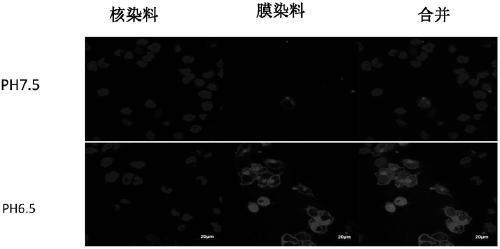
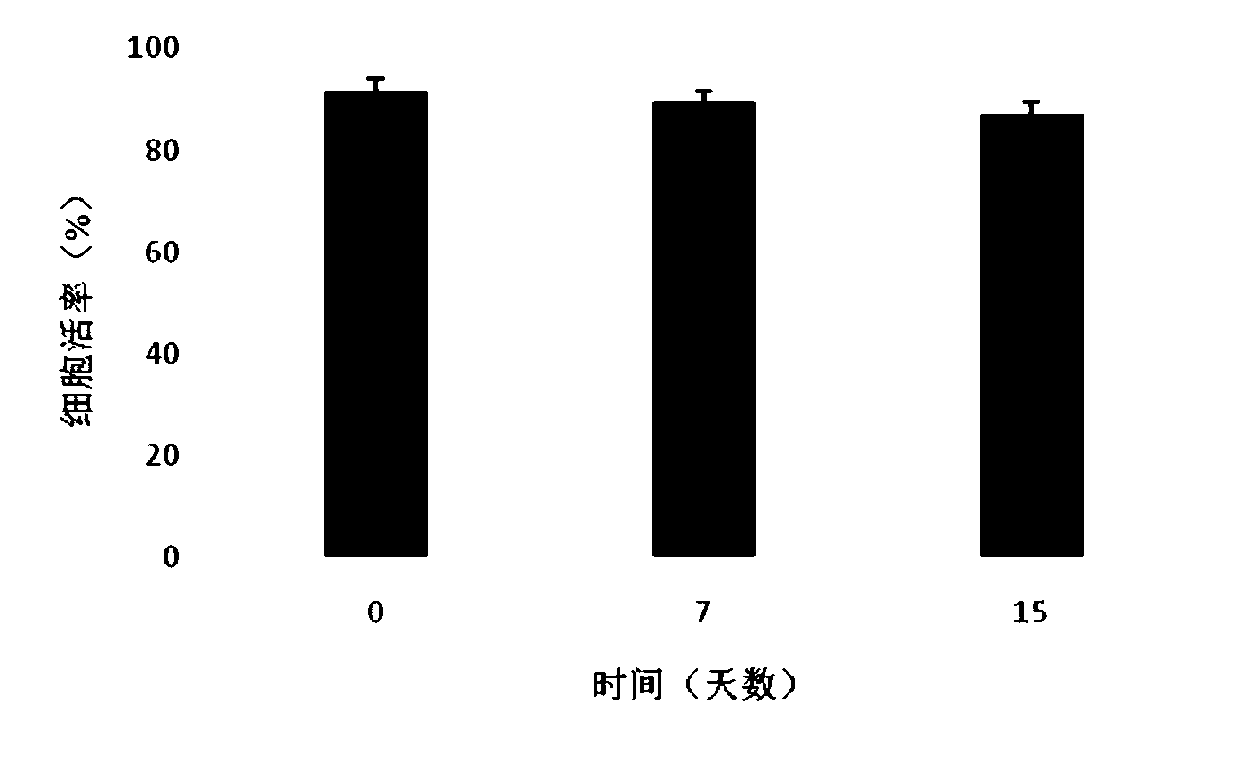
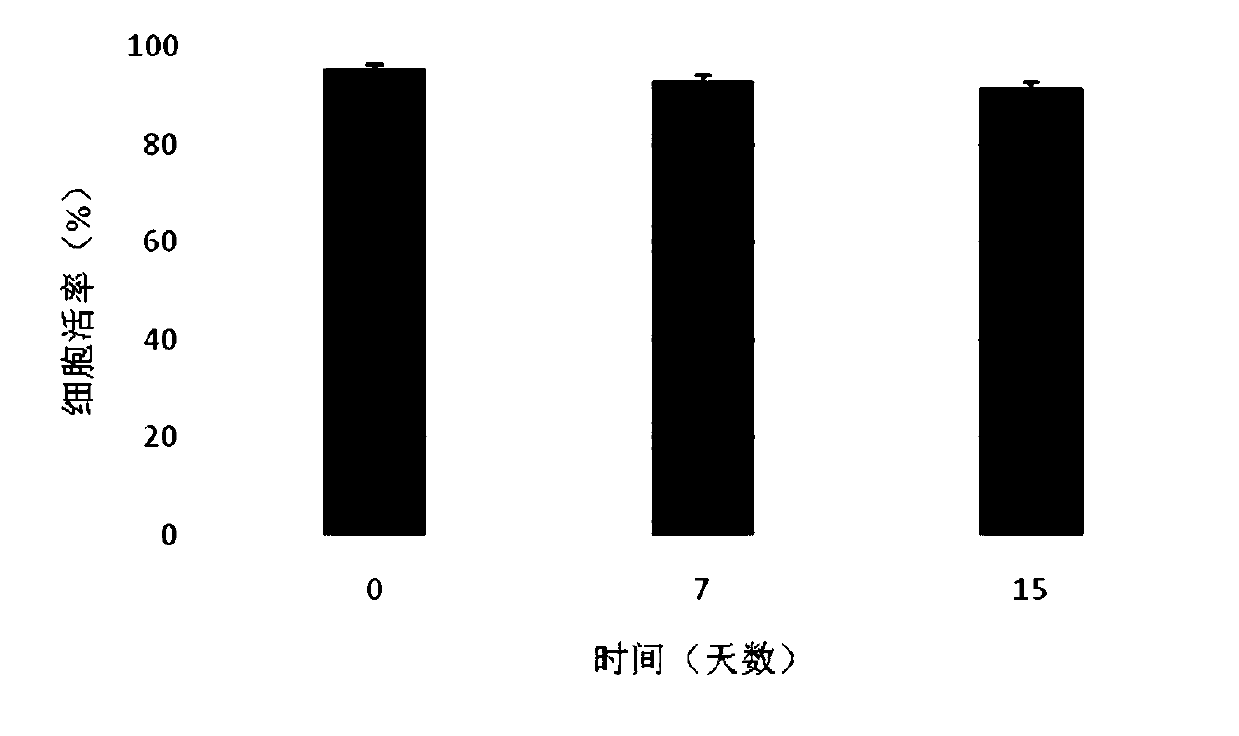
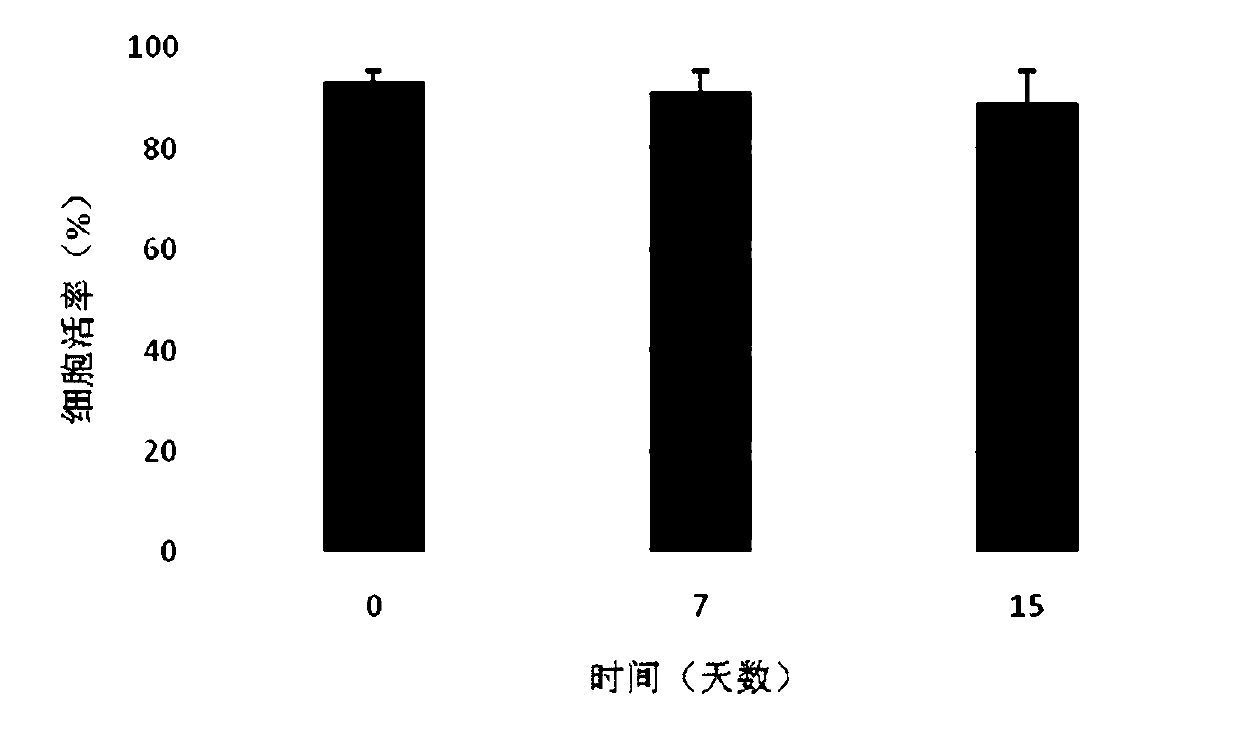
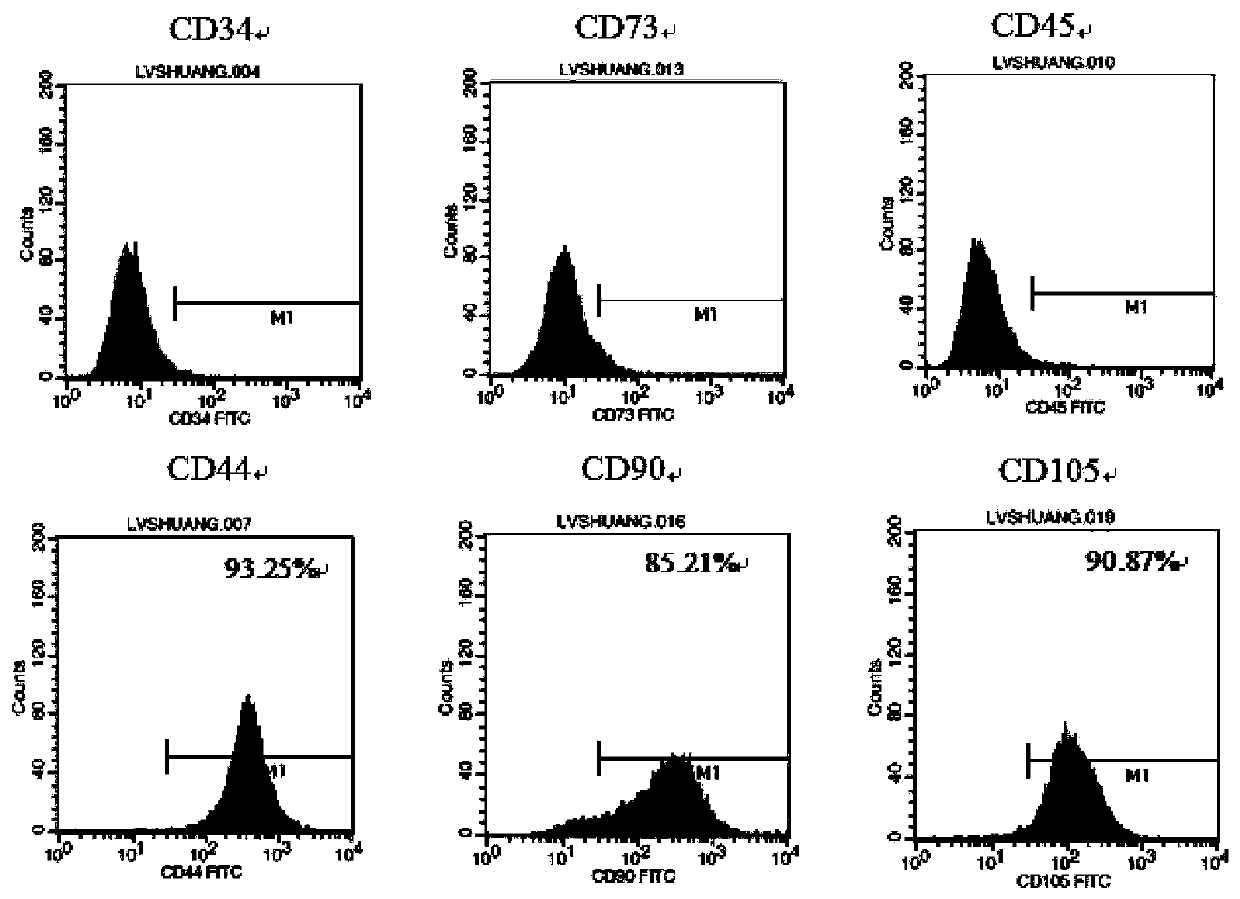
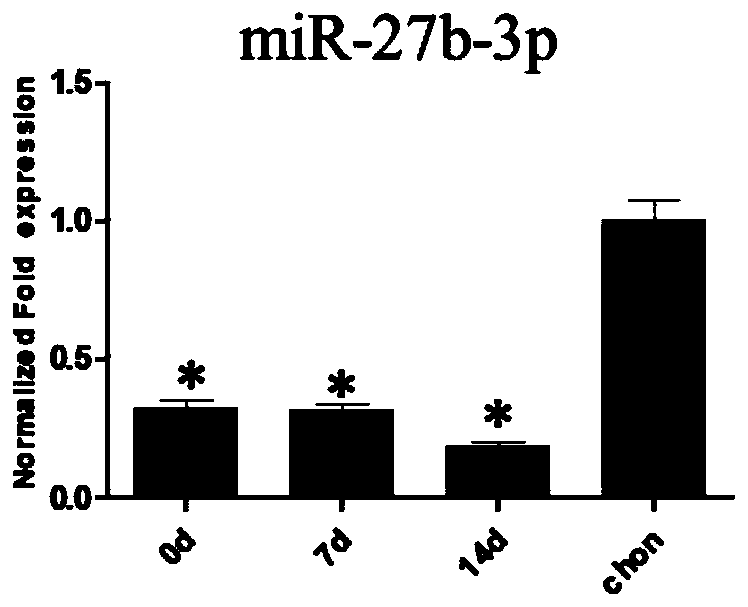
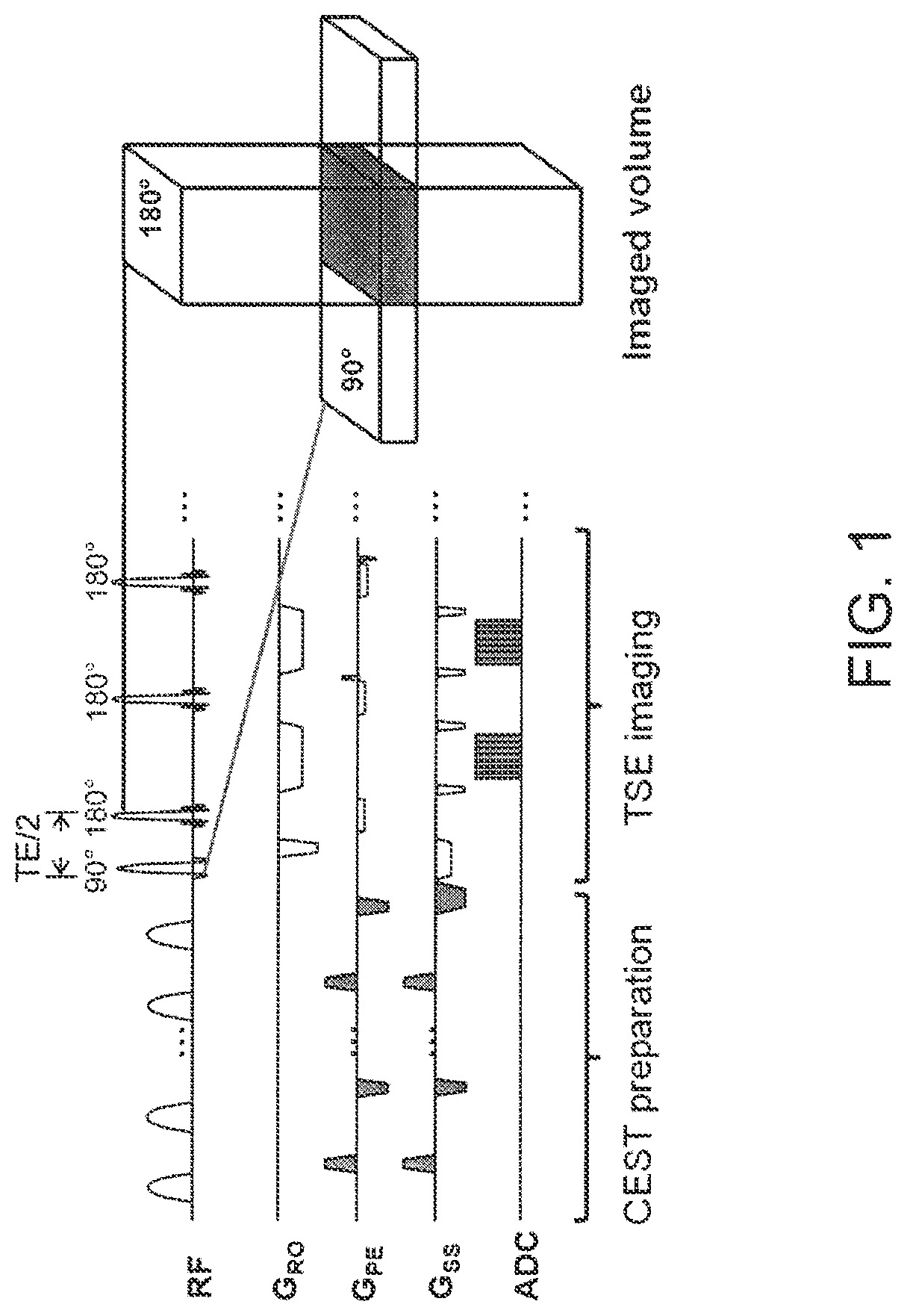
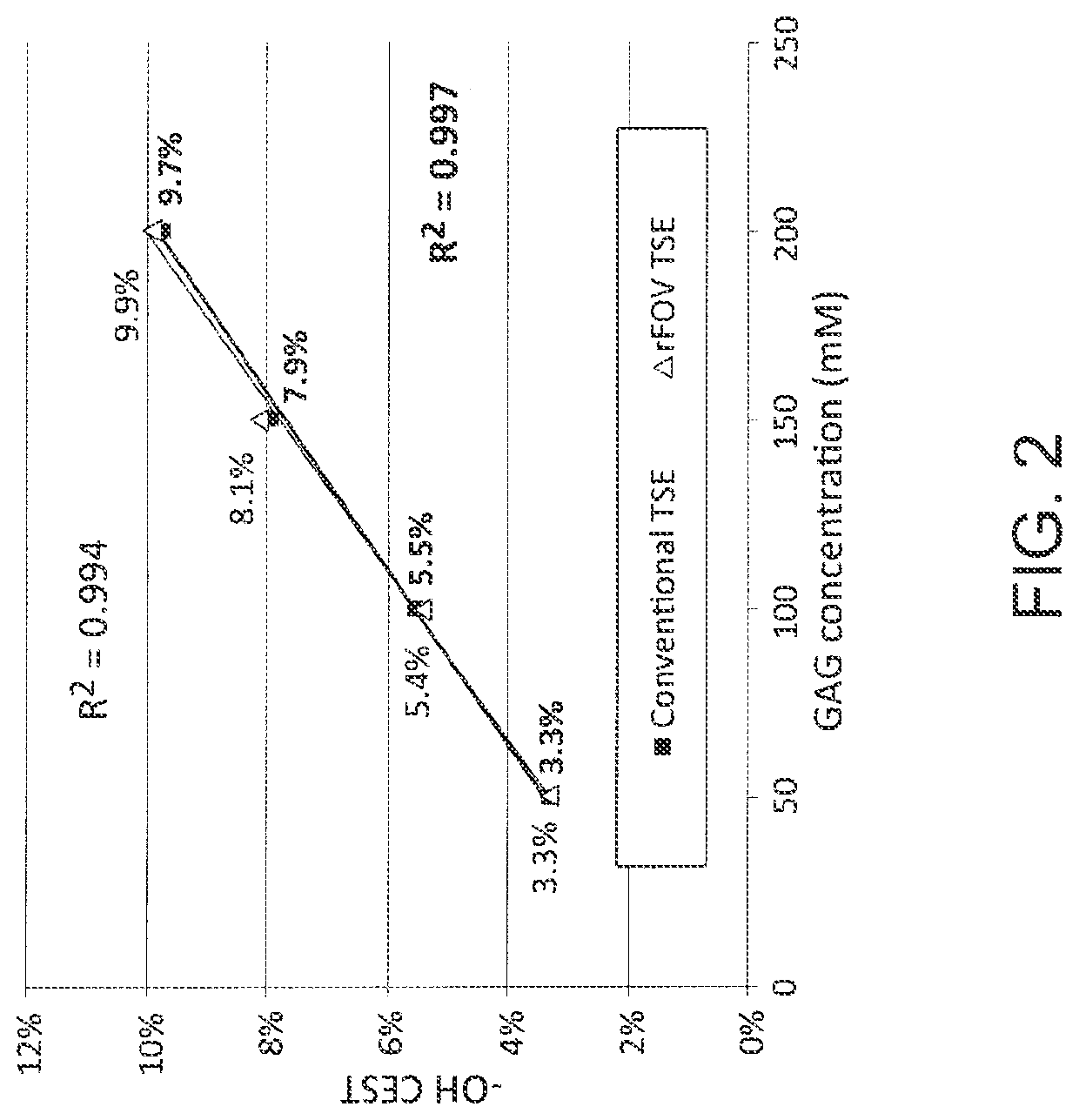
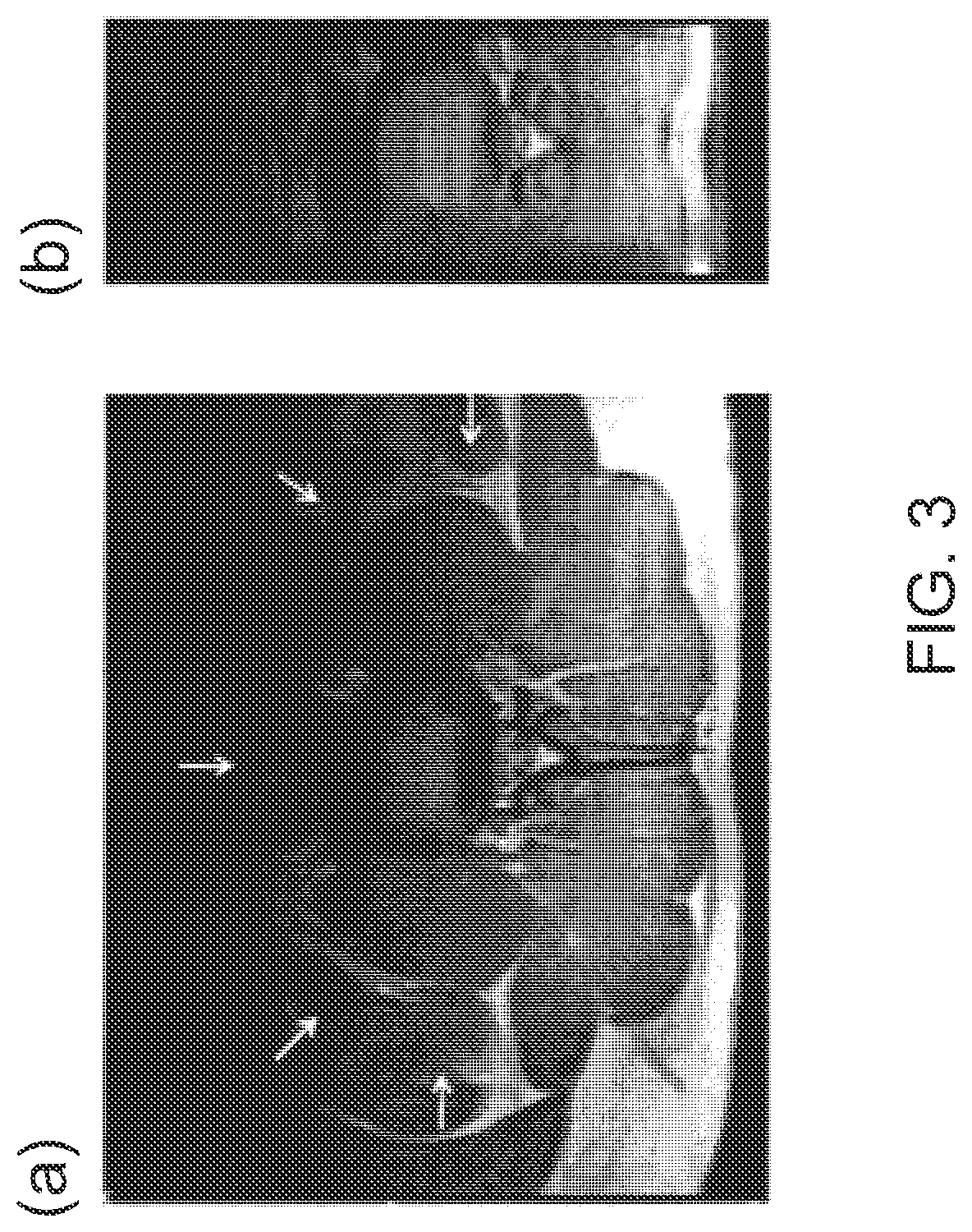
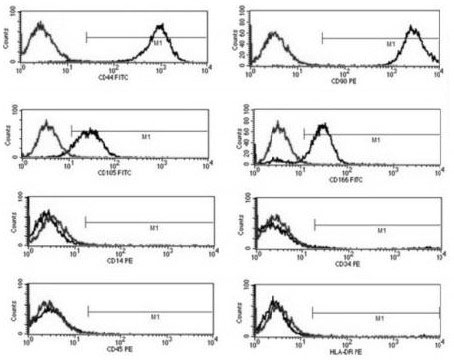
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Articular cartilage injuries" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cartilage structures and functions can relatively easily be harmed, often resulting in damage. Such damage can result from a variety of causes, resulting from a bad fall or sport-accident, previous knee injuries or wear and tear over time. Immobilization for long periods can also result in cartilage damage. Articular cartilage damage might be found on its own but it will more often be found in conjunction with injuries to ligaments and menisci. People with previous repairs to ligaments and or menisci often face greater chances of new articular cartilage damage due to altered mechanics in the joint.
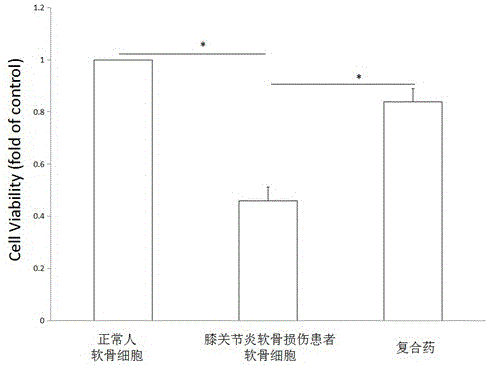
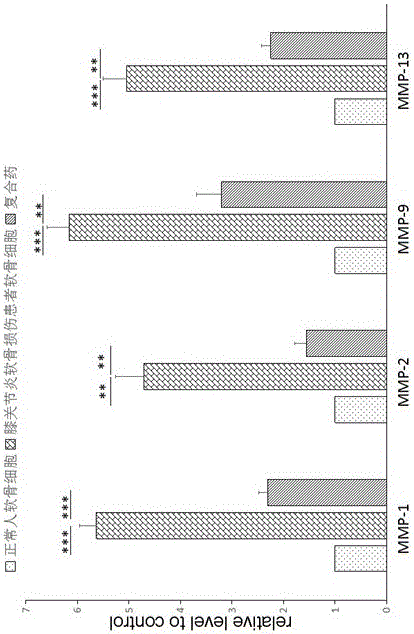
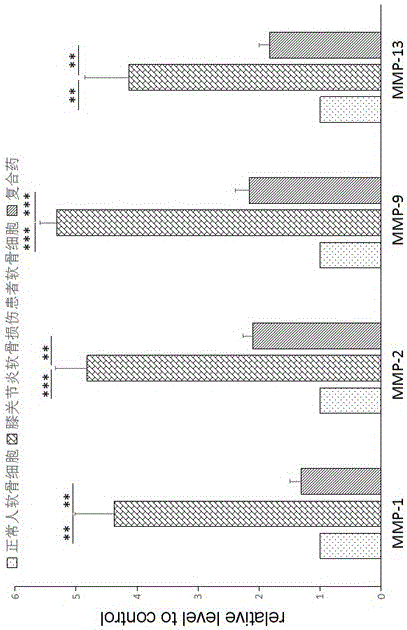
Composition for treatment of articular cartilage damage
InactiveUS7459307B2Good effectEasy to operateBiocideSkeletal disorderCellular componentArticular pain
Disclosed herein is a composition for the treatment of articular cartilage damage or loss or defect. The composition for the treatment of articular cartilage injury of the present invention includes (i) cellular components separated, proliferated, and / or differentiated from the umbilical cord blood, (ii) a culture medium; and (iii) a biocompatible polymer. The composition has very superior ability of proliferation and differentiation and easier to be collected and acquired.
Owner:MEDIPOST +1
Preparation method of cartilage regeneration scaffold material
The invention provides a preparation method of a cartilage regeneration scaffold material. The preparation method is characterized in that fresh skin at back, face or buttock of a dead animal is taken as a raw material and is subjected to treatment processes such as deep and low-temperature treatment, depilation, inactivation of virus, decellularization, structure remodeling, crosslinkage, freeze-drying, re-modification and sterilization, thus obtaining a finished product. The cartilage regeneration scaffold material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention can be used for promoting adhesion and growth of cartilage cells and promoting healing of articular cartilage injuries. The product belongs to a natural extracellular matrix ingredient which is beneficial to adsorption, proliferation and differentiation of the cells, also has a certain mechanical strength, can exist in the body for a long time in the form of a tissue filler, also has good tissue affinity and compatibility, and can be used for inducing cartilage cells to grow therein so as to rebuild the cartilage, promote the adhesion and growth of the cartilage cells, promote the healing of the articular cartilage injuries and restore articular defects, so the cartilage regeneration scaffold material is a novel regeneration scaffold material for effectively restoring articular cartilage defects.
Owner:北京科健生物技术有限公司
Cartilage deficiency prosthesis, preparation method thereof and integrated cartilage-bone repair material
InactiveCN101954121AGood biocompatibilityStable mechanical strengthProsthesisMass ratioArticular cartilage injuries
The invention discloses cartilage deficiency prosthesis, a preparation method thereof and an integrated cartilage-bone repair material. The prosthesis is composed of collagen and proteoglycan based on the mass ratio of 1 / 3-3, wherein, the collagen is I-type collagen or II-type collagen, and the proteoglycan comprises glycosaminoglycan, chitosan or chondroitin sulfate; and natural cartilage matrixes are longitudinally arranged in the prosthesis. The integrated cartilage-bone repair material is made by compounding the prosthesis with a bone matrix material together. The cartilage defect prosthesis of an articular cartilage matrix structure of the invention can meet the repair need of articular cartilage deficiency, effectively improve repair rate of articular cartilage injury and lower disability incidence of a patient.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Tissue engineered cartilage based on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
InactiveCN1565643AConvenient sourceTraumaSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisOrganismSacroiliac joint
The invention belongs to tissue engineering field. It makes self body mesenchymal stem cell as seed cell and porous biological ceramics as bracket material. Adding proliferating agent and differentiating agent when cultivating the complex in vitro, transplanting and restoring articular cartilage injury after cultivating in vitro for a period of time The invention is characterized in that it constructs tissue engineering cartilage by employing marrow mesenchymal stem cell and porous biological ceramics for restoring articular cartilage injury. It has an preferably clinical practice prospect.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Preparation method for gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries
ActiveCN104587531ALong release timeSustained release concentration stableProsthesisHazardous substanceIn vivo
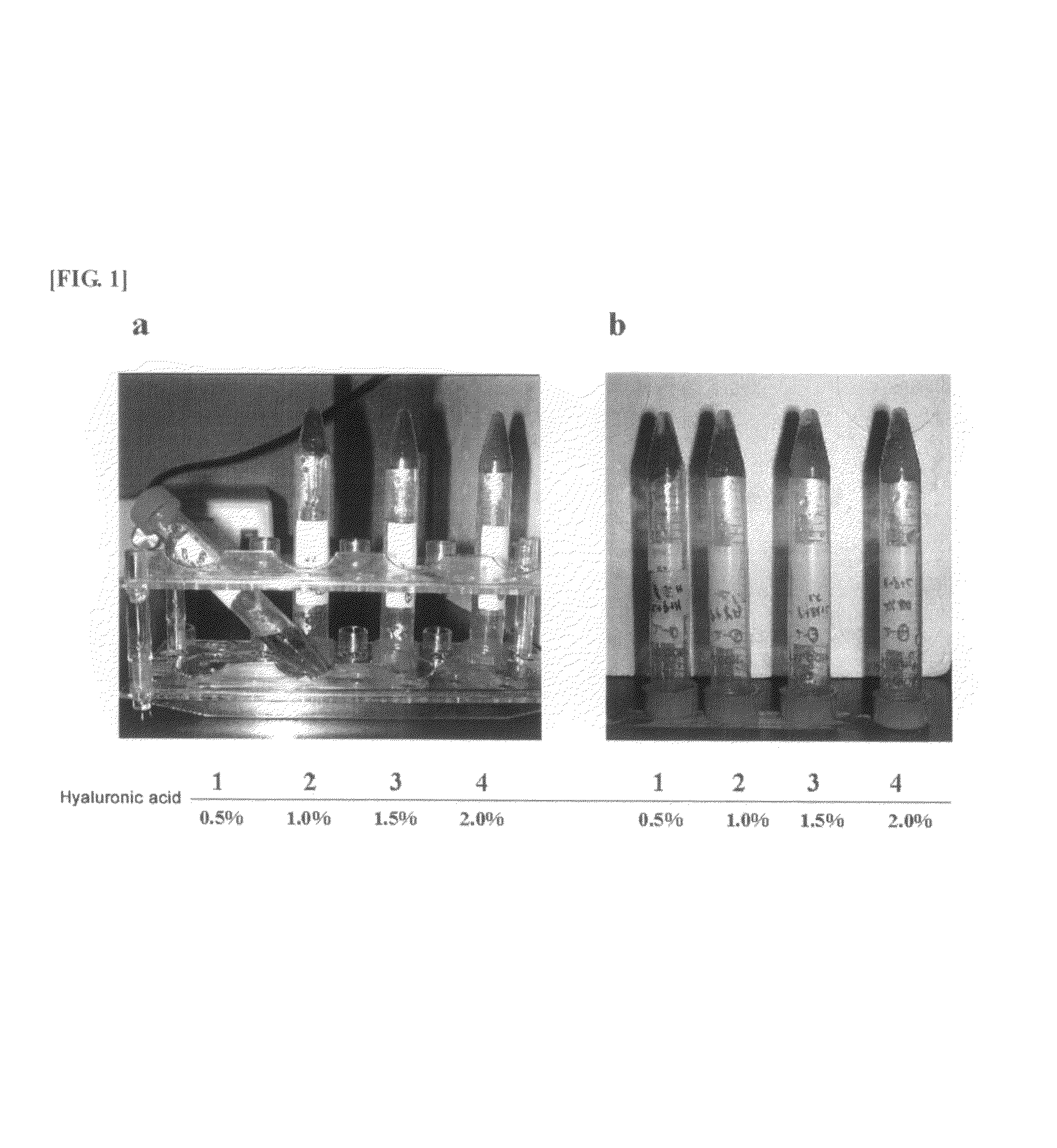
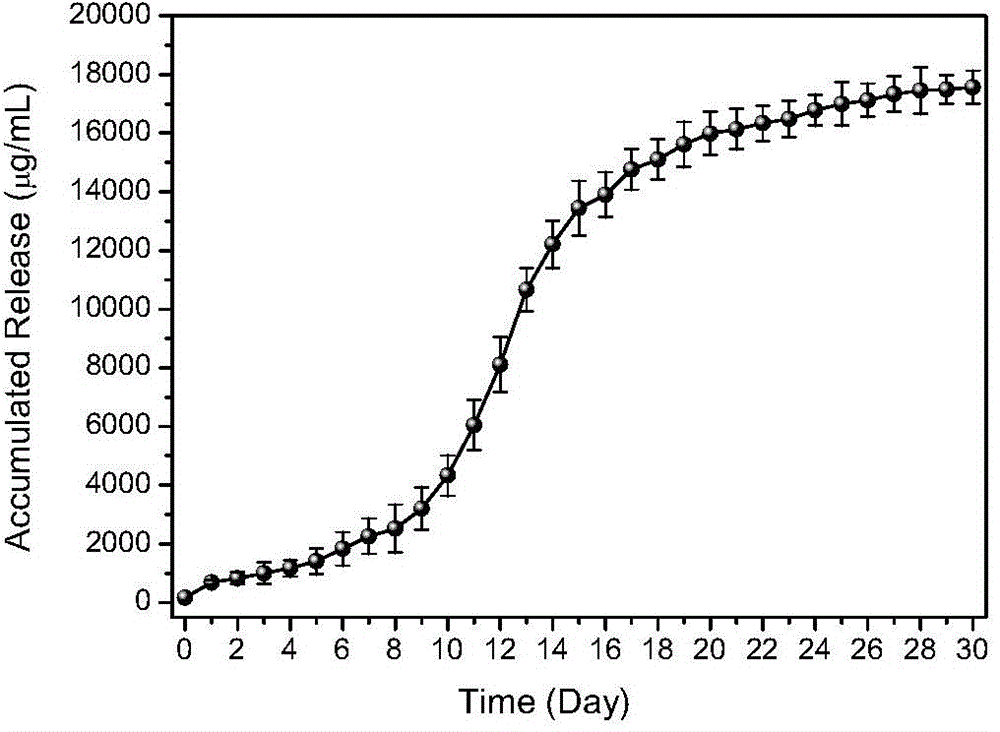
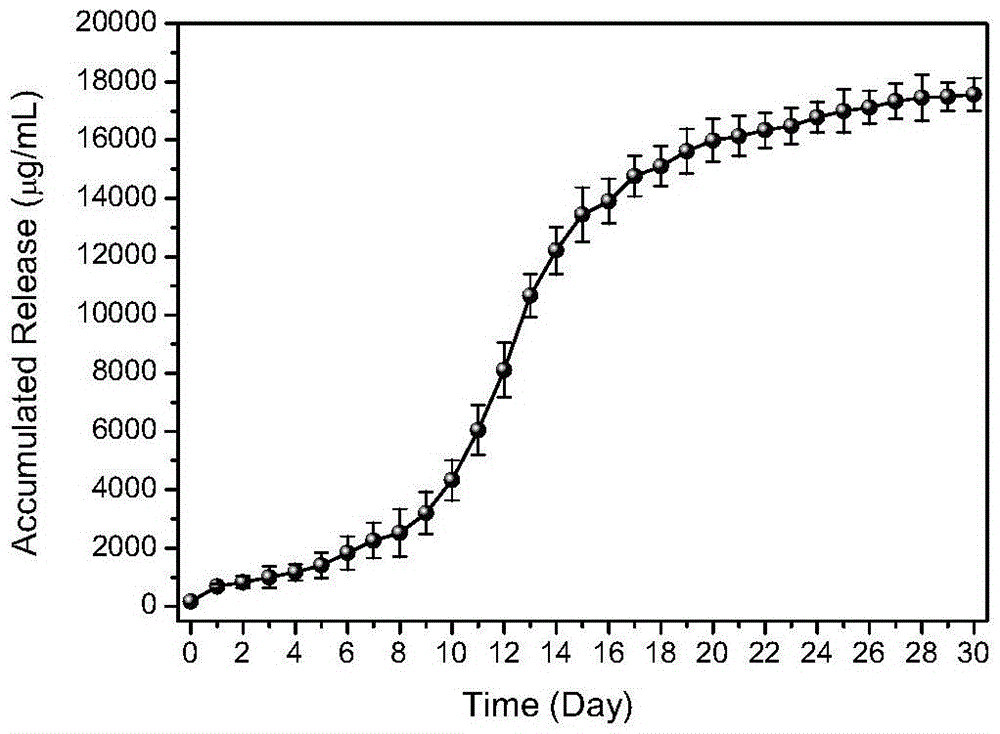
The invention relates to the fields of medicines and medical instruments, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) modifying sodium hyaluronate; (2) dissolving PLGA nano-particles of a controlled-release small molecular compound in the sodium hyaluronate modified in the step (1), and then adding with a photoinitiator to obtain a controlled-release small molecular compound-sodium hyaluronate gel compound system; and (3) injecting / filling the controlled-release small molecular compound-sodium hyaluronate gel compound system to the articular cartilage injuries to be repaired for being irradiated by an ultraviolet point light source, so as to obtain the gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries. The gel scaffold provided by the invention is high in plasticity, and capable of being randomly shaped according to the shapes of cartilage defects; harmful substances are not introduced in the whole process, and the gel scaffold can be used in vivo.
Mesenchymal stem cell preparation for repairing articular cartilage injury or coloboma, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108865986APromote repairGood treatment effectSkeletal disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSynovial CellKnee Joint
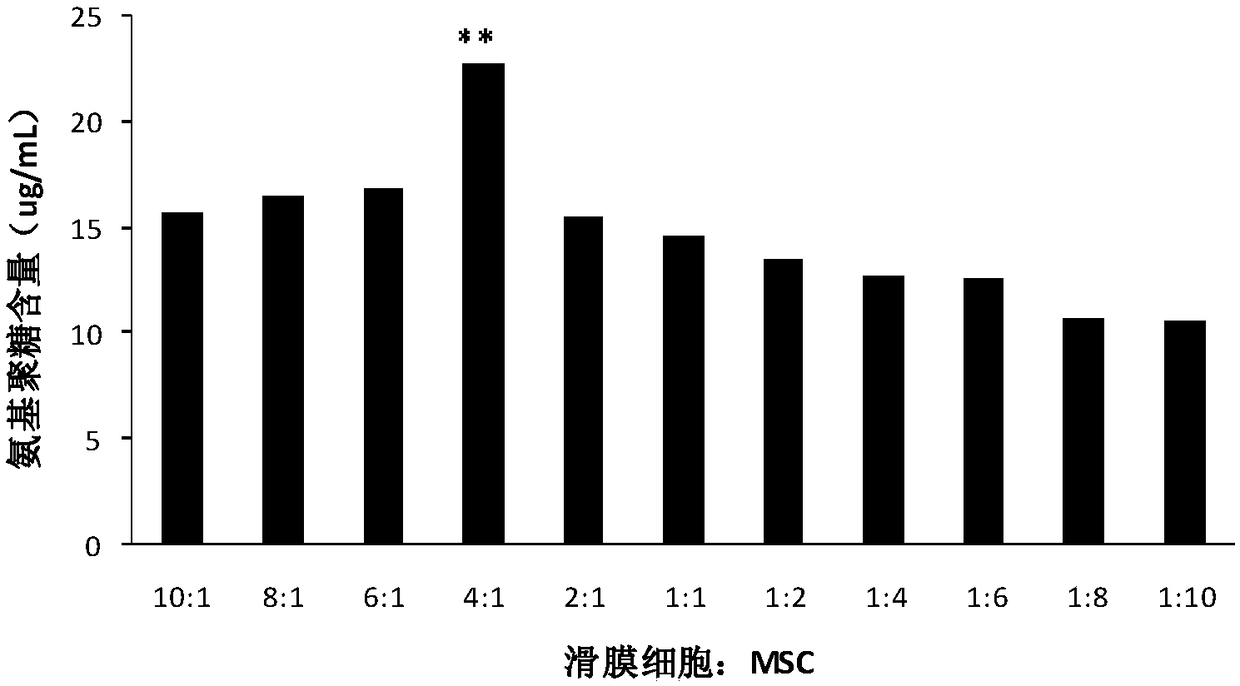
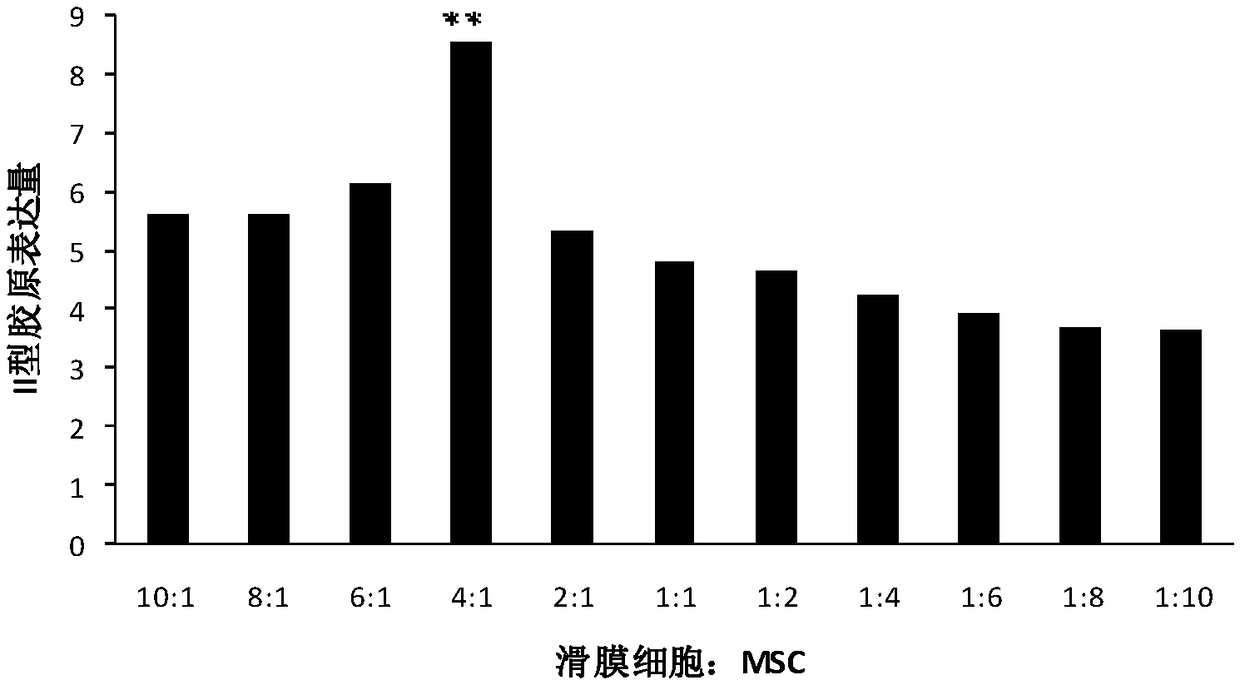
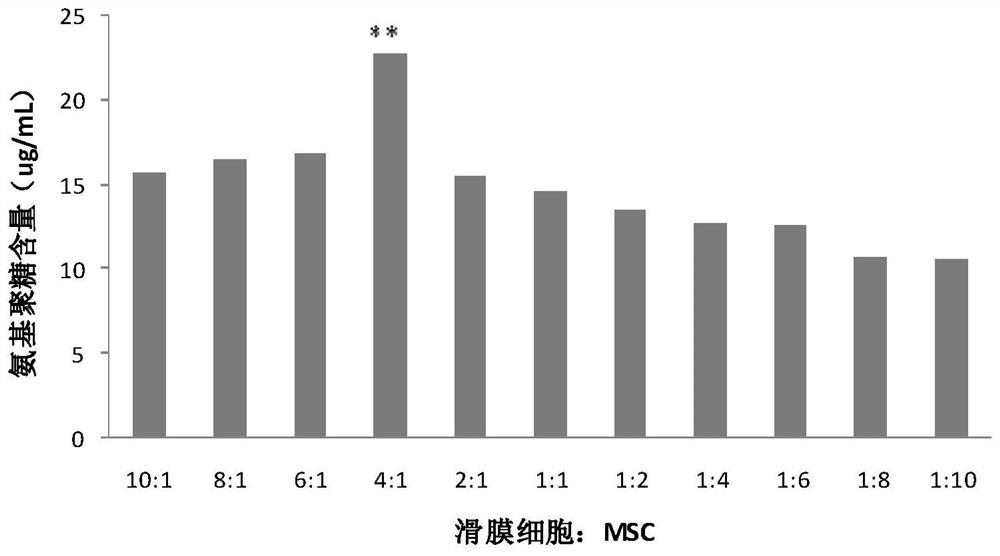
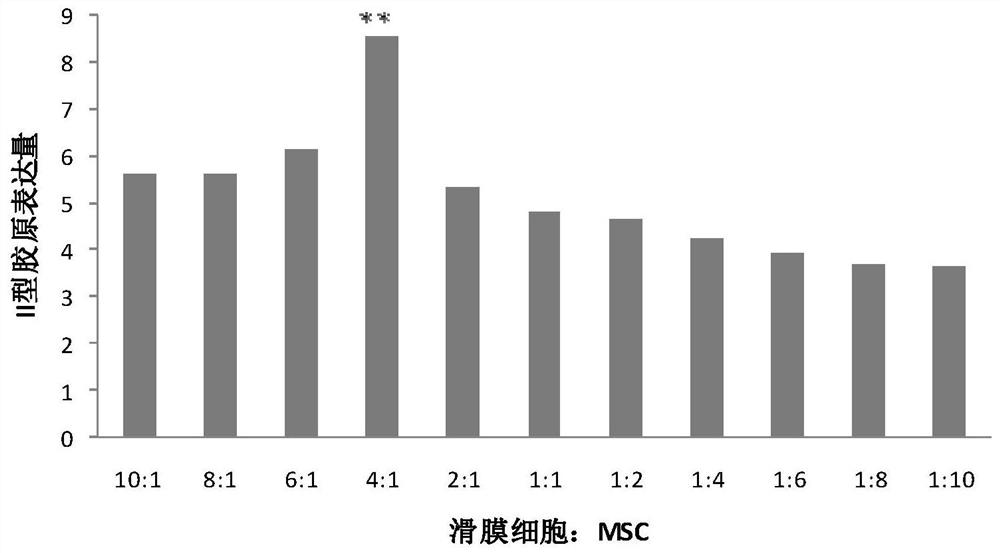
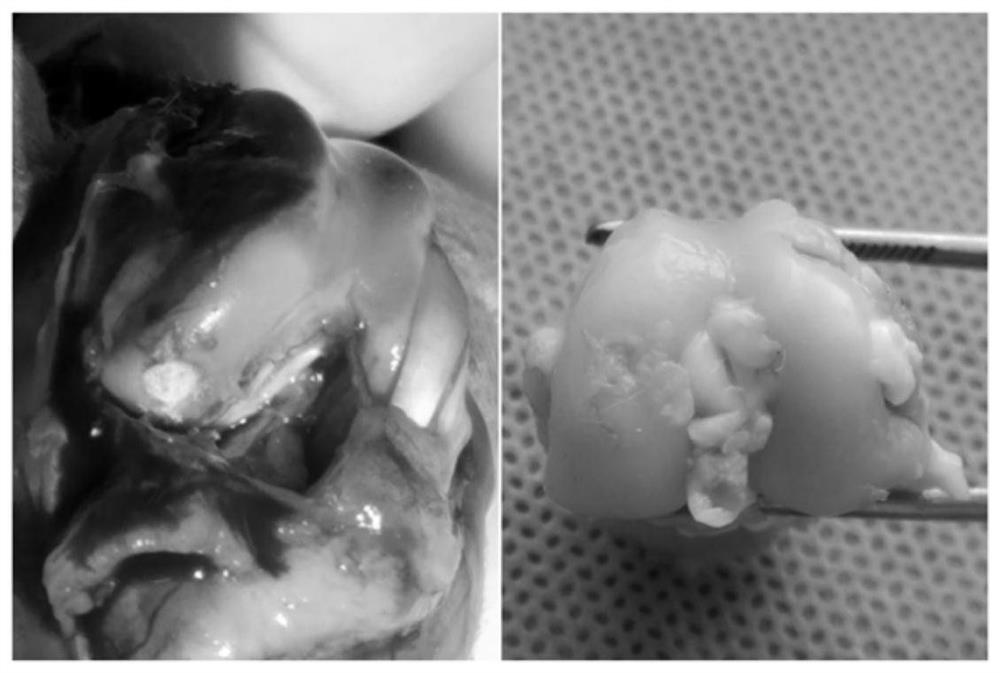
The invention discloses a mesenchymal stem cell preparation for repairing articular cartilage injury or coloboma, a preparation method and application thereof. According to the preparation method, mesenchymal stem cells and synovial cells are indirectly cocultured, so as to obtain the mesenchymal stem cells after coculture, and then the mesenchymal stem cells are cryopreserved, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, which are acquired after the synovial cells and the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are inoculated at density ratio of 4:1 and cocultured, are easier to differentiate towardcartilage direction under a same induction condition. The preparation method utilizes a constructed animal knee joint cartilage injury or coloboma model to prove that the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with the synovial cells have an obvious effect of facilitating the repairing of articular cartilage injury or coloboma. The invention further provides a preparation which is prepared from the cocultured mesenchymal stem cells. The preparation can be applied to clinic repairing of articular cartilage injury or coloboma; the preparation can effectively promote the repairing of articular cartilage injury or coloboma through anticular injection; the therapeutic effect of the preparation is obviously better than that of a pure mesenchymal stem cell preparation.
Owner:马琳 +1
Human tissue factor clotting compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109293780AAvoid stickingPrevent wound infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComposite effectCuticle
The invention discloses a human tissue factor clotting compound and a preparation method thereof. The compound has a local rapid hemostatic function, has the effects of wound infection prevention, wound healing promotion and the like, and has a composite effect different from a conventional local clotting agent. The clotting compound disclosed by the invention is simple to prepare, is applied to rapid hemostasis, antibiosis and wound healing promotion of local known or unknown hemorrhagic spots in operations and epidermis wounds and tissue epidermis wounds caused by trauma, and has advantagesin applications for treating liver injury, articular cartilage injury, eye injury, diabetes, hemophilia and the like.
Owner:厦门宏谱福生物科技有限公司
Manufacturing method of tissue engineered cartilage
InactiveCN1565647AEasy to obtainGood biocompatibilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCartilage cellsAlpha-tricalcium phosphate
The invention belongs to tissue engineering field, and discloses a manufacturing method of tissue engineered cartilage comprising needed degradable porous biological ceramic materials. The invention composite generates cartilage tissue by inorganic biological bracket materials(alpha tricalcium phosphate porous ceramic materials) and tissue cell(cartilage cell) to restore articular cartilage injury. The invention can realize functional restoration of cartilage injury and has a considerate clinical practice prospect.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Cell gel preparation for treating articular cartilage injury and use thereof, and used gel solution for maintaining activity of cryopreserved cells
InactiveCN108670946AGood biocompatibilityHigh activityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryHigh cellGel preparation
The invention discloses a cell gel preparation for treating articular cartilage injury and a use thereof, and a used gel solution for maintaining the activity of cryopreserved cells. The formula of the cell gel preparation comprises, according to the volume percentage, 50% to 95%, of the gel solution and 5% to 50% of a compound electrolyte cell resuspension, and per milliliter of the cell gel preparation contains 0.5*10<5>-2*10<7> cells. The gel solution includes the following components by mass and volume: 1 to 50 mg of a high molecular material stabilizer, 0.1 to 1 mg of chondroitin sulfate,5 to 50 mg of human serum albumin, 30 to 150 [mu]l of glycerol, 1 to 30 [mu]l of DMSO, and 700 to 900 [mu]l of a compound electrolyte injection liquid or amino acid injection liquid or normal salineinjection liquid. The gel preparation has good biocompatibility and can be directly stored at low temperature for a long time and maintain high cell viability, and does not require traditional liquidnitrogen cryopreservation; the cell gel preparation after resuscitation can maintain cell biological characteristics and functions and high survival rate in a joint cavity, and can be used in treatment of articular cartilage injury.
Owner:TIANJIN AMCELLGENE ENG
Wear evaluation method for articular cartilage injuries
ActiveCN105091725AAccurate measurement of wearAccurate volume measurementElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsUsing electrical meansRight femoral headCurve fitting
The present invention discloses a wear evaluation method for articular cartilage injuries. Firstly, the fresh bovine articular cartilage is extracted from a cow knee joint, and then is cut to be sector-shaped, wherein the sector-shaped bovine articular cartilage is 20 mm in thickness and 100 degrees in radian. Secondly, the sector-shaped bovine articular cartilage is fixed onto a sample holder through bone cement. Thirdly, the physiological motion of a femoral head is simulated on a swing tester, so that the frictional wear test can be completed. Fourthly, the worn part of the sector-shaped bovine articular cartilage is divided into 10-50 slices, and the 10-50 slices are scanned in a nuclear magnetic resonance system, wherein the scanning mode is in the form of a 256*256 matrix and the scanning field-of-view is 20*20 mm. The thicknesses of the 10-50 slices are 1mm. Fifthly, the original joint surface and the highlighted worn part of each slice are subjected to the curve-fitting treatment by utilizing the ANALYZE 8.1 software, so that the area of the worn part can be accurately calculated. Sixthly, the area of the worn parts of all the slices is subjected to the integral operation, so that the volume of the worn part of the bovine articular cartilage is obtained. In this way, bovine articular cartilage injuries can be evaluated. Based on the above method, the wear extent of articular cartilage can be accurately measured. Therefore, the method provides a theoretical basis for the research on the frictional wear characteristics of articular cartilage.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Adipose-derived stem cell transfected by magnetic nanoparticle mediated IGF-I gene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104630269AImprove targetingHigh transfection efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMagnetite NanoparticlesIn vivo
The invention relates to the field of articular cartilage injury repair and particularly relates to an adipose-derived stem cell transfected by a magnetic nanoparticle mediated IGF-I gene and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises three steps of ADSCs separation and culture, Fe3O4 MNPs preparation and in vitro transfection. The mediated IGF-I gene with an iron oxide magnetic nanoparticle as a vector is used for transfecting ADSCs to achieve over expression of IGF-I, and the homing rate of stem cells is improved by a dynamically rotating magnetic field in vitro in a targeting manner, and the iron oxide magnetic nanoparticle used in the research is a non-virus gene vector, has the advantages of being safe, harmless, high targeting and efficient and stable expression of a target gene, and the like, can be used for greatly improving the gene transfection efficiency, and more importantly can be used for solving the problem of low homing rate of ADSCs in a scaffold in an implant via the dynamically rotating magnetic field in vitro, and positioning and tracking the stem cell in vivo through magnetic resonance technology.
Owner:HANGZHOU CITY XIAOSHAN DISTRICT TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICAL HOSPITAL
Health food composition
ActiveCN108112997AIncrease gelatinIncreased mucusNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsCartilage cellsHyaluronidase
The invention provides a health food composition used for preventing and treating articular cartilage injury. The health food composition is compounded from bone collagen, hydrolyzed collagen type II,broccoli extract and pine bark extract in specific proportion, wherein the bone collagen can increase colloid and mucus in articulations and accelerate restoration and survival of cartilage tissues and synovial fluid; the hydrolyzed collagen type II is helpful to resist cartilage proteolytic enzyme and recombine injured cartilage cells; sulforaphen in the broccoli extract slows up a cartilage injury progress by preventing the effects of multiple enzymes which result in articulation degeneration in osteoarthritis; and abundant procyanidine contained in the pine bark extract has obvious inhibiting effects on collagenase, elastase, hyaluronidase and the like, thereby reducing the damaging effects of the enzymes on collagen, elastin, hyaluronic acid and other substances.
Owner:BEIJING COMPETITOR SPORTS SCI & TECH
Gradient material for promoting cartilage calcification layer repair and preparation method
ActiveCN113456885APromotes regenerative repairApplications to Promote Synergistic Healing RepairTissue regenerationNon-woven fabricsSpinningGradient material
The invention discloses a gradient material for promoting cartilage calcification layer repair and a preparation method. The gradient material is composed of a superfine fiber microporous membrane, an organic fiber microporous membrane and an organic-inorganic composite fiber microporous membrane, wherein the upper surface and the lower surface of the superfine fiber microporous membrane are covered with the organic fiber microporous membrane and the organic-inorganic composite fiber microporous membrane respectively. The upper layermembrane contains components that promote cartilage healing, an inorganic component in the lower layer membrane is composed of multifunctional inorganic particles which can inhibit inflammation, prevent and control infection and promote regeneration and repair of a cartilage calcification layer, and the gradient material is prepared through a three-step electrostatic spinning technology. The method is convenient to operate, and the gradient material has a remarkable promoting effect on various articular cartilage injury problems, especially on regeneration, repair and reconstruction of a calcified layer, can also promote healing of subchondral bones and cartilage tissues, is adjustable in degradation rate of gradient materials, and has a good regulating effect on various joint lesion inflammations.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent for articular cartilage injury as well as preparation and application of targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent
InactiveCN113440626AImprove permeabilityHigh precisionNanomagnetismEmulsion deliveryExtracellular matrix bindingCell-Extracellular Matrix
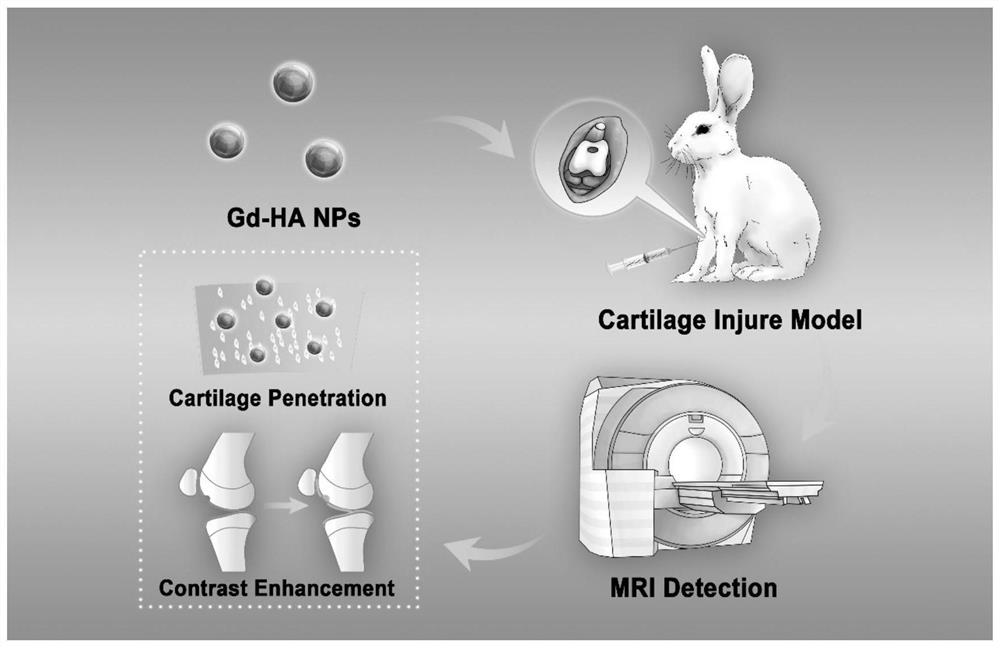
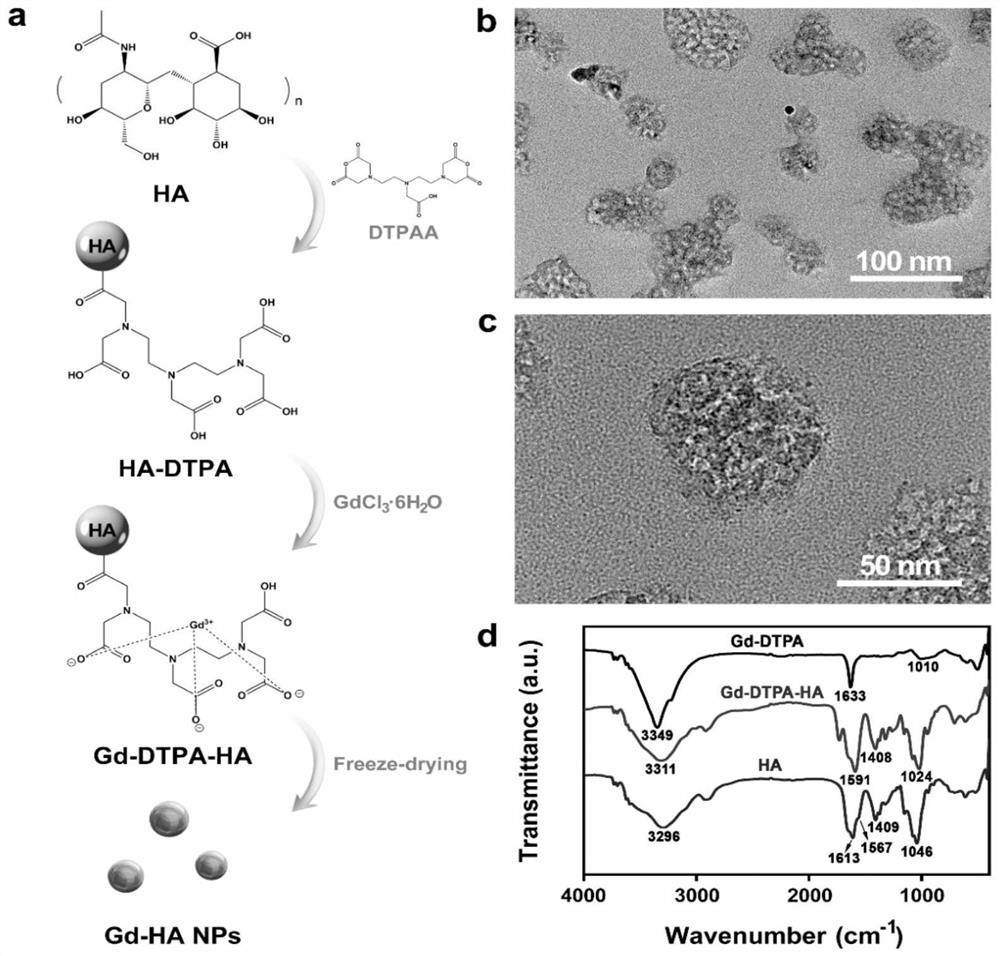
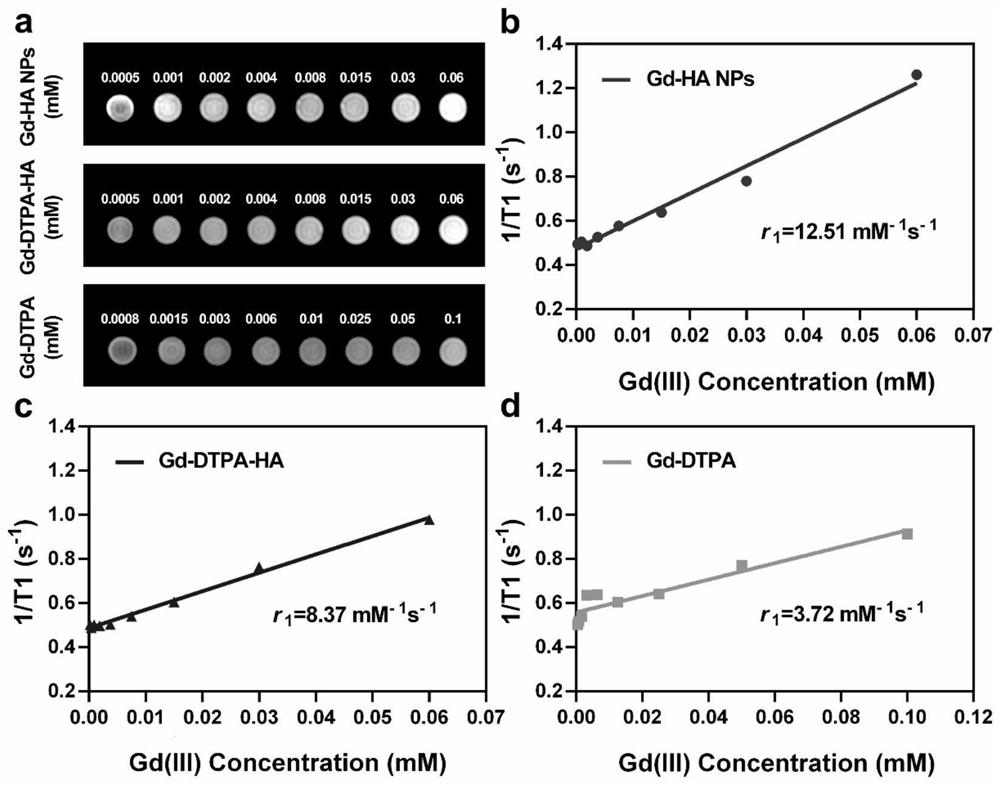
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and relates to a targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent for articular cartilage injury as well as preparation and application of the targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent. The structure of the contrast agent is HA-DTPA-Gd, hyaluronic acid HA and gadolinium ions Gd (III) are linked through diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid DTPA, and the molecular structural formula of the contrast agent is shown in the formula (I). The contrast agent can be injected through an articular cavity, the size of the contrast agent is nanoscale, nanoparticles are combined with an extracellular matrix of a cartilage defect area based on the surface effect of the nanoparticles, specific aggregation in the cartilage injury area is easier, the enhancement degree of a focus area after MRIT1 weighted delay enhancement is more obvious than that of a clinical gadolinium-containing contrast agent, and therefore the cartilage injury focus can be accurately and visually displayed; improvement of accuracy and safety of clinical treatment is facilitated, the curative effect of a knee joint cartilage injury treatment mode is evaluated, and prognosis of a patient is evaluated.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
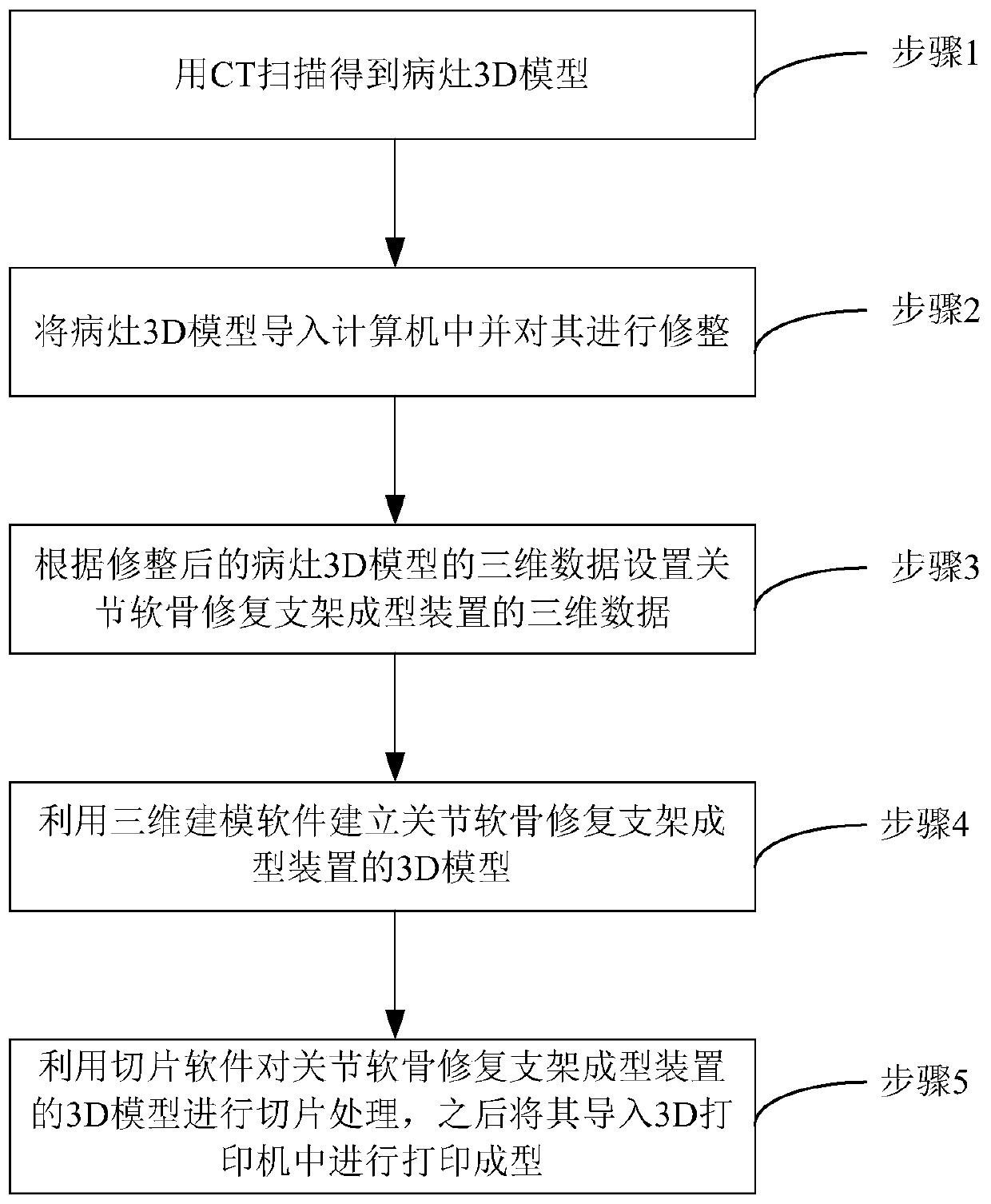
Articular cartilage repair stent forming device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110236739AReduce lossReduce trimmingBone implantJoint implantsCt examinationArticular cartilage injuries
The invention discloses a preparation method of an articular cartilage repair stent forming device. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining three-dimensional data of the joint cartilage injury part of a patient through CT examination, and obtaining a 3D model of the joint cartilage injury through three-dimensional modeling software; trimming the obtained 3D model of the articular cartilage injury by using the three-dimensional modeling software to obtain three-dimensional data of the trimmed articular cartilage injury 3D model; setting three-dimensional data of the articular cartilage repair stent forming device according to the three-dimensional data of the trimmed articular cartilage injury 3D model; drawing a 3D model of the articular cartilage repair stent forming device by utilizing the three-dimensional modeling software according to the three-dimensional data of the articular cartilage repair stent forming device; carrying out slicing treatment on the 3D model of the articular cartilage repair stent forming device in the step 4 by utilizing 3D printing slicing software, and then introducing the 3D model of the articular cartilage repair stent forming device subjected to slicing treatment into a 3D printer for 3D printing and forming.
Owner:BEIJING WANJIE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Cartilage tissue cell viability assaying method
ActiveCN105779558AGood for maintaining activityOptimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisWater bathsCartilage cells
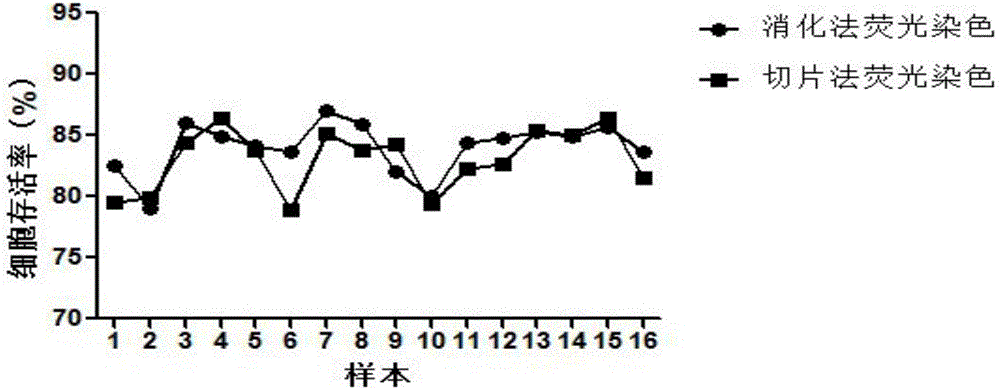
The invention discloses a cartilage tissue cell viability assaying method. The cartilage tissue cell viability assaying method includes: shearing cartilage tissues into small fragments and digesting the small fragments by 0.25% trypsin-EDTA2Na water bath; centrifuging and then continuing digesting by 0.2% type-II collagenase water bath; after the cartilage tissues become flocculent, adding a DMEM culture solution to suspend digestion and filtering by a 200-mesh screen, centrifuging filtrate and discarding liquid supernatant; adding FDA and EB into a cell suspension and incubating away from light; counting green and red cells in an image by IPP image analysis software and computing cartilage tissue cell viability according to a formula. The cartilage tissue cell viability assaying method is simpler to operate and beneficial to digesting and separating cartilage cells sufficiently, reduces damage to the cartilage cells during digesting and separating, is conducive to maintaining cell viability, avoids complexity caused by different excitation wavelengths of a double-fluorescent stain, and is used for screening articular cartilage injury treatment schemes and evaluating tissue bank cartilage preservation effects.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Application of miR-27 or analog thereof to in vitro restraining of differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to hypertrophic chondrocyte
InactiveCN109833328AImprove the level ofPromote damage repair effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCartilage injuryApoptosis
The invention provides an application of miR-27 or an analog thereof to in vitro restraining of differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to hypertrophic chondrocyte, and belongs to the technical field of medicines for inducing differentiation from the mesenchymal stem cells to chondrocyte and cartilage injury, an application of miR-27 to restraining of the mesenchymal stem cells to the hypertrophic chondrocyte, an application of the miR-27 to promotion of differentiation of the hypertrophic chondrocyte to the chondrocyte, and an application of miR-27 to preparation of medicines for treating cartilage injury. When the articular cartilage is damaged, the miR-27 or the analog thereof is used for restraining the differentiation of the mesenchymal stem cells to hypertrophic chondrocyte, and the chondrocyte apoptosis and the subsequent ossification process are prevented, so that the miR-27 can maintain and stabilize normal physiological function of the chondrocyte, and articular cartilage injury is promoted to regenerate and repair.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
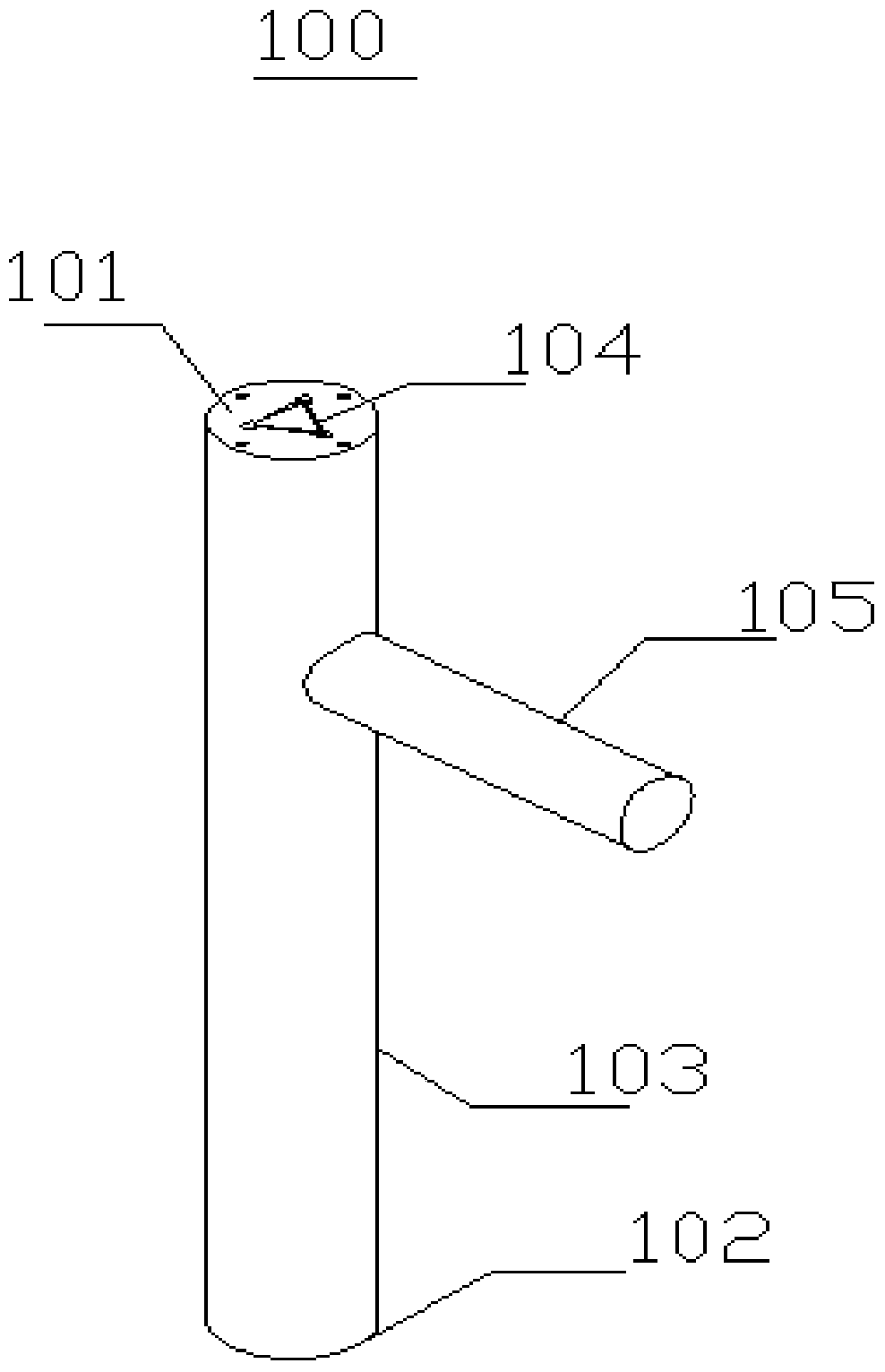
Repairing tool for articular cartilage injuries
The invention discloses a repairing tool for articular cartilage injuries. The repairing tool comprises a rod piece, the rod piece comprises a first section and a second section, the first section isused for receiving rotation driving, the end of the second section is provided with a spherical head, the repairing tool further comprises an annular elastic cover, and the end of the first section, the annular elastic cover and the end of the second section are sleeved in sequence; friction resistance between the annular elastic cover and the first section is set to be within a preset range, andwhen the resistance between the annular elastic cover and the first section is larger than the preset range, the portion between the annular elastic cover and the first section is idle. According to the repairing tool for the articular cartilage injuries, the two ends and middle of the rod piece are connected through the annular elastic cover, when the resistance is large, the annular elastic cover decouples transmission, in this way, through reasonable pressure selection, the spherical head can get rid of injured cartilages, and gets stuck when meeting normal cartilages, and thus the probability that normal cartilage tissue is gotten rid of is lowered.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Medicine for blocking inflammation factors of patient suffering from articular cartilage injuries in knee arthritis
InactiveCN106822876AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSuperoxide dismutase
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology and relates to a medicine for blocking inflammation factors of a patient suffering from articular cartilage injuries in knee arthritis. The medicine is characterized by being prepared from components as follows: 1*10<7> cell / ml umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, 10-25 ng / ml superoxide dismutase and 5-15 ng / ml vitamin D. The medicine is a novel medicine combination for treating Parkinson's disease clinically and can remarkably reduce the rising LDH level of lymphocyte of a Parkinson patient. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, superoxide dismutase and vitamin D compound drugs can be used for treating articular cartilage injuries in knee arthritis and have a good effect.
Owner:SHANDONG JINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Imaging biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of back pain and related conditions
The present invention teaches novel methods of diagnosing and prognosing conditions associated with tissue degeneration and / or pain, including intervertebral disc degeneration, discogenic pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and articular cartilage injury. Using the inventive noninvasive imaging methods, the diagnosis and prognosis of back pain and related conditions can be quickly and accurately determined by detecting one or more biomarkers disclosed herein.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell and PRP combined preparation for repairing articular cartilage injury as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112294845ARepair damageGood effectCell dissociation methodsSkeletal disorderMesenchymal stem cellTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to the technical field of cell preparations, in particular to a synovial mesenchymal stem cell and PRP combined preparation for repairing articular cartilage injury as well as apreparation method and application thereof. The synovial mesenchymal stem cell and PRP combined preparation comprises synovial mesenchymal stem cells and PRP. The synovial mesenchymal stem cell and PRP combined preparation provided by the invention can effectively repair the articular cartilage injury, and the effect is better than the treatment effect of combination of sodium hyaluronate and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:国大生命科学产业集团(深圳)有限公司
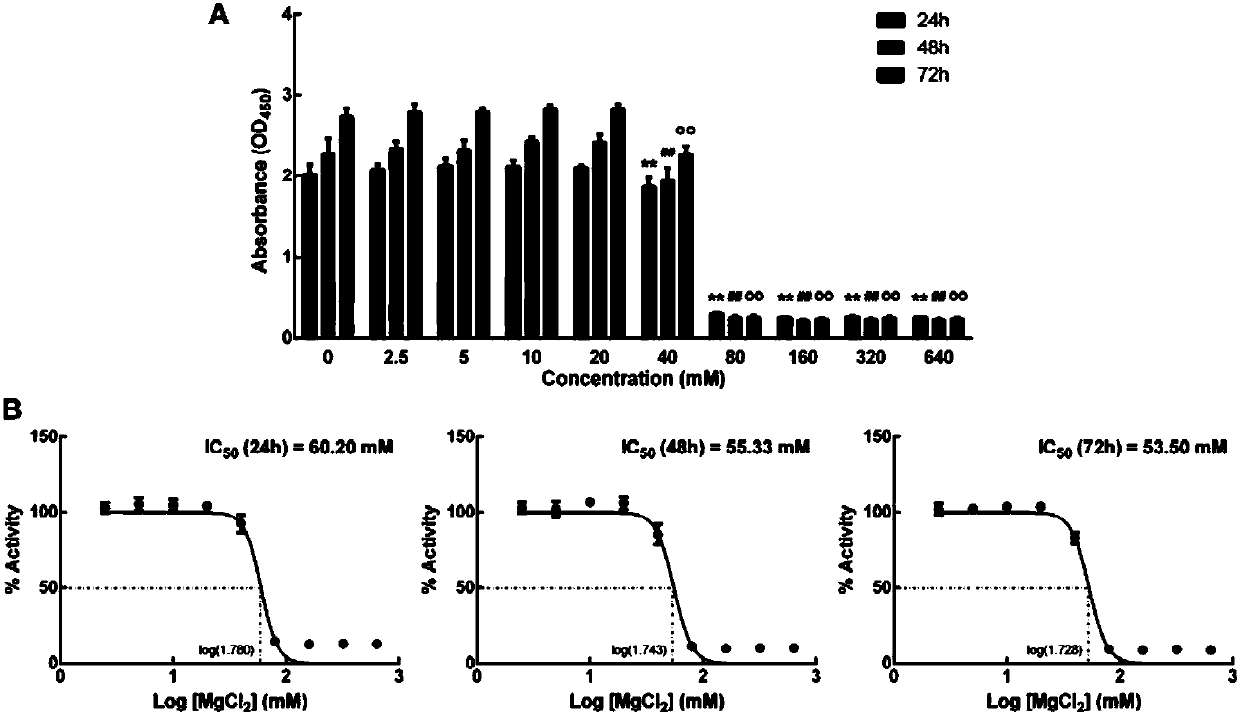
Application of magnesium chloride solution to preparation of medicines for treating osteoarticular diseases
InactiveCN107714718AExpansion of indications for medicationPromote proliferationInorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTreatment effectM2 polarization
The invention discloses the application of a solution containing magnesium chloride serving as an effective component to the preparation of medicines for treating osteoarticular diseases. The solutionis prepared by taking normal saline as a solvent, and the magnesium chloride concentration of the solution is 10 to 20 mmol / L. The osteoarticular diseases comprise articular cartilage injury disease,articular cartilage degenerative disease, arthritis disease and the like. According to the invention, the magnesium chloride solution can promote cartilage cell proliferation and cell activity, has the effects of inhibiting macrophagocyte from being polarized to the M1 state and promoting M2 polarization, can effectively control inflammatory reaction caused by the macrophagocyte, is favorable fortissue healing, has a good treatment effect on the osteoarticular diseases and can promote tissue repairing.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Cartilage repair material containing translationally controlled tumor protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
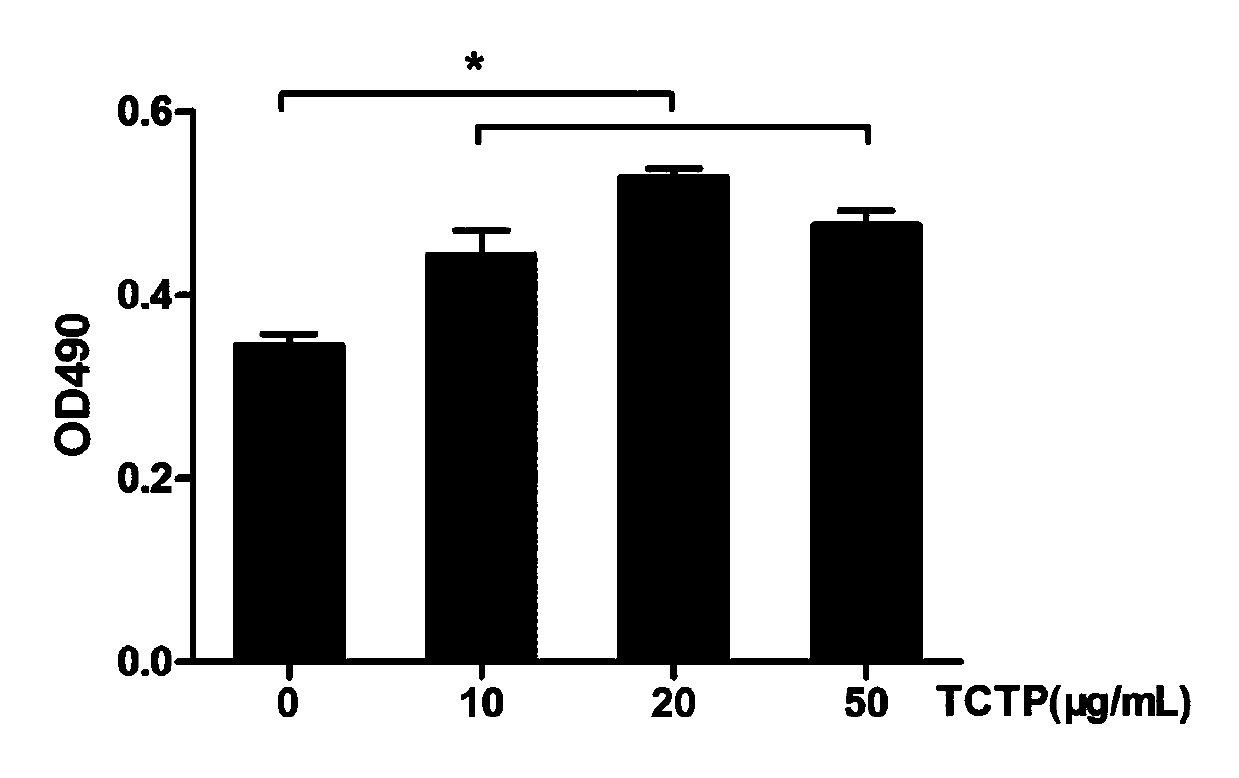
InactiveCN111558086APromote proliferationBioabsorbableTissue regenerationProsthesisCartilage cellsCartilage lesion
The invention provides a preparation method of a cartilage repair material containing translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) and application of the cartilage repair material in treating articular cartilage injury. The cartilage repair material constructed by the invention contains TCTP, so that the cartilage repair material has a strong cartilage cell proliferation promoting effect; the cartilage repair material has a 3D complex structure, the in-vivo survival microenvironment of cartilage cells is well simulated, the TCTP-containing cartilage repair material provides a suitable microenvironment for the growth and metabolism of the cartilage cells, and the rapid proliferation of the cartilage cells is ensured. According to the repair material disclosed by the invention, collagen sponge and sodium alginate are combined to serve as a scaffold, so that the cartilage repair material has the characteristics of bioabsorbability and no toxicity, has good tissue intermiscibility and cell adsorbability, and has a remarkable promoting effect on cartilage injury repair.
Owner:广州市红十字会医院
Articular Cartilage Mesh Fixation System
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Preparation method of gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage damage
The invention relates to the fields of medicines and medical instruments, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) modifying sodium hyaluronate; (2) dissolving PLGA nano-particles of a controlled-release small molecular compound in the sodium hyaluronate modified in the step (1), and then adding with a photoinitiator to obtain a controlled-release small molecular compound-sodium hyaluronate gel compound system; and (3) injecting / filling the controlled-release small molecular compound-sodium hyaluronate gel compound system to the articular cartilage injuries to be repaired for being irradiated by an ultraviolet point light source, so as to obtain the gel scaffold for repairing articular cartilage injuries. The gel scaffold provided by the invention is high in plasticity, and capable of being randomly shaped according to the shapes of cartilage defects; harmful substances are not introduced in the whole process, and the gel scaffold can be used in vivo.
Owner:NANJING ZHENQUAN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
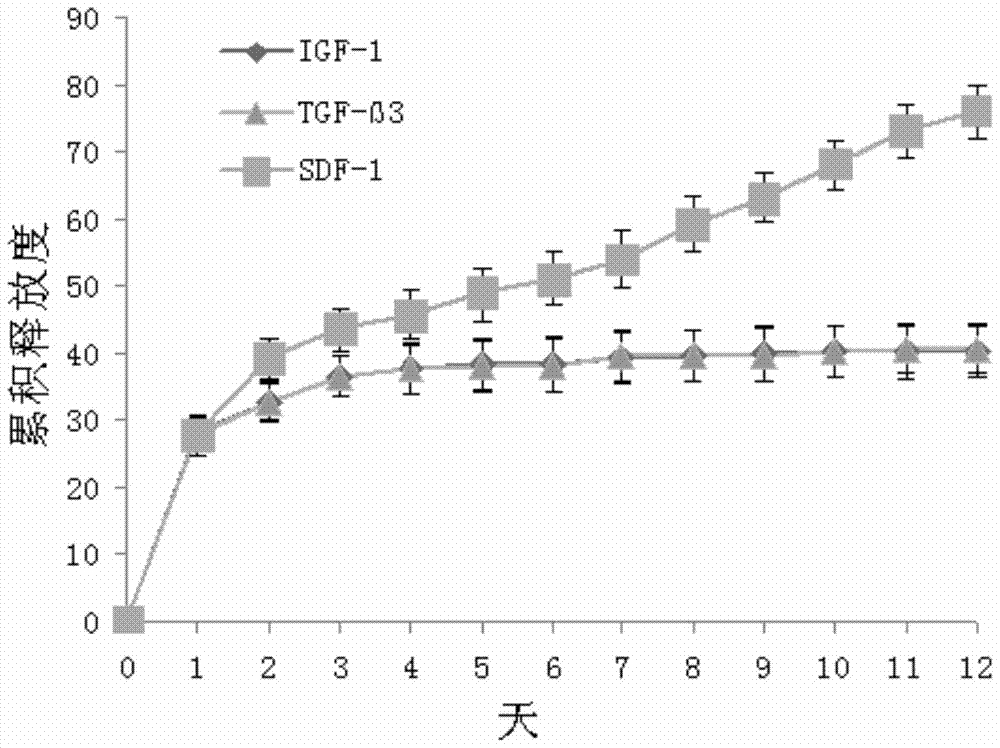
A multi-cytokines sequential slow-release microsphere-hydrogel composite system and its preparation method
InactiveCN104622795BImprove repair effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryMicrosphereCytokine
Owner:HANGZHOU CITY XIAOSHAN DISTRICT TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICAL HOSPITAL
Repair tooling for articular cartilage damage
The invention discloses a repairing tool for articular cartilage injuries. The repairing tool comprises a rod piece, the rod piece comprises a first section and a second section, the first section isused for receiving rotation driving, the end of the second section is provided with a spherical head, the repairing tool further comprises an annular elastic cover, and the end of the first section, the annular elastic cover and the end of the second section are sleeved in sequence; friction resistance between the annular elastic cover and the first section is set to be within a preset range, andwhen the resistance between the annular elastic cover and the first section is larger than the preset range, the portion between the annular elastic cover and the first section is idle. According to the repairing tool for the articular cartilage injuries, the two ends and middle of the rod piece are connected through the annular elastic cover, when the resistance is large, the annular elastic cover decouples transmission, in this way, through reasonable pressure selection, the spherical head can get rid of injured cartilages, and gets stuck when meeting normal cartilages, and thus the probability that normal cartilage tissue is gotten rid of is lowered.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Mesenchymal stem cell preparation for repairing articular cartilage damage/defect, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108865986BPromote repairGood treatment effectSkeletal disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSynovial CellArticular cavity
Owner:马琳 +1
Pressure device for detecting patellofemoral cartilage injury and quantitative evaluation method
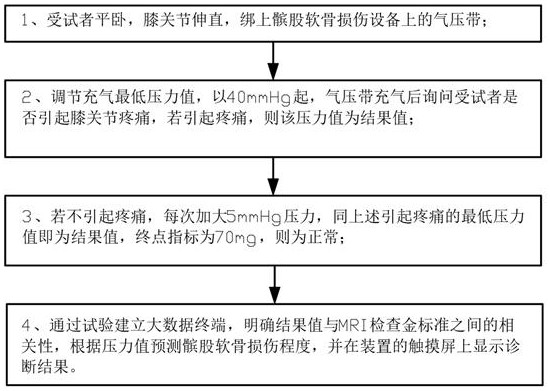
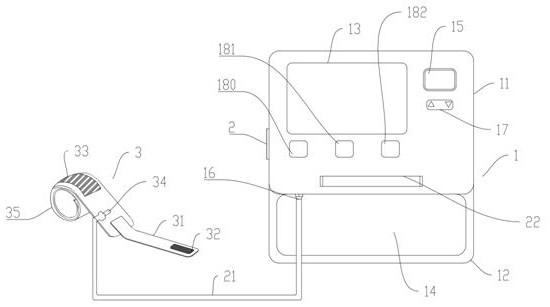
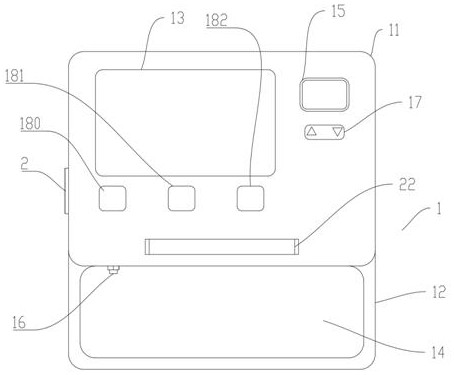
PendingCN113143219ALow costAccurate assessmentDiagnostics using pressureSensorsMedical equipmentCartilage lesion
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, in particular to a pressure device for detecting patellofemoral cartilage injury and a quantitative evaluation method. The device comprises a case part and a pressure belt, the case part is composed of a lower case box and an upper sliding cover display interface, and a touch screen is arranged on the sliding cover display interface; a display screen is arranged on the right side of the touch screen, a pressure adjusting button is arranged below the display screen, three buttons are arranged below the touch screen and are an equipment starting button, an inflation starting button and a deflation button in sequence from left to right, a handle is arranged at the sideline of a display interface of the sliding cover, an air pressure belt storage groove is formed in the case box, an air pressure outlet is formed in the inner wall of the air pressure belt containing groove and connected with a pressure belt through a guide pipe. The patellofemoral articular cartilage injury is quantitatively evaluated through the minimum pressure value of patellofemoral joint pain, and the non-invasive, convenient and accurate patellofemoral articular cartilage injury evaluation method is constructed.
Owner:昆山市第一人民医院
Composite material for repairing articular cartilage injury and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113244458AWide variety of sourcesIncrease network densityCell dissociation methodsConnective tissue peptidesAutologous bloodCollagenan
The invention relates to a composite material for repairing articular cartilage injury. The composite material comprises liquid collagen prepared from animal skin tissues, PRP (platelet-rich protein) prepared from autologous blood and having a certain number of platelets, and a calcium ion activator with the mass percent concentration of 5-10%, wherein the collagen, the PRP and the calcium ion activator are mixed in a volume ratio of (10-15): (10-15): 1, and the collagen and the PRP are the same in volume. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sequentially preparing the collagen and the PRP, mixing the collagen and the PRP, and then mixing the calcium ion activator. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to operate, does not need complex equipment, and is wide in raw material source; and by selecting the animal skin tissues and the autologous blood of a patient, the cost can be obviously reduced, exogenous thrombin does not need to be added, the probability of adverse reactions is reduced, and release of growth factors in the PRP can be slowed down.
Owner:康膝生物医疗(深圳)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com