Special bioactive organic fertilizer for peanuts and application thereof
A bio-organic fertilizer and bio-active technology, which is applied to peanut-specific bio-active organic fertilizers and its application fields, can solve the problems of not being suitable for fresh tobacco leaves and the shortage of peanut-specific fertilizers, and reduce the incidence rate, improve soil physical and chemical properties, and improve growth and development. and the effect of seed setting rate promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Preparation of Peanut Special Bioactive Organic Fertilizer
[0049] 1. Prepare raw materials
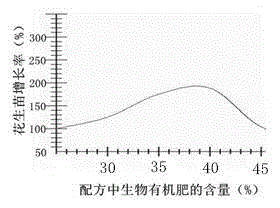
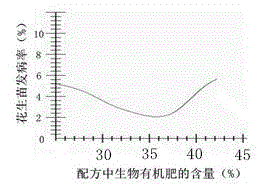
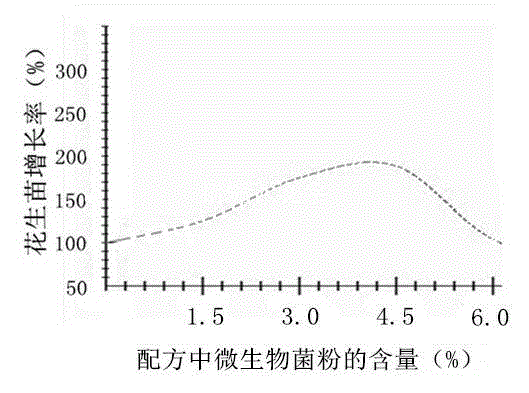
[0050] Prepare each component according to the following parts by weight: 38 parts of bio-organic fertilizer, 4 parts of microbial bacterial powder, 3.5 parts of heavy superphosphate, 2.5 parts of potassium ore powder, 2 parts of iron sulfate, 1.5 parts of calcium sulfate, 0.5 part of zinc sulfate, molybdenum 2 parts of ammonium chloride, 4 parts of ferric chloride, 9 parts of clay, and 12 parts of borax.
[0051] The bio-organic fertilizer is an organic fertilizer obtained by treating unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves with houseflies.
[0052] The microbial powder is Azotobacter delbrueckii with a weight ratio of 1.5:1:0.5 ( Beijerinckia derxii ), Bacillus japonicus ( Bacillus popilliae ) and Enterobacter cloacae ( Enterobacter cloacae ) mixed bacteria powder.
[0053] 2. The preparation steps are as follows:
[0054] S1. Utilize the housefly to process unsui...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 Preparation of Peanut Special Bioactive Organic Fertilizer
[0063] 1. Prepare raw materials
[0064] Prepare each component according to the following parts by weight: 38 parts of bio-organic fertilizer, 4 parts of microbial bacterial powder, 3.5 parts of heavy superphosphate, 2.5 parts of potassium ore powder, 2 parts of iron sulfate, 1.5 parts of calcium sulfate, 0.5 part of zinc sulfate, molybdenum 2 parts of ammonium chloride, 4 parts of ferric chloride, 9 parts of clay, and 12 parts of borax.
[0065] The bio-organic fertilizer is an organic fertilizer obtained by treating unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves with houseflies.
[0066] The microbial powder is a nitrogen-fixing bacterium phenococcus ( Azotobacter chroococum ), Bacillus japonicus ( Bacillus popilliae ) and Enterobacter cloacae ( Enterobacter cloacae ) mixed bacteria powder.
[0067] 2. The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3 Preparation of Peanut Special Bioactive Organic Fertilizer
[0069] 1. Prepare raw materials
[0070] Prepare each component according to the following parts by weight: 40 parts of bio-organic fertilizer, 3 parts of microbial powder, 3 parts of heavy superphosphate, 3 parts of potassium mineral powder, 1.5 parts of iron sulfate, 1.5 parts of calcium sulfate, 0.8 part of zinc sulfate, molybdenum 2.5 parts of ammonium acid, 3.5 parts of ferric chloride, 8 parts of clay, 12 parts of borax;
[0071] Described bio-organic fertilizer is the organic fertilizer obtained by housefly treatment that is not suitable for fresh tobacco leaves;
[0072] The microbial powder is a nitrogen-fixing bacterium phenococcus ( Azotobacter chroococum ), Bacillus japonicus ( Bacillus popilliae ) and Enterobacter cloacae ( Enterobacter cloacae ) mixed bacteria powder.
[0073] 2. The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com