B cell epitope of Tarp protein of chlamydia trachomatis and application of B cell epitope
A Chlamydia trachomatis and B cell technology, applied in the fields of biomedical technology and immunology, can solve the problems of lack of prevention and treatment methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1. Prediction and identification of Chlamydia trachomatis Tarp protein B cell epitope
[0065] 1. Design of Chlamydia trachomatis Tarp protein B cell epitope
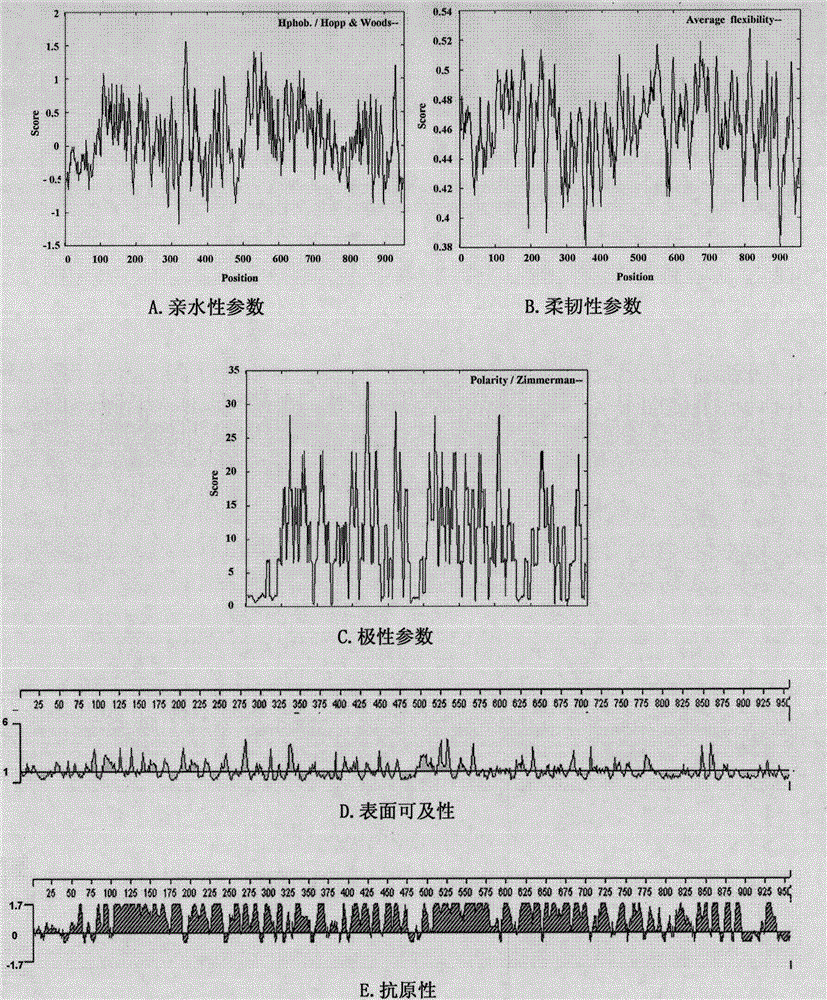
[0066] Obtain the Chlamydia trachomatis (Ct) Tarp protein gene sequence and amino acid sequence from the network resource database (Genbank, Swiss-Prot); use the online network resource (EXPASY) and the biological software DNASTAR to analyze the antigenicity and surface accessibility of the Ct Tarp protein amino acid sequence , flexibility and transmembrane region and other parameters were analyzed ( figure 1 ), supplemented by the analysis results of the secondary structure of the CtTarp protein, analysis and comparison of various parameters to comprehensively judge the B cell dominant epitope of the CtTarp protein.
[0067] After the above epitope prediction, combined with repeated tests and selections by the inventors, the result was an amino acid sequence derived from the CtTarp protein, which is a p...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2, Research on the Immunogenicity and Immunoprotection of Ct Tarp Protein B Cell Epitope Polypeptide
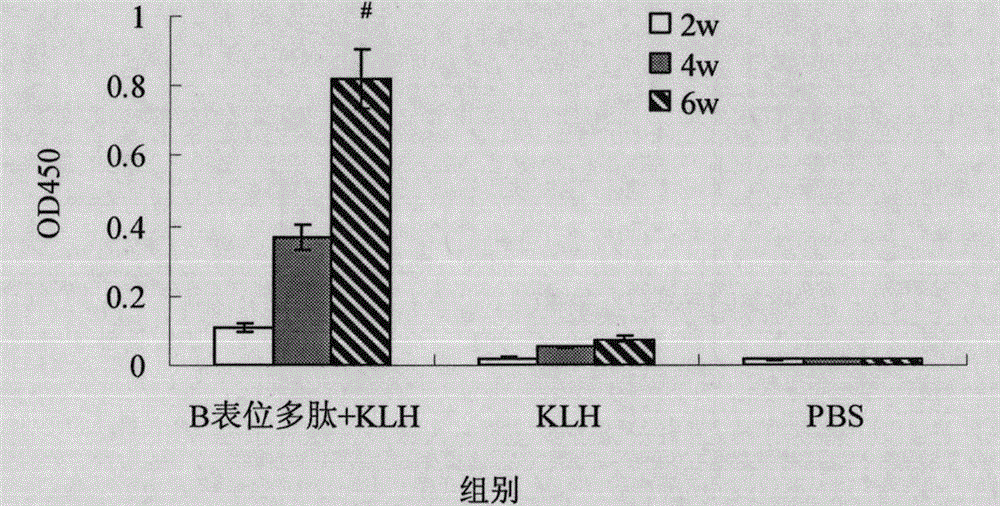
[0075] Female BALB / c mice aged 6-8 weeks were randomly divided into 3 groups, 6 mice in each group: the first group was the Ct Tarp protein B cell epitope immunization group, the second group was the KLH immunization control group, and the third group was the PBS control group. B cell epitope peptides were first coupled with KLH, and then the conjugates were fully emulsified with Freund's adjuvant (FCA) 1:1 (W / W), respectively, at 0, 2, and 4 weeks, 50 μg per mouse B cell epitope polypeptide, multi-point subcutaneous immunization of mice on the back. Tail vein blood and vaginal secretions were collected 2w, 4w, and 6w after immunization, and ELISA was used to detect polypeptide-specific IgG antibodies in serum and sIgA antibodies in secretions. The remaining mice in each group were challenged with E serotype Ct, and the activities of the mice and the severity...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3, Antigenicity Research of CT Tarp Protein B Cell Epitope Polypeptide
[0086] 1. Immunoprecipitation and Western blot detection
[0087] Hela229 cells infected with Chlamydia for 48 hours were treated with cell lysate and then incubated with synthetic peptide immune serum for 4 hours. C overnight, then incubate with Protein G Agarose at 4°C for 3h, centrifuge, discard the supernatant, add the pellet to the loading buffer, perform SDS-PAGE protein electrophoresis, transfer to the membrane, and immunize mice with epitope peptides diluted 1:100 Serum was used as the primary antibody, HRP-labeled anti-mouse IgG (H+L) (purchased from eBioscience) was used as the secondary antibody, and the binding ability of B cell epitope immune serum to Tarp protein was detected by Western blot method. At the same time, Hela229 cells not infected with Chlamydia were used as negative control.
[0088] The results show( Figure 7 ), the B cell epitope protein immune serum can sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com