Method for preserving edible mushrooms
A technology for edible fungi and preservatives, applied in the application, food preservation, food science and other directions, can solve the problem that edible fungi cannot be reasonably preserved, and achieve the effect of long shelf life and zero salt water discharge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The technical solution disclosed in this embodiment is specifically as follows:
[0065] A method for preserving edible mushrooms, comprising the following steps:
[0066] 1) Raw material selection: choose fresh, mildew-free, and evenly sized Flammulina velutipes, and remove roots, feet and foreign matter;
[0067] 2) Bacteria reduction treatment of raw materials: in 95°C water, according to the material-to-liquid ratio (i.e. the mass ratio of Flammulina velutipes to water) of 1:2, add Flammulina velutipes and keep for 30 minutes to inactivate enzymes and microorganisms in the tissue;
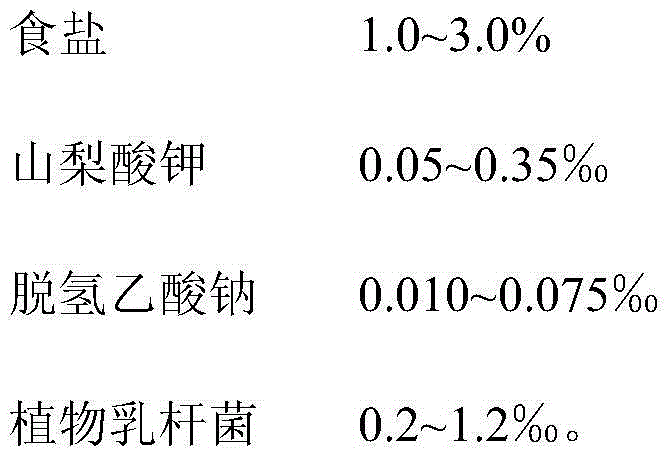
[0068] 3) Sulfur-free color protection and crispness: add citric acid, erythorbic acid sodium salt, EDTA-disodium and calcium chloride to the water after adding Flammulina velutipes. Its ratio is respectively 0.5%, 0.2%, 0.15‰, 0.5% of the total mass (water and fresh Flammulina velutipes); soaking time is 6min;
[0069] 4) Cooling: Put ozone in the water, the ozone concentration is 3.0...
Embodiment 2-5
[0076] Carry out by following steps and process parameter, all the other are with embodiment 1.
[0077]
[0078] The above edible fungus preservation method has low production cost and high production efficiency, and 1 ton of raw materials can produce about 0.4 to 0.5 tons of edible fungus semi-finished products with good quality and convenient preservation.
Embodiment 6
[0080] A method for preserving edible mushrooms, carried out according to the following steps:
[0081] 1) Raw material selection: select fresh, mildew-free, and evenly sized pear mushrooms to remove roots, feet and foreign matter;
[0082] 2) Bacteria-reducing treatment of raw materials: Add Flammulina velutipes in water at a ratio of 1:3 to liquid at 98°C and keep for 35 minutes to inactivate enzymes and microorganisms in the tissues;
[0083] 3) Sulfur-free color protection and crispness protection: add citric acid, erythorbic acid sodium salt, EDTA-disodium and calcium chloride to the water after putting in the mushroom; the proportions are 0.4% and 0.5% of the total mass (water and fresh Flammulina velutipes) respectively. %, 0.10‰, 0.6%; soaking time is 5min.
[0084] 4) Cooling: Put ozone in the water, the ozone concentration is 4.0mg / L, make cooling water, and achieve sterility, put the sterilized mushrooms into the cooling water, and cool to below 25°C;
[0085] 5) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com