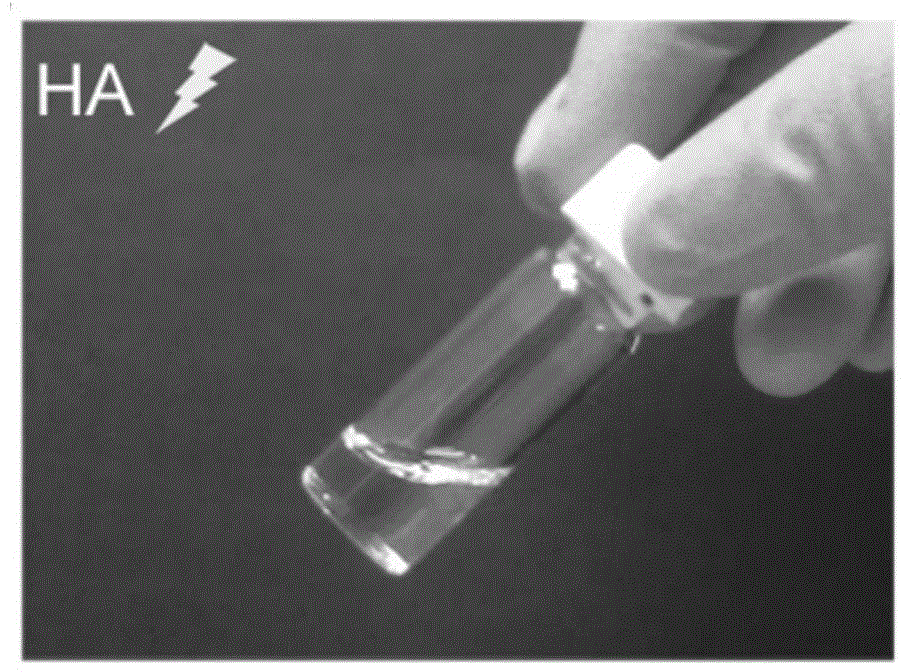
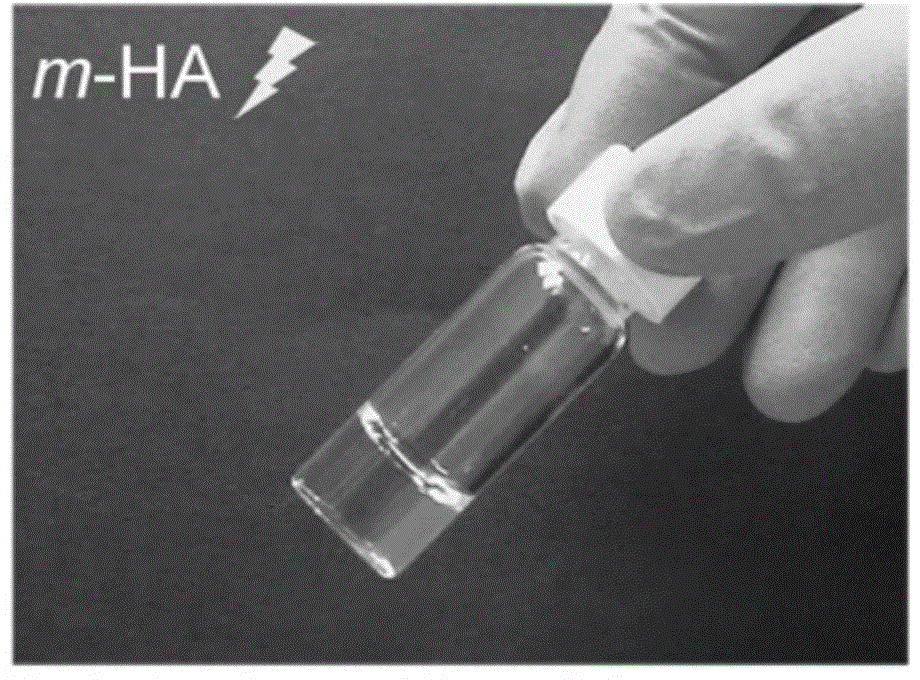
Preparation method for gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries
A technology for cartilage damage and joint repair, applied in medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of growth factor immunogenicity that cannot be used in vivo, gene transfection technology safety tumorigenicity, unfavorable differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, etc. , to achieve the effects of clinical application, cartilage damage repair, light intensity and light time shortening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] This embodiment is a method for preparing a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0072] (1) Modification of sodium hyaluronate;
[0073] (2) Dissolve the PLGA nanoparticles of KGN in the sodium hyaluronate modified in step (1) at a concentration of 10um / L, and then add the photoinitiator Irgacure 2595 to obtain the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel Glue compound system, by weight, the amount of photoinitiator added is 1 / 9 of the small molecular compound;
[0074] (3) Inject / fill the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel complex system into the articular cartilage damage to be repaired and irradiate with ultraviolet point light source, 20 μW / cm 2 The ultraviolet point light source was irradiated for 20 seconds to obtain a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage.
[0075] The preparation method of the PLGA nanoparticles of the KGN comprises ...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This embodiment is a method for preparing a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0082] (1) Modification of sodium hyaluronate;
[0083] (2) Dissolve the PLGA nanoparticles of KGN in the sodium hyaluronate modified in step (1) at a concentration of 2um / L, and then add the photoinitiator Irgacure 2595 to obtain the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel Glue compound system, by weight, the amount of photoinitiator added is 1 / 10 of the small molecule compound;
[0084](3) Inject / fill the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel complex system into the articular cartilage damage to be repaired and irradiate with ultraviolet point light source, 10 μW / cm 2 The ultraviolet point light source was irradiated for 40 seconds to obtain a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage.
[0085] The preparation method of the PLGA nanoparticles of the KGN comprises th...
Embodiment 3
[0091] This embodiment is a method for preparing a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0092] (1) Modification of sodium hyaluronate;
[0093] (2) Dissolve the PLGA nanoparticles of KGN in the sodium hyaluronate modified in step (1) at a concentration of 60um / L, then add the photoinitiator Irgacure 2595 to obtain the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel Glue compound system, by weight, the amount of photoinitiator added is 1 / 8 of the small molecule compound;
[0094] (3) Inject / fill the slow-release small molecule compound-sodium hyaluronate gel complex system into the articular cartilage damage to be repaired and irradiate with ultraviolet point light source, 6 μW / cm 2 The ultraviolet point light source was irradiated for 1 min to obtain a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage.
[0095] The preparation method of the PLGA nanoparticles of the KGN comprises the followi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com