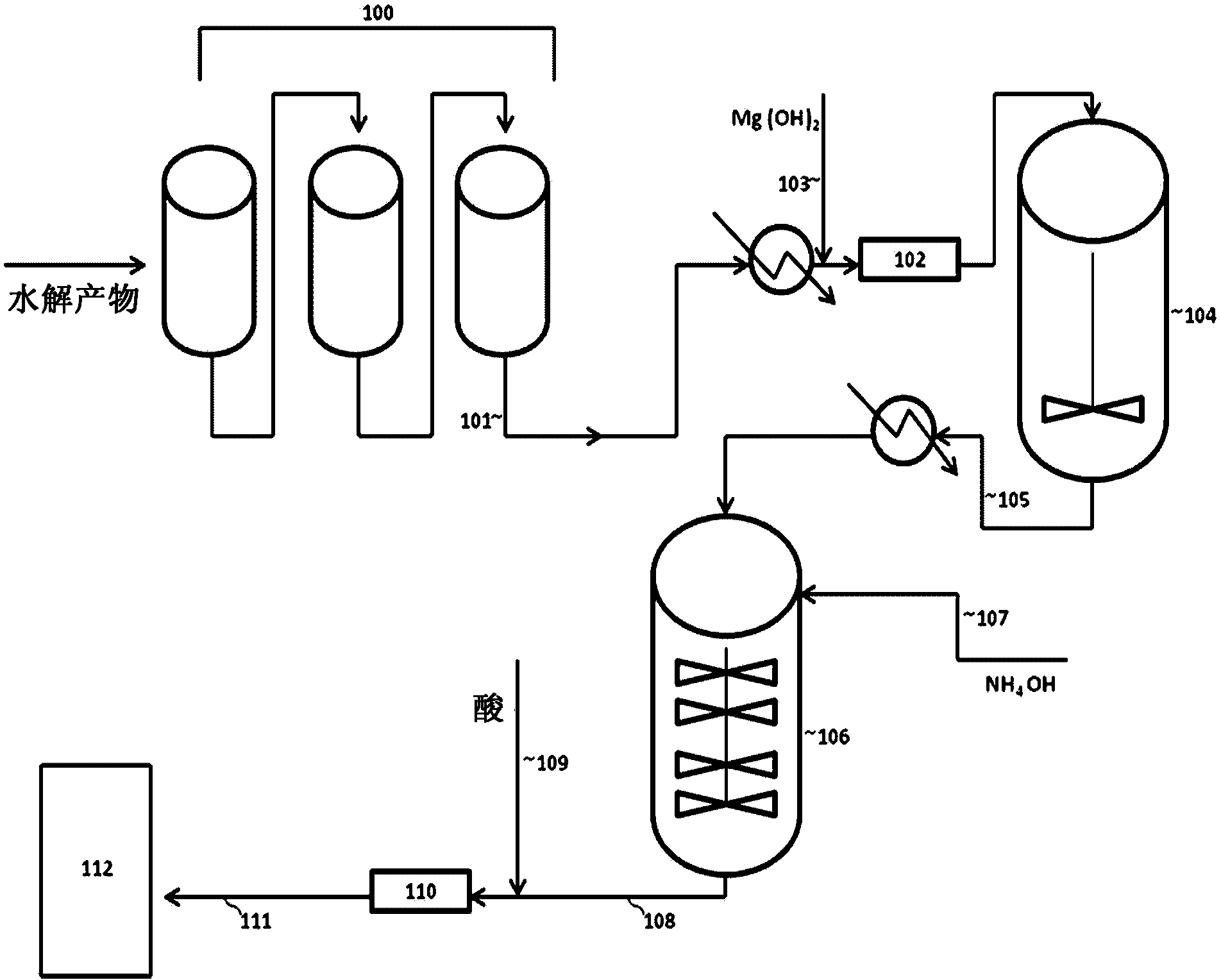
[0099] The hydrolyzate DP 110105 obtained from sugar cane was placed in a 1 L reactor vessel suitable for overhead stirring, heated to 47°C by means of a heating mantle and mixed vigorously. While the hydrolyzate solution was warming, the target amount of magnesium hydroxide slurry (ie supersaturated solution of magnesium hydroxide in water) was weighed. The total amount of magnesium hydroxide added to the hydrolyzate was determined from the titration of the hydrolyzate solution with sodium hydroxide. See Martinez et al., 2001, Biotechnol. Prog. 17(2):287-293. A magnesium hydroxide slurry was added to the hydrolyzate solution at a dose of 15.73 g / Kg hydrolyzate at 47°C while the solution was vigorously mixed and held for 5 minutes. Aft...
Embodiment 3
[0111]Example 3: Two-step batch detoxification procedure of sugarcane hydrolyzate DP 110505 with magnesium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide - effect of pH (Section 5.3)
[0112] Materials and methods (Section 5.3.1)
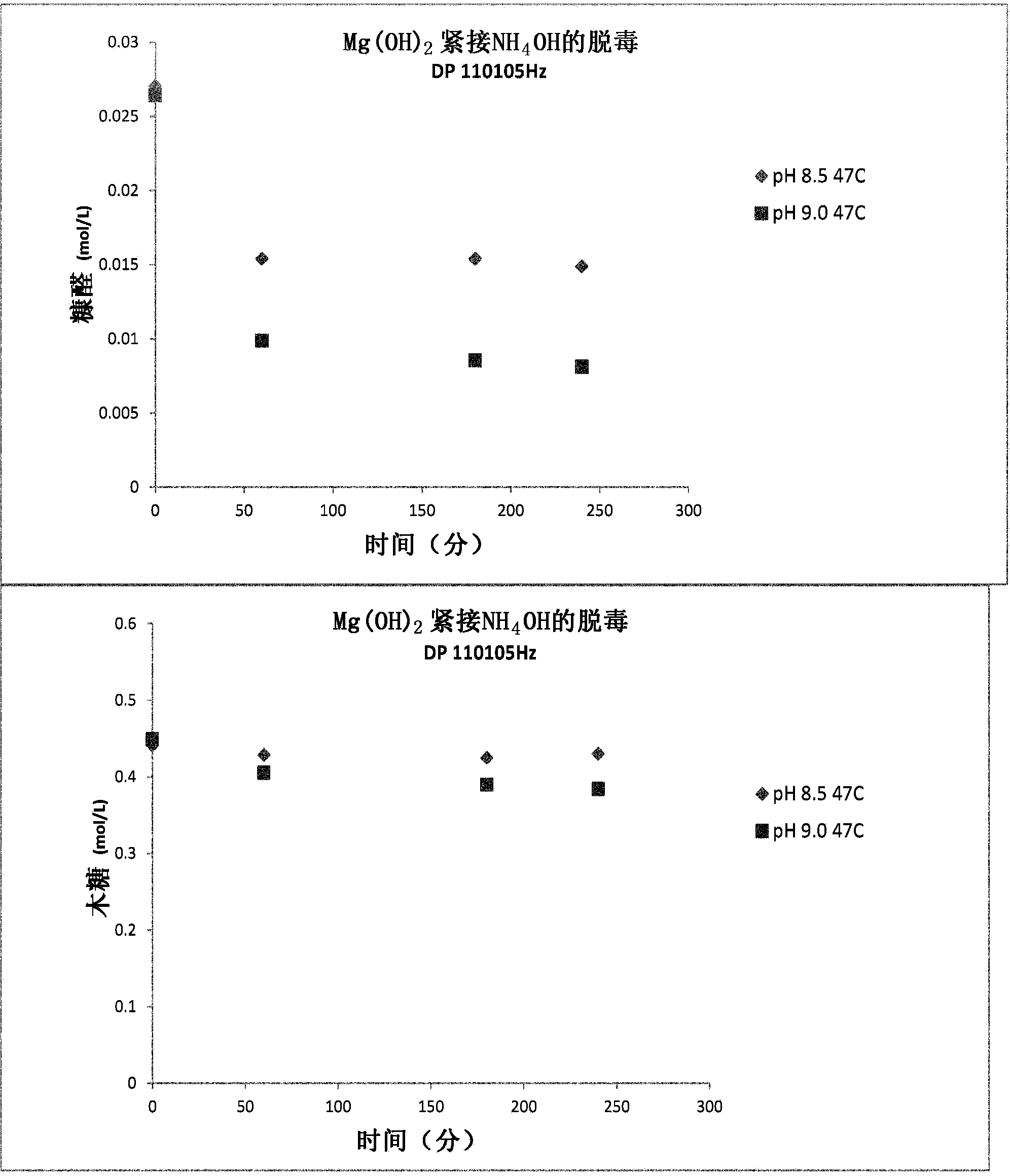
[0113] Detoxification from sugarcane DP110105 was performed using a two-step batch detoxification process using magnesium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide in a manner similar to that described in Section 5.2.1.2. Experiments were performed to measure the effect of pH on selectivity (furfural elimination versus xylose degradation) at various time points after ammonium hydroxide.
[0114] Yellow hydrolyzate DP 110105 (800 g) was placed in a 1 L unbaffled reactor vessel suitable for overhead stirring, heated to 47°C by a heating mantle and stirred at 420 rpm. After heating the hydrolyzate solution to the desired temperature, a slurry of magnesium hydroxide was added rapidly to the hydrolyzate solution at 47°C to pH 5.8 while stirring and held for 5 minutes. Ammoni...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com