Preparation method of microorganism-nano particle composite system used for degrading phenol
A nanoparticle and microbial technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of lack of synergy between microorganisms and nanomaterials, complex preparation methods, and difficulty in promotion. The effect of overcoming the difficulty of desorption, simple preparation method and accelerating the biodegradation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Composite system of microorganisms and nanoparticles for degrading phenol
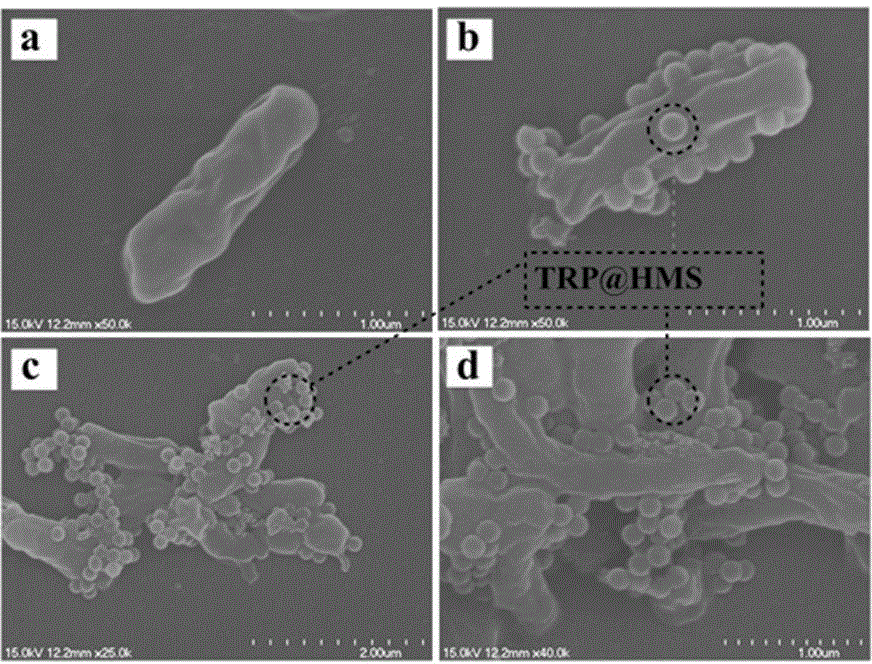
[0036] (1) Introduce polymer into hollow porous silica (HMS)
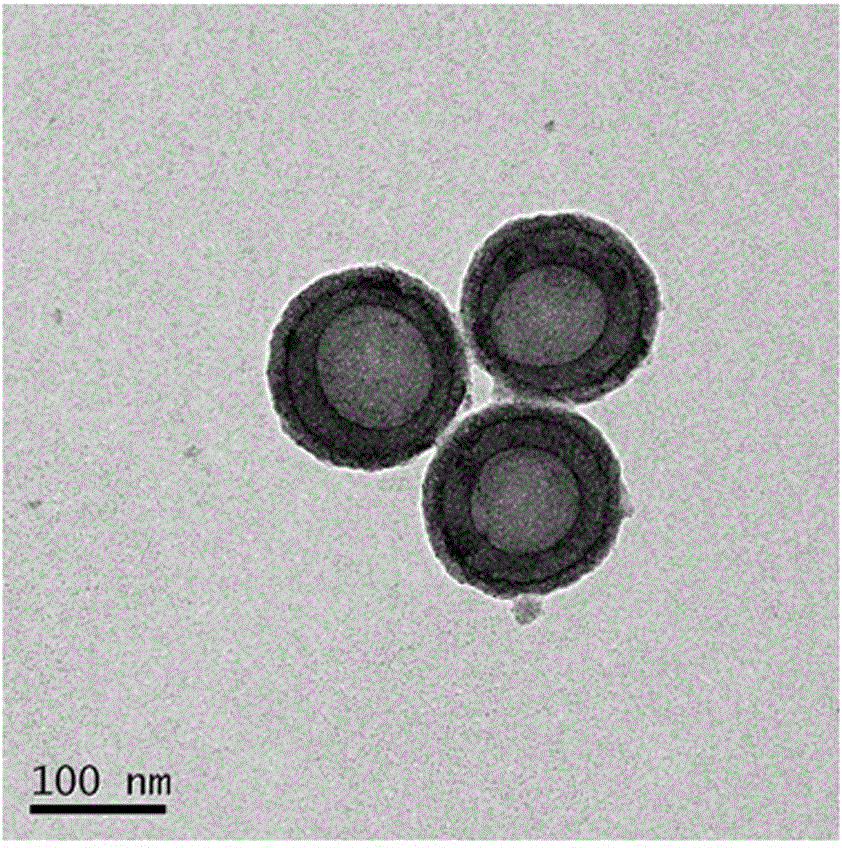
[0037]Dissolve 2ml of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane and 0.8g of succinic anhydride in 10ml of dimethylsulfoxide, then disperse 50mg of hollow porous silica (HMS) into this solution, stir at room temperature for 5h, centrifuge, The precipitate was vacuum-dried to obtain surface-modified hollow porous silica HMS-COOH; the obtained HMS-COOH nanoparticles were dispersed to contain 113 mg N-isopropylacrylamide, 1 mmol N,N-methylenebisacrylamide, 1.0 mmol methyl Acrylamide and 7mg of azobisisobutyronitrile in 10ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, stirred for 12 hours, let the monomer and initiator small molecules enter the cavity of the nanoparticle; centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and redisperse the remaining precipitate Into 10 ml dimethyl sulfoxide, under the protection of nitrogen, polymerize at 70°C for 7 hours, centrifuge, prec...
Embodiment 2
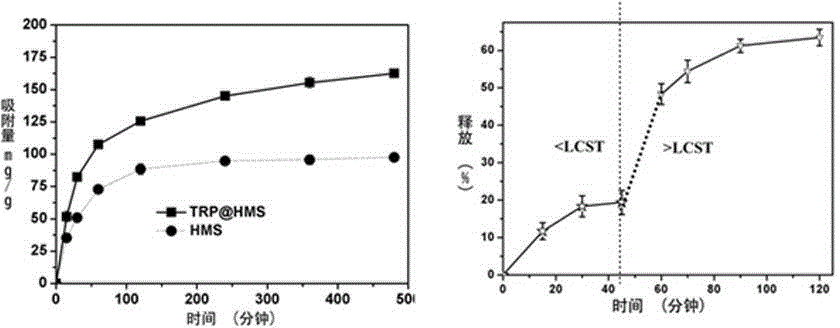
[0046] Disperse 50 mg TRPHMS and HMS separately to 20 ml 500mg L -1 In the phenol solution, samples were taken at different times to measure the adsorption capacity. The TRPHMS adsorbed to saturation was obtained by centrifugation, and then placed in clear water at different temperatures to test the concentration of phenol in the water, so as to determine the desorption of phenol from nanoparticles.
[0047] attached image 3 The adsorption of TRPHMS and HMS above and the desorption of TRPHMS at different temperatures (below and above the nanoparticle LCST (lower critical solution temperature)), it can be clearly seen from the figure that compared with HMS, the introduction of polymer After TRPHMS adsorption rate and adsorption capacity are increased. In addition, in the case of desorption, after the temperature rises (greater than LCST), the desorption speed of TRPHMS is faster than when the temperature is lower than LCST, indicating that the hollow porous nanoparticles of ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Divide 150 ml of Pseudomonas putida LB culture solution into three equal portions, two of which were grafted with TRPHMS according to the above example, and the other portion was centrifuged for later use. Add two parts of BacteriaTRPHMS and pure bacterial liquid Bacteria to 100 ml 500 mg L -1 The phenol solution was made into three samples; the pure bacterial solution and one BacteriaTRPHMS sample were placed at room temperature; the other BacteriaTRPHMS sample was placed alternately at room temperature and in a 37°C water bath; samples were taken separately to test the concentration of phenol at different times. The steps of alternating water bath treatment are 1h at room temperature and 20 min in 37°C water bath
[0050] attached Figure 4 is the variation of phenol concentration in different samples at different times. It can be seen from the figure that the composite system degrades phenol faster than the simple bacteria, which is due to the adsorption of nanopar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com