A process for producing propylene using oxygen-containing compounds as raw materials
A compound and propylene technology, applied in the field of propylene production, can solve the problem of high yield of by-products such as aromatic hydrocarbons and alkanes, and achieve the effects of high propylene selectivity, improved atom utilization, and inhibition of hydrogen transfer reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
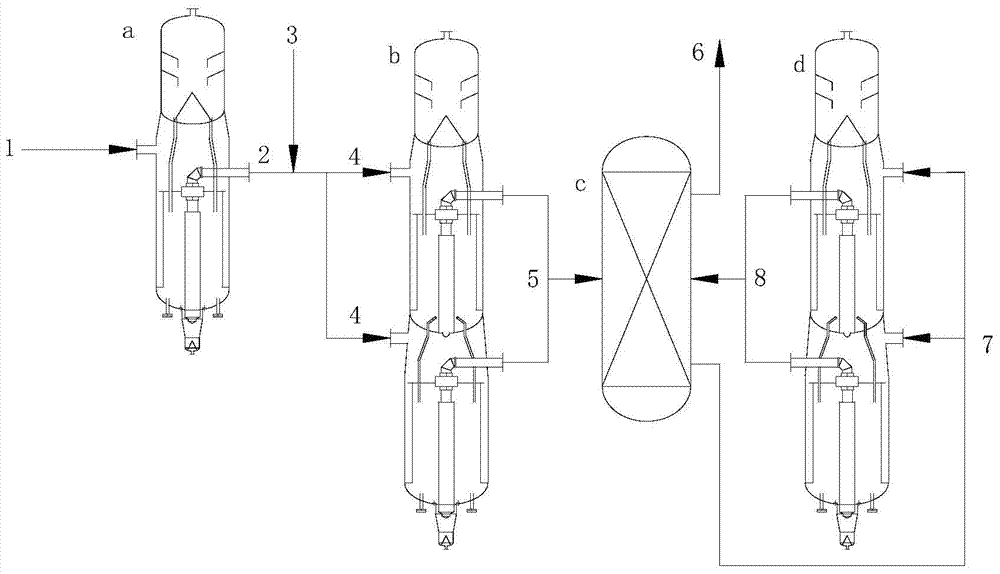
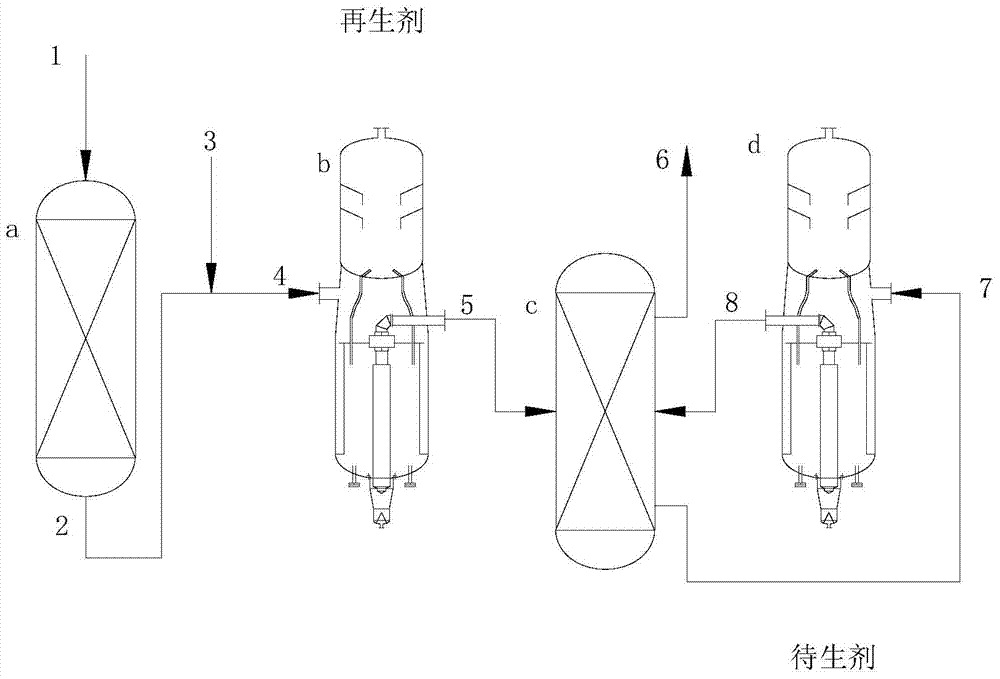
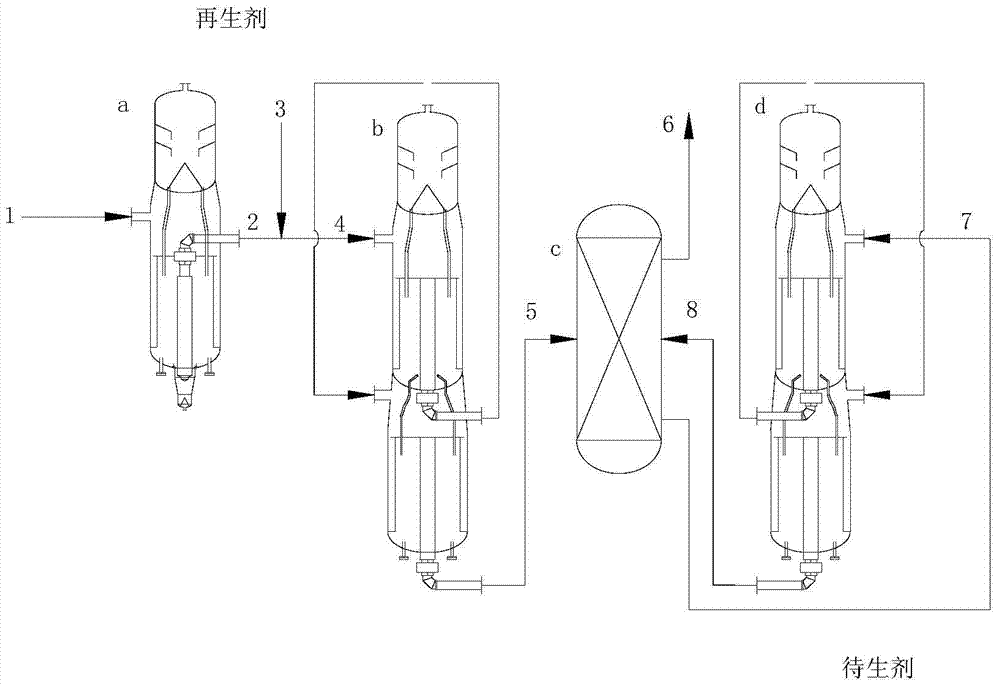
[0041] The process for producing propylene from oxygenates includes the following steps:
[0042] 1) The oxygenate stream 1 containing methanol is continuously fed into the first reaction zone a at 400 °C, 1 MPaG, and the mass space velocity of methanol is 1 h -1 The etherification reaction occurs in contact with the catalyst under certain conditions, and the reaction generates an oxygen-containing compound stream 2, and the first reaction zone a includes a fixed-bed reactor filled with an alumina catalyst;
[0043] 2) The oxygenate stream 2 at the outlet of the first reaction zone a is mixed with the diluent 3 and the stream 4 is passed into the second reaction zone b at 450 °C, 0.1 MPaG, oxygenate partial pressure 5 kPa, mass space velocity 0.5 h -1 Under certain conditions, it contacts with the molecular sieve catalyst to produce olefins, and generates a mixed hydrocarbon stream 5 including the target product propylene. The second reaction zone b comprises a moving bed rea...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The process for producing propylene from oxygenates includes the following steps:
[0051] 1) The oxygenate stream 1 containing dimethyl ether is continuously fed into the first reaction zone a at 200 ℃, 0.1MPaG, and the oxygenate mass space velocity is 20 h -1 The etherification reaction occurs in contact with the catalyst under certain conditions, and the reaction generates an oxygen-containing compound stream 2, and the first reaction zone a includes a moving bed reactor filled with a molecular sieve catalyst;
[0052] 2) Mix the oxygenate stream 2 from the outlet of the first reaction zone a and the stream 4 of the diluent 3 into the second reaction zone b at 550 °C, 1 MPaG, oxygenate partial pressure 50 kPa, mass space velocity 10.0 h -1 Under certain conditions, it contacts with the molecular sieve catalyst to produce olefins, and generates a mixed hydrocarbon stream 5 including the target product propylene. The second reaction zone b comprises two moving bed react...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The process for producing propylene from oxygenates includes the following steps:
[0060] 1) The oxygenate stream 1 containing methanol and dimethyl ether is continuously fed into the first reaction zone a at 250 °C, 0.5 MPaG, and the oxygenate mass space velocity is 10 h -1 The etherification reaction occurs in contact with the catalyst under certain conditions, and the reaction generates an oxygen-containing compound stream 2. The first reaction zone a includes two moving bed reactors arranged in series and filled with molecular sieve catalysts;
[0061] 2) The oxygenate stream 2 at the outlet of the first reaction zone a is mixed with the diluent 3 and the stream 4 is passed into the second reaction zone b at 500 °C, 0.3 MPaG, oxygenate partial pressure 15 kPa, mass space velocity 5.0 h -1 Under certain conditions, it contacts with the molecular sieve catalyst to produce olefins, and generates a mixed hydrocarbon stream 5 including the target product propylene. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com