A kind of method and device for preparing isopropyl acetate by reaction of propylene and acetic acid
A technology of isopropyl acetate and propylene, which is applied in the field of preparing isopropyl acetate and devices by reacting propylene and acetic acid, can solve the problem of no mention of tail gas recovery method of isopropyl acetate device, no involvement of device tail gas recovery method, and loss of propylene increase the amount of acetic acid to achieve the effect of reducing the amount of circulating acetic acid, saving equipment investment, and increasing the processing load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
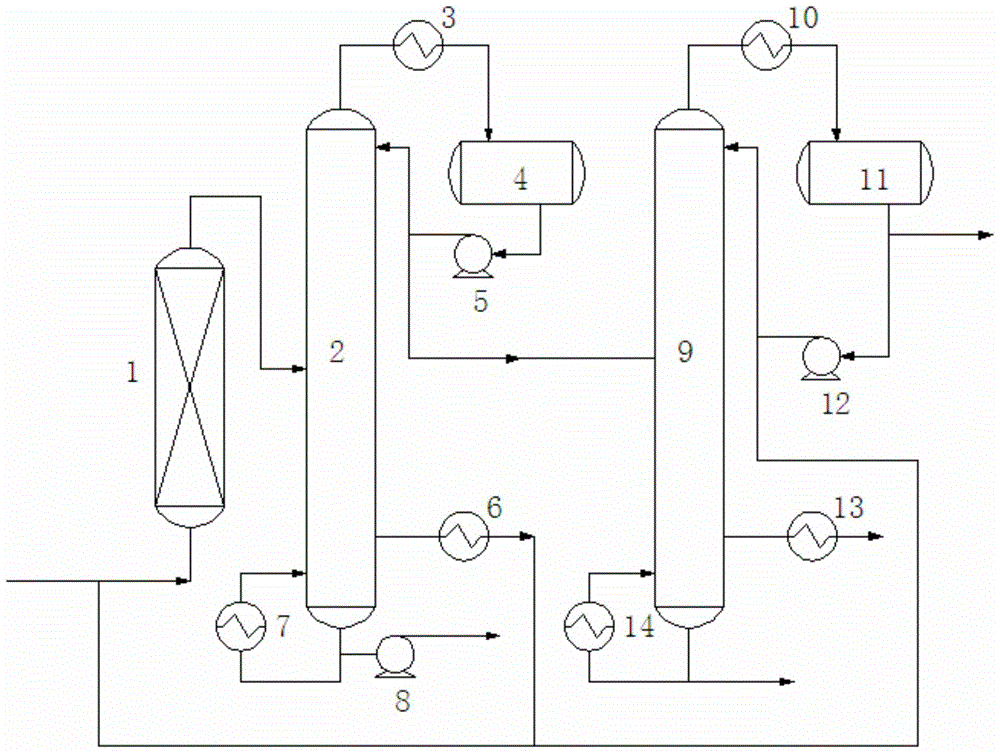
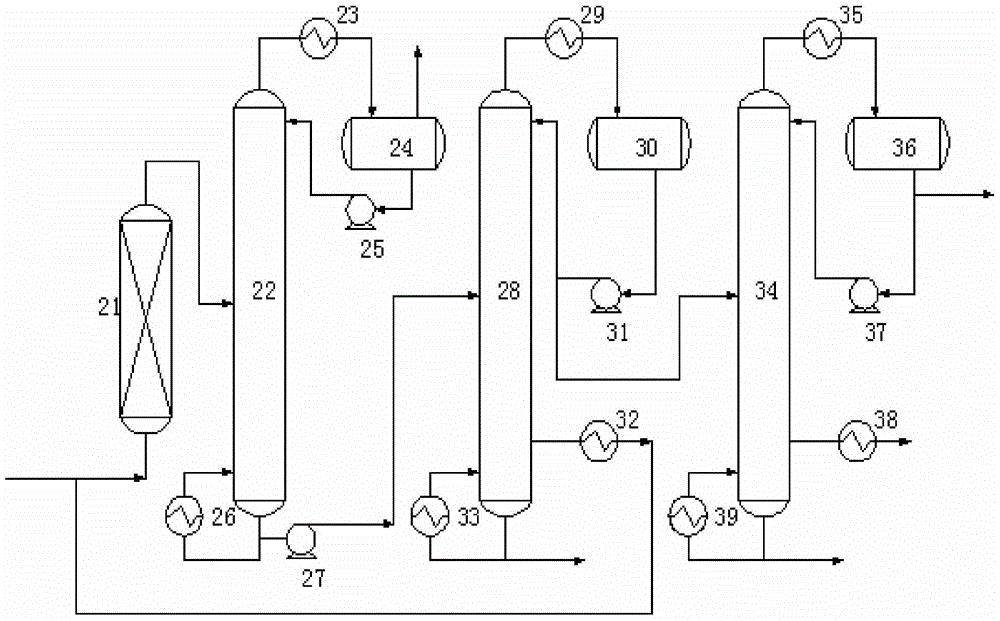
[0046] The inert component n-pentane is mixed with propylene and acetic acid at a flow rate of 2400kg / h and sent to fixed-bed reactor 1 equipped with ion exchange resin for reaction, wherein the molar ratio of n-pentane to propylene is 2:1 , the reaction temperature is 90°C, the reaction pressure is 1.5MPa, and the molar ratio of acetic acid to propylene is 2:1. The reacted mixture (composed of: 19.65% by weight of acetic acid, 31.67% by weight of isopropyl acetate, 0.55% by weight of propylene, 47.06% by weight of n-pentane, and 1.07% by weight of other by-products) is sent to the deheavy fraction tower 2, where The operating conditions of sub-column 2 are: the pressure at the top of the tower is normal pressure, the temperature at the top of the tower is 60°C, the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 110°C, the reflux ratio is 1:1, isopropyl acetate, light components below C6, unreacted The propylene and inert components are evaporated from the top of the tower, condens...
Embodiment 2
[0051]The inert component 2-methylbutane is mixed with propylene and acetic acid at a flow rate of 4800kg / h and then sent into the fixed-bed reactor 1 equipped with ion exchange resin for reaction, wherein the 2-methylbutane and propylene The molar ratio is 4:1, the reaction temperature is 70°C, the reaction pressure is 1.2MPa, and the molar ratio of acetic acid to propylene is 1:1. The reacted mixture (composed of: 0.20 wt% acetic acid, 24.58 wt% isopropyl acetate, 0.54 wt% propylene, 73.85 wt% 2-methylbutane, 0.83 wt% other by-products) is sent to the deheavy fraction tower 2 , the operating conditions of the deheavy component tower 2 are: the pressure at the top of the tower is normal pressure, the temperature at the top of the tower is 90°C; the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 130°C, the reflux ratio is 0.5:1, isopropyl acetate, light components below C6 , unreacted propylene and inert components are steamed from the top of the tower, condensed and then sent to t...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The inert component cyclopentane is mixed with propylene and acetic acid at a flow rate of 3600kg / h and sent to fixed bed reactor 1 equipped with ion exchange resin for reaction, wherein the molar ratio of cyclopentane to propylene is 3:1 , the reaction temperature is 80°C, the reaction pressure is 1.0MPa, and the molar ratio of acetic acid to propylene is 1.5:1. The reacted mixture (composed of: 7.47% by weight of acetic acid, 28.43% by weight of isopropyl acetate, 0.24% by weight of propylene, 62.07% by weight of cyclopentane, and 1.79% by weight of other by-products) is sent to the deheavy fraction tower 2, where The operating conditions of sub-column 2 are: the pressure at the top of the tower is normal pressure, the temperature at the top of the tower is 80°C; the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 120°C, the reflux ratio is 1:1, isopropyl acetate, light components below C6, unreacted The propylene and inert components are evaporated from the top of the towe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com