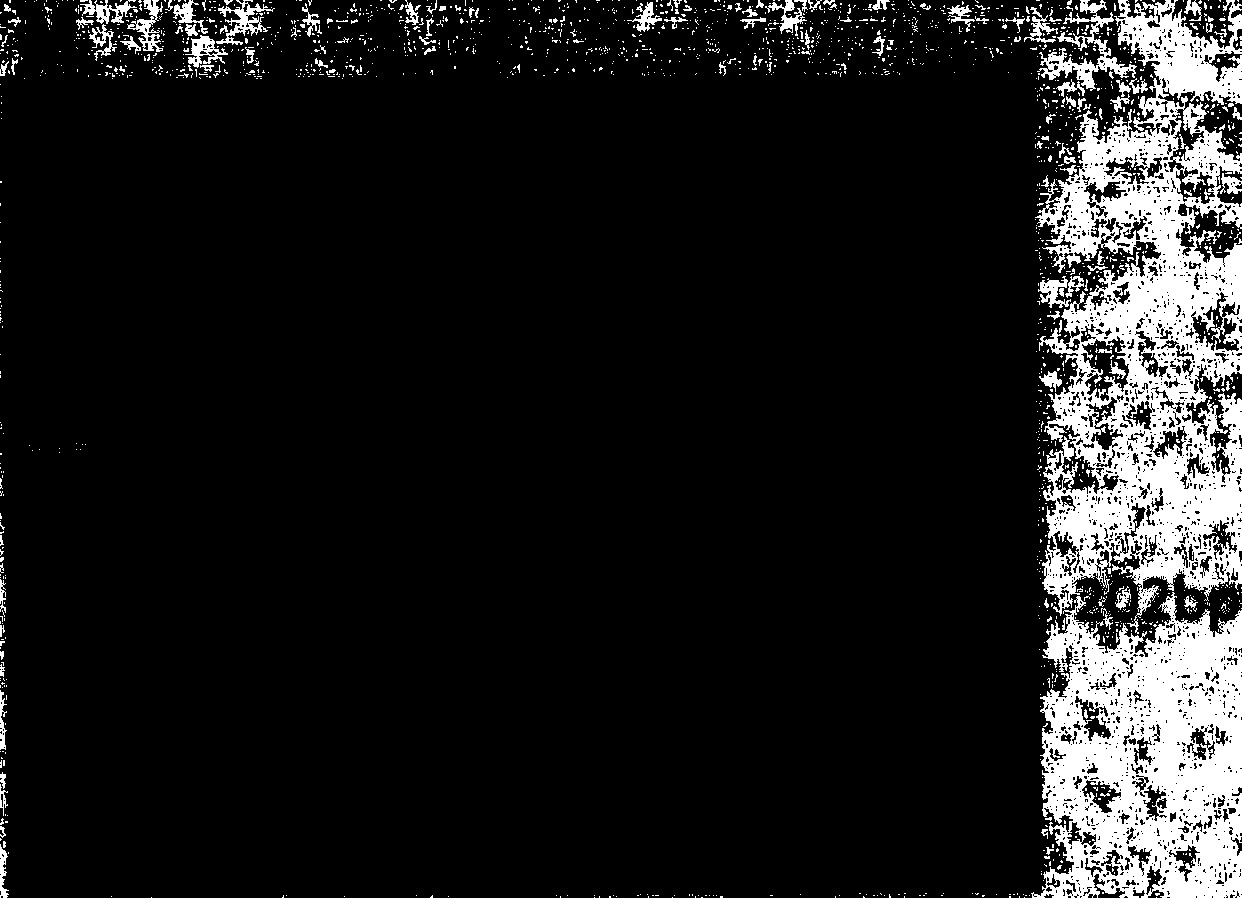Method for detecting horsemeat in food
A technology for horse meat and food, applied in the field of detection of horse meat components in food using PCR technology, can solve problems such as endangering life and health, lack of sound and unified rapid detection standards for cooked meat products, and harming the interests of consumers, etc., to overcome excessive fragments Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The 6 pairs of primers provided by the present invention, the length of the target fragment amplified by PCR reaction is as follows, No. 1 primer pair: 183bp; No. 2 primer pair: 202bp; No. 3 primer pair: 231bp; No. 4 primer pair: 266bp; No. 5 primer pair: Primer pair: 268bp; primer pair No. 6: 300bp.
[0019] 1. Genomic DNA extraction of meat products
[0020] Process the sample into minced meat, take 30mg and add it to a 1.5ml EP tube; add 500μl lysate (1M tris-Hcl pH8.0; 0.5M EDTA pH8.0; 5M Nacl; 0.5% N-Lanroyl Sarc0sine; proteinase K; RNaseA ) at 70°C for 0.5-1h or overnight at 50°C, centrifuge (12000r / min, 5-15min), take the supernatant; add an equal volume of phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) for extraction; take Add 40μl Nacl and 1ml ice ethanol to 400μl water phase, place on ice for 30min; centrifuge (12000r / min, 5min), discard supernatant; wash 3 times with 1ml70% absolute ethanol, dry in the air; add 70-100μlTE, let stand for 30min .
[0021] ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Validation of commercially available processed horse meat products
[0056] 1. Extracting the genomic DNA of horse meat: the method is the same as that of extracting the genomic DNA of meat products in Example 1.
[0057] 2. PCR verification:
[0058] Using the aforementioned genomic DNA as a template, PCR was performed with the 6 pairs of primers provided in the present invention.
[0059] Reaction system: 20 μl (template: 1 μl; dNTP 0.4 μl; 10×PCR buffer 21 μl; upstream and downstream primers 0.8 μl; rTaq 0.4 μl; ddH 2 O14.6 μl).
[0060] Reaction conditions:
[0061] Step 1: 94°C for 5 minutes;
[0062] Step 2: 94°C for 30s, 62°C for 30s, 72°C for 30s, 30 cycles
[0063] The third step: 5min at 72°C.
[0064] 3. Agarose gel electrophoresis verification
[0065] 2% agarose gel was prepared, and the gel preparation process was the same as that described in Example 1. Voltage 50V, electrophoresis 1h, PCR amplification results were analyzed by gel phase formation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com