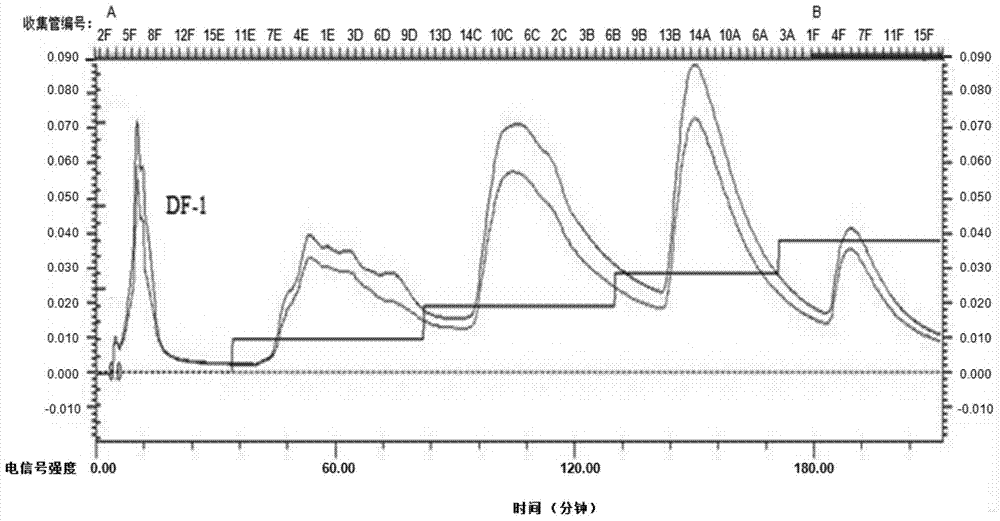
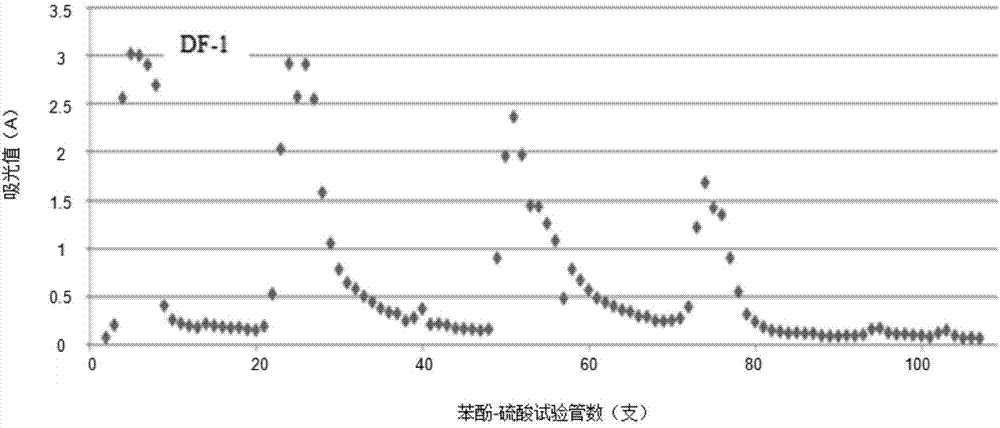
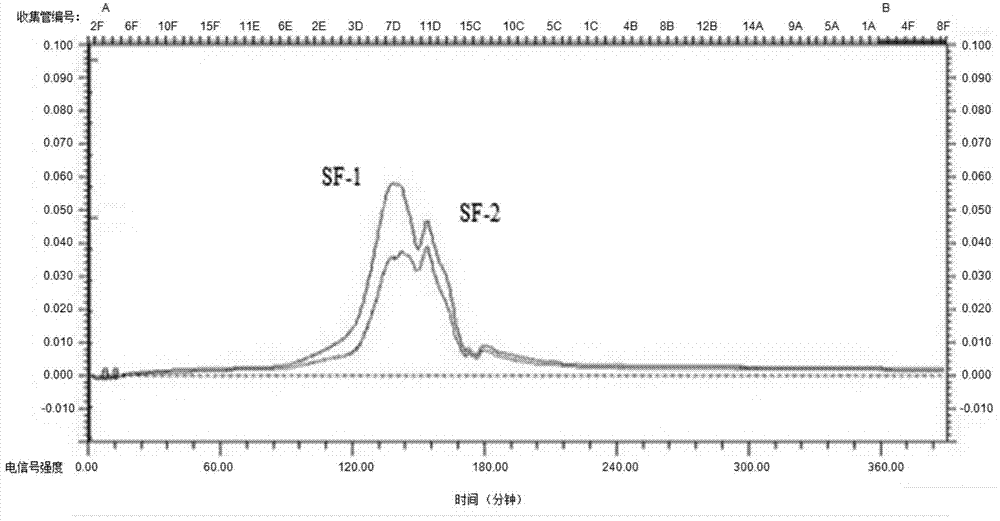
Extraction and purification method and application of fermented astragalus polysaccharide
A purification method, technology of astragalus polysaccharides, applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, digestive system, pharmaceutical formulas, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the yield of fermented astragalus polysaccharides, reduce complex operation steps, facilitate full development and high efficiency Utilization, the effect of easy separation and extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] In this example, the bacterial species co-fermented with Astragalus is a non-lactolytic streptococcus isolated from chicken intestines ( Streptococcus alactolyticus ) LZMYFGM9, its deposit number is CGMCC No.4227. Preservation date: October 19, 2010; Preservation unit: General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee; Preservation unit abbreviation: CGMCC; Preservation unit address: No. 3, Yard No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing; the strain See Chinese patent document ZL 201210141827.5 (name of invention: a non-lactolytic streptococcus and its application) for its culture characteristics.
[0049] In this example, the determination of the protein content in the fermented astragalus polysaccharides was carried out by using the BCA protein concentration determination kit of Suleibao Company.
[0050] The mass fraction of crude drug Radix Astragali in the present embodiment fermented Radix Astragali is...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The extraction and purification of crude drug astragalus polysaccharide includes the following steps:
[0064] (1) Weigh 312 g of crude drug Astragalus root powder (passed through a 20-mesh sieve), soak in 20 times the amount (6240 mL) of 85% ethanol at room temperature for 8 h, soak at 85 °C for 1 h, filter, and extract the residue once more . The dregs were dried in a blast drying oven at 50 ℃ until there was no alcohol smell and used to extract the crude drug astragalus polysaccharide.
[0065] (2) Add 10 times the amount (mL / g) of pure water to the dregs obtained in step (1), soak at room temperature for 8 h, then soak in a water bath at 85 °C for 1 h, and pour out the supernatant. Repeat this step two more times. The three supernatants were combined, after centrifugation, the supernatant was concentrated to 1:5 using a Sartorius Vivaflow 200 ultrafilter with a molecular weight cut-off of 5000 Dal, and then assisted by heating in a water bath at 90 °C to concentra...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0078] (1) Weigh 400 g of the fermented astragalus freeze-dried powder prepared in Example 1 (through a 20-mesh sieve), soak in 20 times the amount (8000 mL) of ethanol with a volume percentage of 85% at room temperature for 9 hours, soak at 85°C for 1 hour, and filter , and the filter residue was extracted once more. The dregs are dried in a blast drying oven at 50°C until there is no alcohol smell and used to extract fermented astragalus polysaccharides.
[0079] (2) Add 15 times the amount (mL / g) of pure water to the dregs obtained in step (1), soak at room temperature for 9 hours, then soak in a water bath at 85°C for 1 hour, and pour out the supernatant. Repeat warm immersion and extraction of the filter residue twice: add 15 times the amount (mL / g) of pure water to the medicinal residue, soak at room temperature for 9 hours, then soak in a water bath at 85°C for 1 hour, and pour out the supernatant.
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com