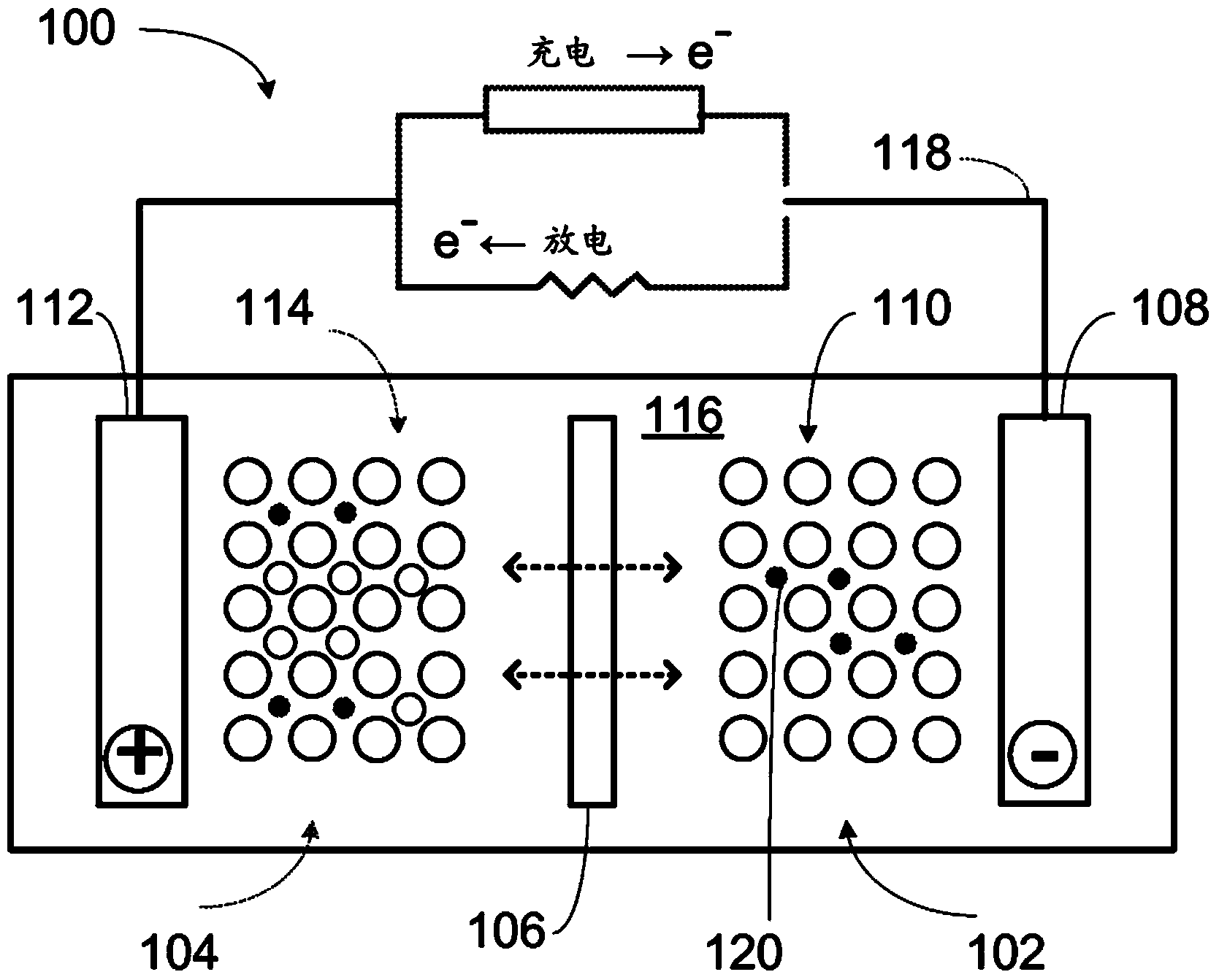
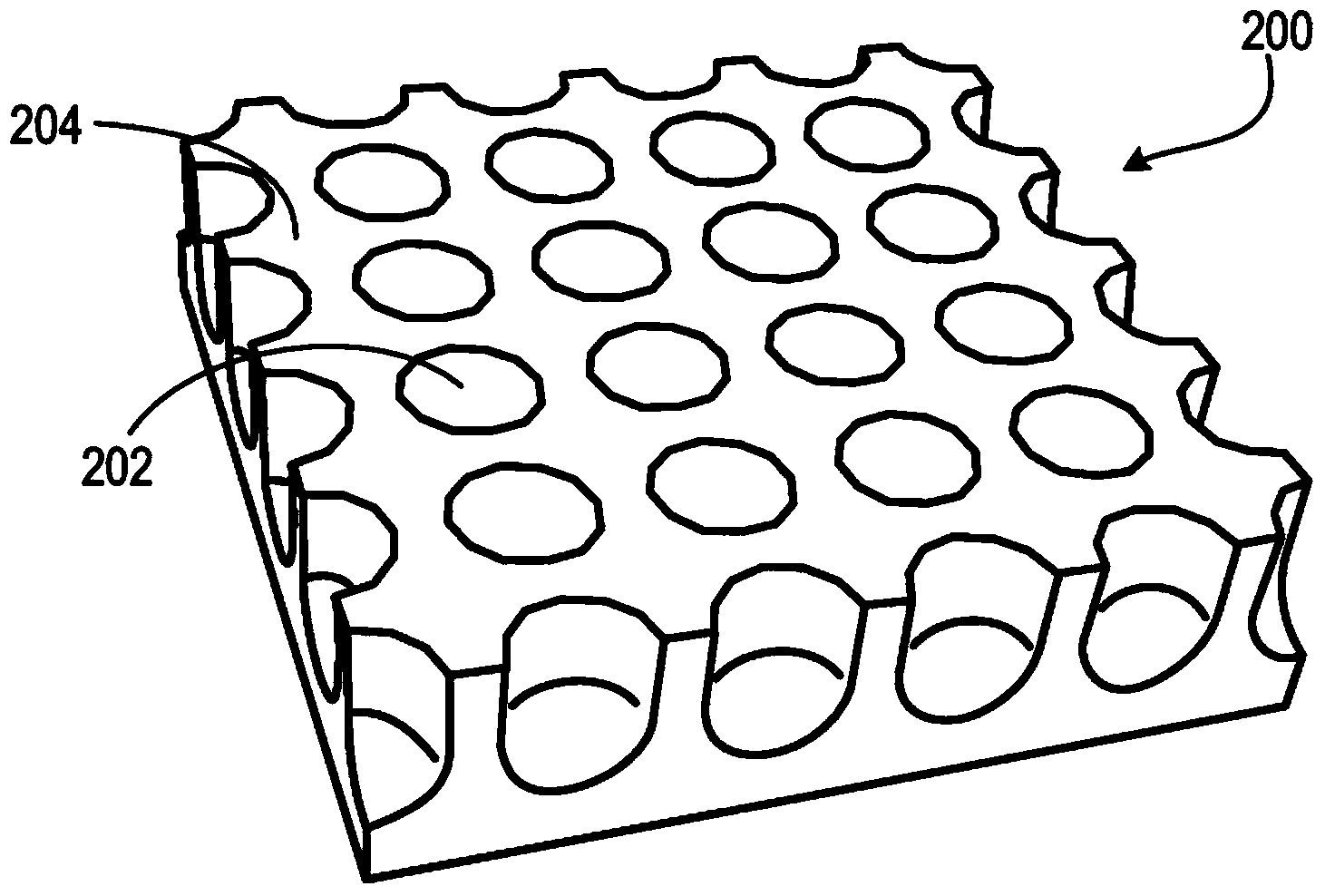
Nanoporous silicon and lithium ion battery anodes formed therefrom
A lithium-ion battery and electrode technology, applied in battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, electrode manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Example 1: Li-ion battery electrode with nanoporous silicon nanowires.
[0075] Nanoporous silicon nanowires were prepared by immersing a boron-doped silicon wafer (resistivity 3 ) in the etchant solution for 3 hours. The obtained nanoporous nanowires were sequentially passed through deionized water (DI-H 2 O), concentrated nitric acid (HNO 3 ), and again DI-H 2 O was washed and then collected by scraping off the wafer using a razor blade. Figure 5A showing a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of a nanoporous silicon nanowire 500, and Figures 5B-5D A transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of a nanoporous silicon nanowire 500 is shown. The nanoporous silicon nanowire 500 is highly porous at the surface, with the pores 510 having a diameter and wall thickness of about 8 nm. Figure 5D The high-resolution TEM image in shows crystalline nanowires with clear lattice fringes corresponding to Si(111). The crystal structure is also known as Figure 5E Thi...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2: Nanoporous silicon from bulk silicon. Nanoporous silicon particles, including nanoporous silicon nanoparticles, are prepared from bulk-sized, boron-doped silicon with a suitable doping level (resistivity <20 mΩ·cm). In other examples, the dopant can be iron, chromium, phosphorus, arsenic, aluminum, or combinations thereof. The bulk sized silicon is crushed into small pieces having a size of about or less than 5 mm. This small size silicon is further processed by one of several methods.
[0088] In the first method, the small-sized silicon is ground into a fine powder using a ball mill until a size of about 1 micron is obtained. In a second method, the small-sized silicon is ground into a fine powder using a ball mill, down to a size of less than 1 micron (eg, about 200 nm or about 100 nm). In the third method, the small-sized silicon is further ground into a fine powder using a ball mill until the size is about 200 nm. Si:H 3 BO 3 =5: (0.5-10) mass rat...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3: Li-ion battery electrodes with nanoporous silicon particles.
[0091] Metallurgical grade silicon (-99%) was used as received without further purification to remove common impurities (eg, Fe, Al). To produce nanoporous silicon structures, the silicon is ground into small particles (eg, a few micrometers - tens of micrometers) using wet ball milling techniques. In the ball milling process, ethanol or other non-oxidant solvents may be used as additives. The silicon:sphere:additive mass ratio is typically about 1:5:1, although other ratios may also be used. As obtained, micro-sized silicon was collected and washed with dilute hydrofluoric acid (HF, 1-5% by weight) to remove oxides on the surface of the particles. The silicon particles were impregnated with AgNO 3 and HF etchant solution, and kept still for about 2 hours to obtain nanoporous silicon particles. In one example, in the etchant solution, AgNO 3 and HF concentrations were 20mM and 5M, respectiv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com