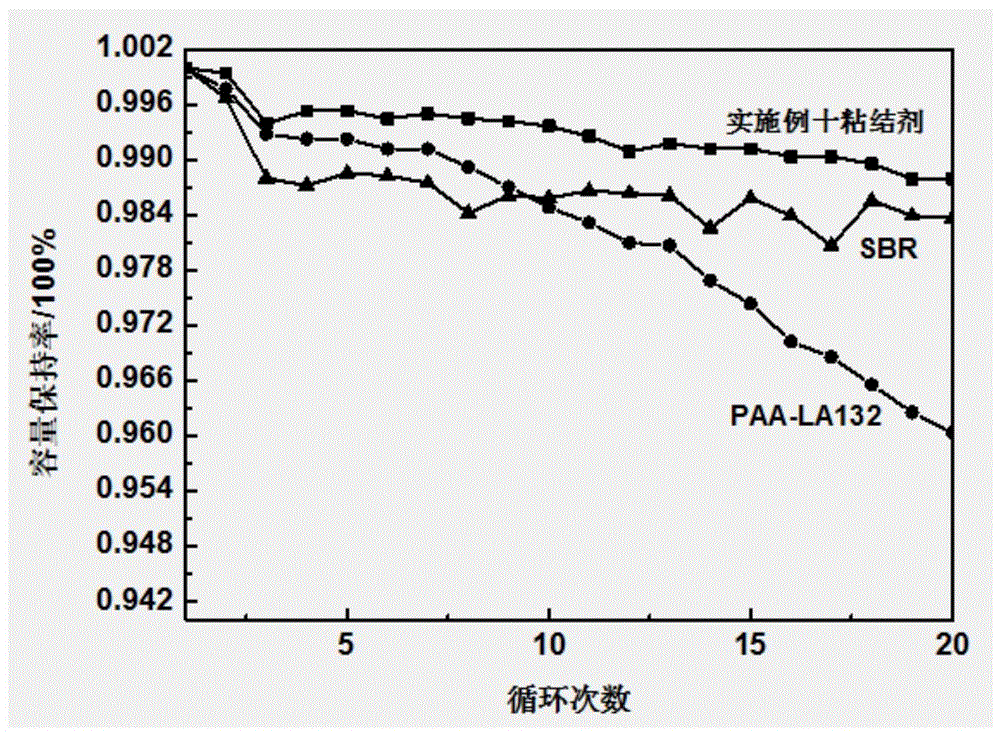
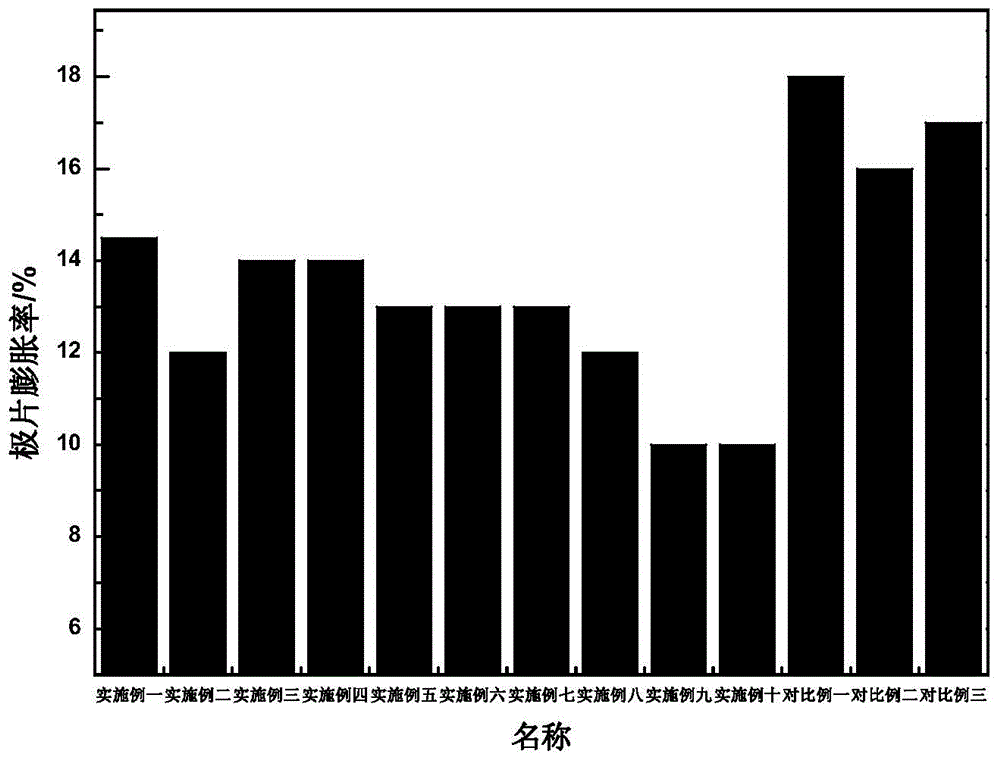
Polyacrylate aqueous binder for lithium-ion battery electrode material, preparation method and lithium-ion battery pole piece
A technology of polyacrylate and water-based binders, which is applied in the field of lithium-ion battery pole pieces, preparation, and water-based binders for lithium-ion battery positive and negative materials. It can solve the problem of insufficient flexibility and adhesion of water-based binders And problems such as poor flexibility and limited effect of pole piece expansion, to achieve a significant effect of inhibiting expansion, adjustable softness, and the effect of inhibiting expansion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0052] The preparation method of lithium ion battery electrode material aqueous binding agent of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) Dissolve all the hydrophilic monomers and 1-80% (mass fraction) of the lipophilic monomers in deionized water, fully stir at a temperature of 40-90°C, and the stirring speed is 100-500 rpm, high-purity N 2 Oxygen removal for 0.5-2.5 hours;
[0054] (2) Add 0.2 to 2% of the total mass of the hydrophilic monomer and the lipophilic monomer to initiate the polymerization reaction, and the remaining lipophilic monomer is added in batches or dropwise during the reaction, and the polymerization temperature is 50-90 ℃, the time of the polymerization reaction is 5-15 hours, the stirring speed is 100-500 rpm, after the reaction is complete, the residual monomer is removed under reduced pressure, and the filter cloth is passed through 100-400 mesh to obtain a solid content of 15-50%. Water-based binder with a viscosity of 50-...
Embodiment 1
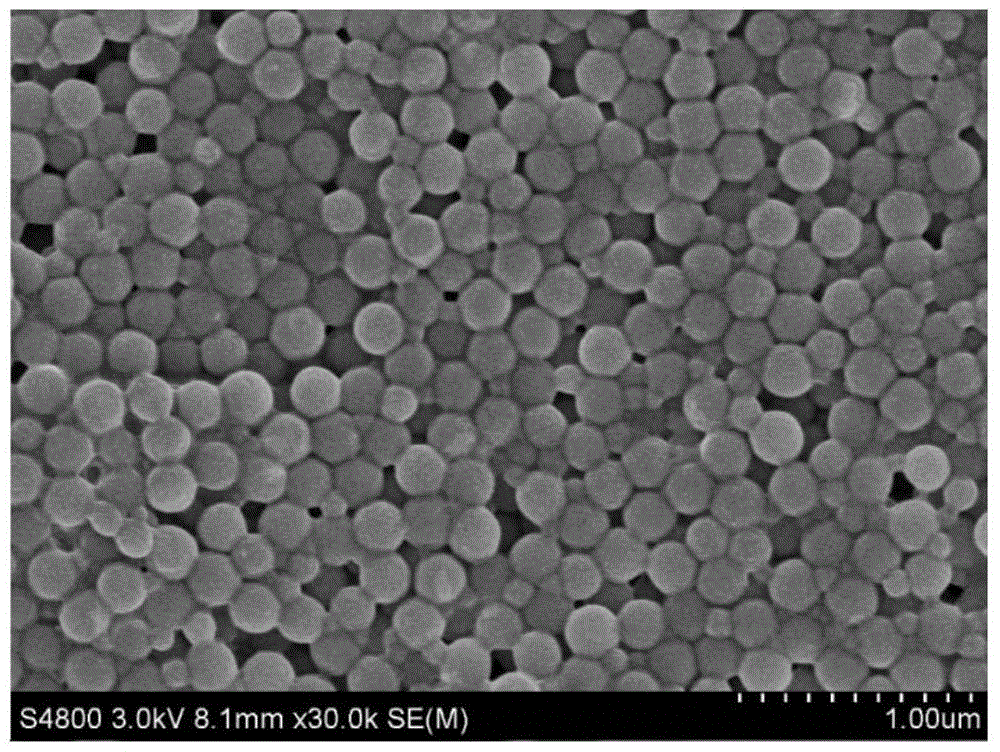
[0058] In this example, lithium methacrylate (MALi) is used as the hydrophilic monomer, butyl acrylate (BA) is used as the lipophilic monomer, MALi:BA=80:20 (mass ratio, the same below), and 80g lithium methacrylate (MALi) and 150g of deionized water were added to the reaction kettle, stirred at 50°C until fully dissolved, the stirring speed was 300 rpm, 10g of butyl acrylate (BA) was added, and high-purity N 2 Drive oxygen for 0.5 hours, add 0.5g of ammonium persulfate, heat up to 70°C, add the remaining 10g of lipophilic monomer dropwise into the reactor, stir at 300 rpm, add 0.1g of divinylbenzene, and react for 10 hours Finally, cross 300 mesh filter cloths to obtain a water-based binder emulsion with a solid content of 40%. figure 1 It is a scanning electron micrograph of the water-based binder prepared in Example 1.
Embodiment 2
[0060] This example uses lithium methacrylate (MALi) as the hydrophilic monomer, isooctyl acrylate (EHA), and styrene (St) as the lipophilic monomer, MALi:EHA:St=40:50:10, 40g Lithium methacrylate (MALi) and 400g of deionized water were added to the reaction kettle, stirred at 60°C until fully dissolved, the stirring speed was 200 rpm, and 40g of isooctyl acrylate (EHA) and styrene (St) were added Mix raw materials, pass high-purity N 2 Drive oxygen for 1 hour, add 0.5g of ammonium persulfate, heat up to 70°C, add the remaining 20g of lipophilic monomer dropwise into the reactor, stir at 300 rpm, add 0.4g of divinylbenzene, and react for 10 hours Finally, cross 100 mesh filter cloths to obtain a water-based binder emulsion with a solid content of 20%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com