Cartilage tissue cell viability assaying method
A cartilage tissue and detection method technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of high cost and difficult implementation, and achieve the effects of reliable results, avoiding damage, and convenient reagent configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
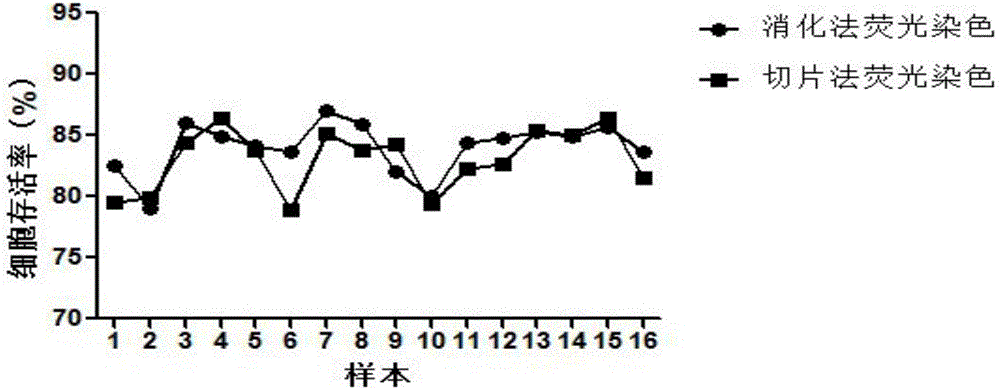
[0048] Example 1: Cut the cartilage tissue into small pieces of 1mm×1mm×1mm; digest with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA2Na in a 37°C water bath for 80 minutes; centrifuge and then continue to digest with 0.2% type II collagenase in a 37°C water bath for 2 hours; Most of the cartilage is digested and turned into flocculent, add DMEM culture medium to stop the digestion, filter through a 200-mesh screen, take the filtrate and centrifuge at 1200rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant; add FDA (50mg / l) and EB (10mg / l) to the cell suspension l), incubate at 37°C in the dark for 20 minutes; after centrifugation, make the bottom cells into cell smears and detect them under 450nm wavelength laser excitation, use IPP image analysis software to count the green and red cells in the picture, and calculate the survival rate of cartilage tissue cells 68.37%. The cell survival rate was 83.04% detected by tissue section fluorescence method.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Cut the cartilage tissue into small pieces of 1mm×1mm×1mm; digest with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA2Na in a 37°C water bath for 40 minutes; centrifuge and then continue to digest with 0.2% type II collagenase in a 37°C water bath for 4 hours; Most of the cartilage was digested and became flocculent. Add DMEM culture medium to stop the digestion and then filter through a 200-mesh screen. Take the filtrate and centrifuge at 1500rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant; add FDA (50mg / l) and EB (10mg / l) to the cell suspension. l), incubate at 37°C in the dark for 20 minutes; after centrifugation, make the bottom cells into cell smears and detect them under 450nm wavelength laser excitation, use IPP image analysis software to count the green and red cells in the picture, and calculate the survival rate of cartilage tissue cells 83.97%. The cell survival rate was 83.04% detected by tissue section fluorescence method.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Cut the cartilage tissue into small pieces of 1mm×1mm×1mm; digest with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA2Na in a 37°C water bath for 20 minutes; centrifuge and then continue to digest with 0.2% type II collagenase in a 37°C water bath for 8 hours; Most of the cartilage is digested and turned into flocculent, add DMEM culture medium to stop digestion, filter with 200 mesh screen, take the filtrate and centrifuge at 1400rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant; add FDA (50mg / l) and EB (10mg / l) to the cell suspension l), incubate at 37°C in the dark for 20 minutes; after centrifugation, make the bottom cells into cell smears and detect them under 480nm wavelength laser excitation, use IPP image analysis software to count the green and red cells in the picture, and calculate the survival rate of cartilage tissue cells 76.59%. The cell survival rate was 83.04% detected by tissue section fluorescence method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com