Microbial preparation for purifying sewage and deodorizing garbage and preparation method thereof
A technology for micro-ecological preparations and sewage purification, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of short duration of action, long activation time, and poor treatment effect. , to achieve the effect of environmental improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0022] The preparation method of the composite bacteria is divided into two steps, one step and two steps.
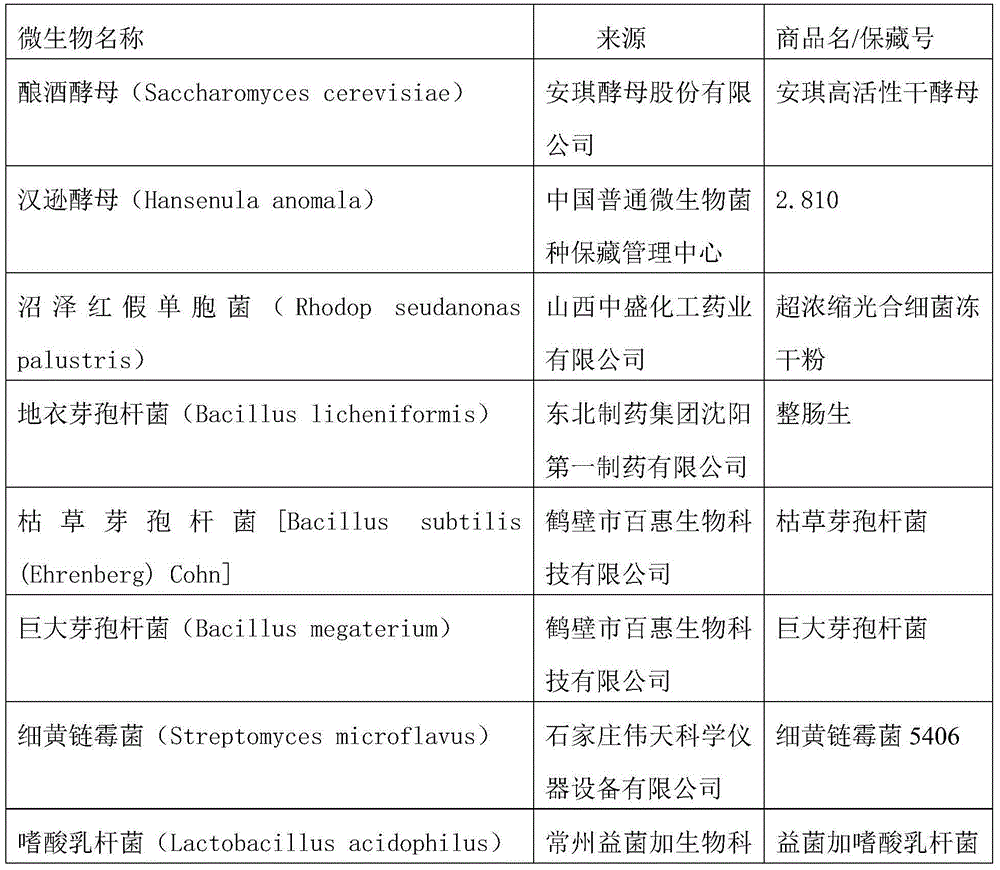
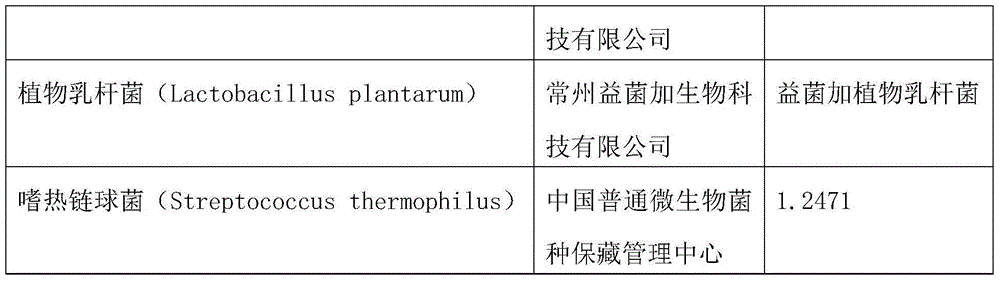
[0023] The above "level one" refers to the pure culture of each component. Pick the colonies of each microorganism, inoculate them into 100-200mL liquid medium, place them in a constant temperature shaker at 30-35°C, 100-200r / min and cultivate them for 16-24 hours; however, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum do not shake , static cultivation. The inoculation amount of each microorganism was basically the same.
[0024] The above "secondary" is a mixed culture. The specific method is: prepare 5-10L liquid medium, inoculate the cultures of S. Intermittent stirring (60-120r / min mechanical stirring, once every 3-5h, 1-2min each time) at 32°C for 12-24h; after that, inoculate Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, Lactobacillus acidophilus, plant For Lactobacillus and Streptococcus thermophilus, continue to culture for 16-24 hou...
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1.1 Preparation of liquid medium
[0038] Take 8% molasses, 2% salt, 1% urea, and 2% compound growth factors according to the mass ratio, add dechlorinated tap water to prepare 5 tons of medium. Among them, 2 tons are put into 3-ton seed tanks, 2.5 tons are put into 10-ton fermentation tanks, and the remaining 0.5 tons are reserved.
[0039] 1.2 Preparation of composite strains
[0040] The spare liquid culture medium was divided into several 200mL Erlenmeyer flasks, 100mL in each bottle, and sterilized by high-pressure steam at 121°C for 15min. Finally, in the ultra-clean workbench, use an inoculation loop to pick some colonies from the slant of the test tubes of each component, inoculate them into each bottle of culture medium, and place them in a constant temperature shaker at 32°C and 150r / min for 24 hours. Lactobacillus acidum and Lactobacillus plantarum were cultured statically.
[0041] Take 10L of spare liquid medium, inoculate Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Hanse...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 2.1 Preparation of liquid medium
[0051] Take 8% molasses, 2% salt, 1% urea, and 2% compound growth factors according to the mass ratio, and add dechlorinated tap water to prepare 10 tons of medium. Among them, 4 tons are put into seed tanks, 5 tons are put into 20-ton fermentation tanks, and the remaining 1 ton is reserved.
[0052] 2.2 Preparation of composite strains
[0053] The spare liquid culture medium was divided into several 200mL Erlenmeyer flasks, 100mL in each bottle, and sterilized by high-pressure steam at 121°C for 15min. Finally, in the ultra-clean workbench, use an inoculation loop to pick some colonies from the slant of the test tubes of each component, inoculate them into each bottle of culture medium, and place them in a constant temperature shaker at 32°C and 150r / min for 24 hours. Lactobacillus and Lactobacillus plantarum static culture. Take 10L of spare liquid medium, inoculate Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Hansenula, Rhodopseudomonas palustris,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com