Catalyst for degrading antibiotics in water through photocatalysis as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
A photocatalyst and antibiotic technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of antibiotics entering the soil, ecological environment and human health hazards, water environment hazards, etc., and achieve the effects of easy control, high catalytic efficiency and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Preparation of nano-powder precursor solution:
[0025] Stir and mix 0.895g of strontium acetate, 1.553g of antimony pentoxide (the molar ratio of strontium acetate to antimony pentoxide is 1.36:2) and 70 ml of deionized water at room temperature, adjust the pH to 5 with 4 mol / L nitric acid, Obtain nanopowder precursor liquid.
[0026] (2) Preparation of nano powders under hydrothermal conditions:
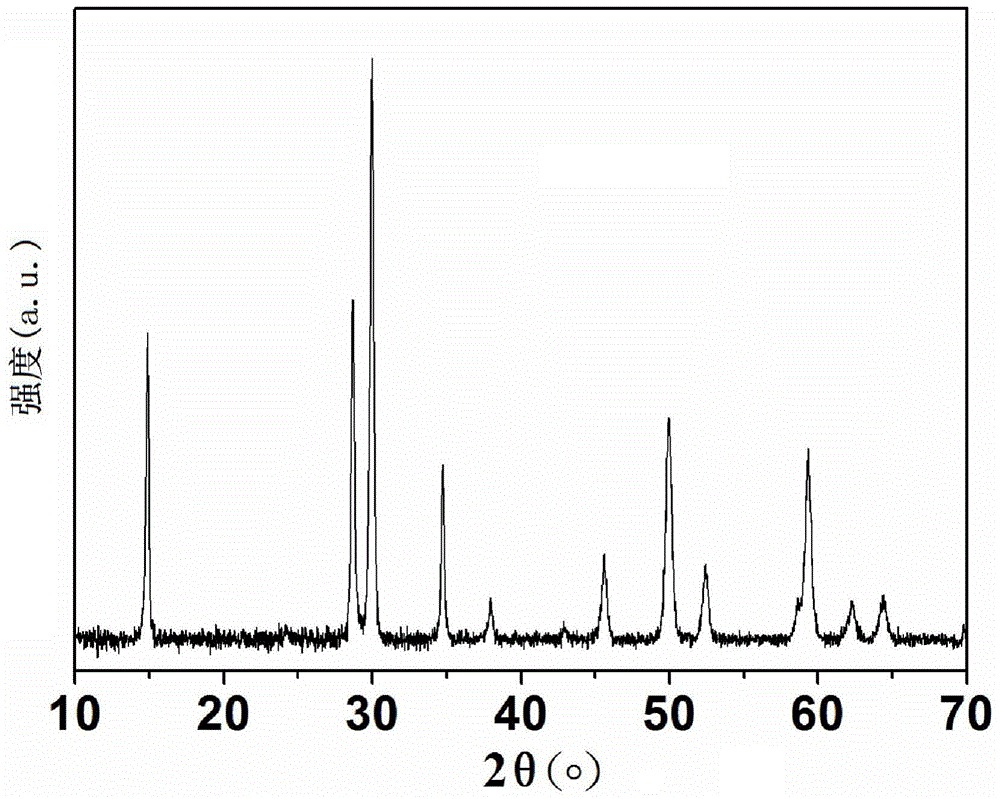
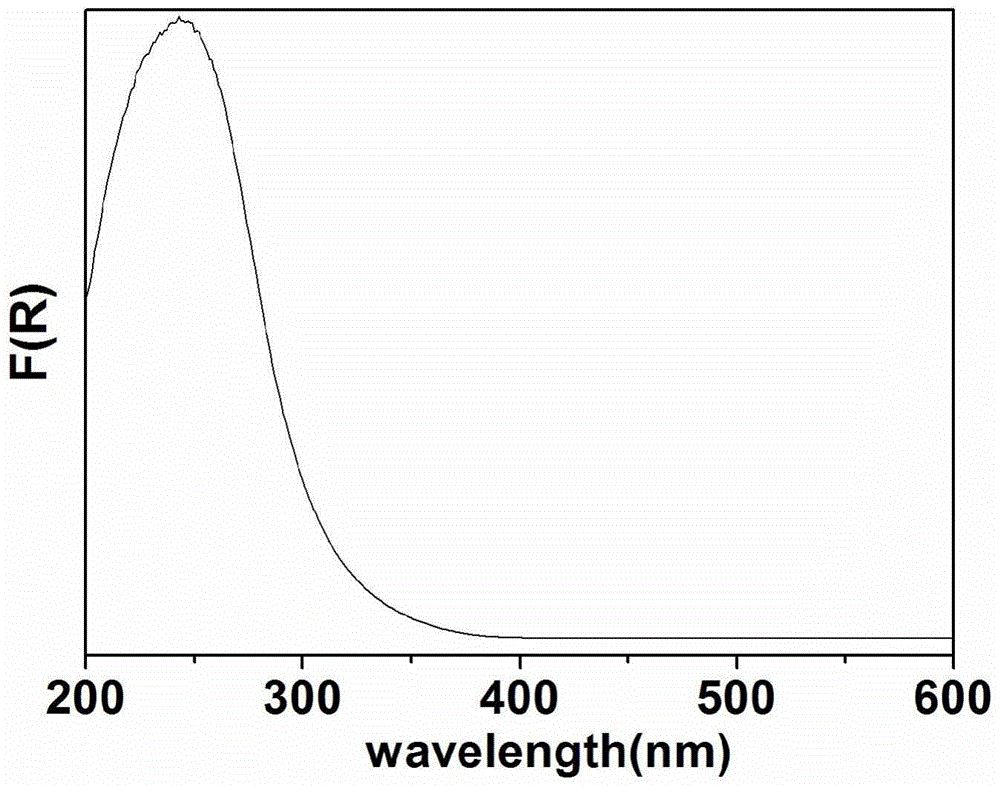
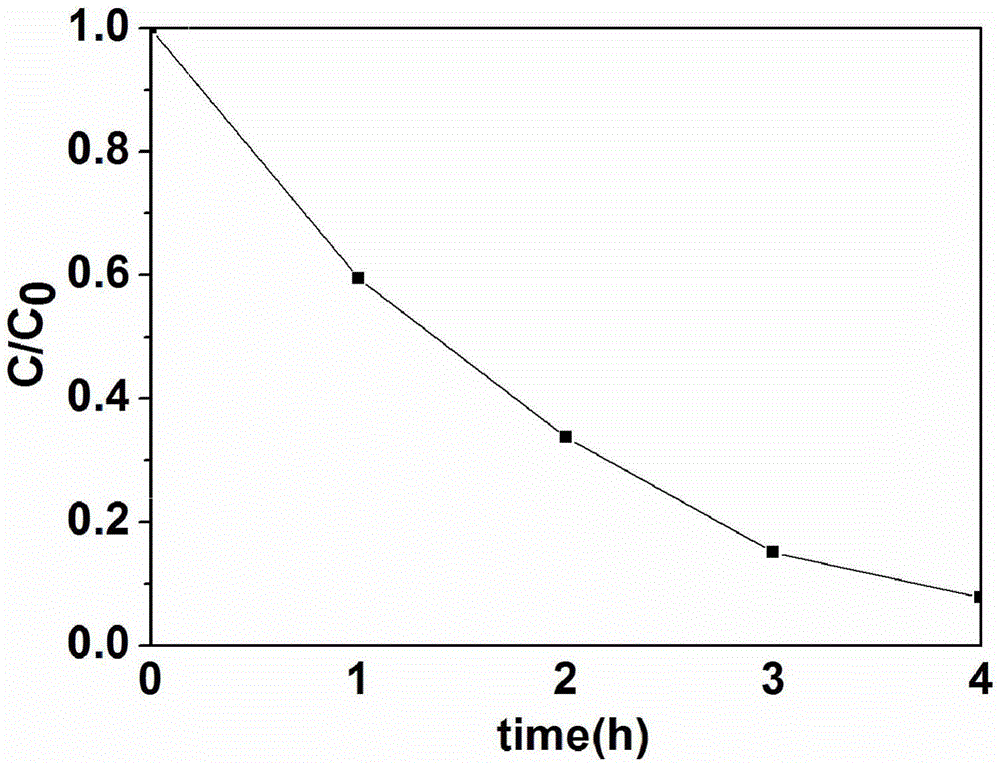
[0027] Put the above-mentioned nano-powder precursor solution in a 100 ml high-pressure reactor, heat it up to 100 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and keep it warm for 24 h for hydrothermal reaction. Washed with absolute ethanol for 3 times, put in a drying oven and dried at 80°C to obtain Sr 1.36 Sb 2 o 6 catalyst of light.
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Preparation of nano-powder precursor solution:
[0030] Stir and mix 0.700g strontium acetate, 0.971g antimony pentoxide (the molar ratio of strontium acetate to antimony pentoxide is 1.70:2) and 65ml deionized water at room temperature, and adjust the pH to 1 with 6mol / L nitric acid to obtain nano Powder precursor.
[0031] (2) Preparation of nano powders under hydrothermal conditions:
[0032] Put the above-mentioned nano-powder precursor solution in a 100ml high-pressure reactor, heat it up to 180°C at a rate of 3°C / min and keep it warm for 10 hours for hydrothermal reaction. After the reaction is completed, naturally cool to room temperature and take it out. Washed with water and ethanol for 4 times, put into a drying oven and dry at 70°C to obtain Sr 1.36 Sb 2 o 6 catalyst of light.
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Preparation of nano-powder precursor solution:
[0035] Stir and mix 0.391g of strontium acetate, 0.647g of antimony pentoxide (the molar ratio of strontium acetate to antimony pentoxide is 1.90:2) and 75ml of deionized water at room temperature, and adjust the pH to 4 with 5mol / L nitric acid to obtain nano Powder precursor.
[0036] (2) Preparation of nano powders under hydrothermal conditions:
[0037] Put the above-mentioned nano-powder precursor solution in a 100ml high-pressure reactor, heat up to 200°C at a rate of 5°C / min and keep it warm for 6 hours for hydrothermal reaction. After the reaction is completed, naturally cool to room temperature and take it out. Washed with water and ethanol for 4 times, put into a drying oven and dry at 60°C to obtain Sr 1.36Sb 2 o 6 catalyst of light.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com