Method for extracting and preparing lignin composite nano fibers in situ
A technology of lignocellulose and lignin, which is applied to the chemical characteristics of fibers, conjugated artificial filaments, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to obtain smooth fibers, complex extraction of industrial lignin, and unfavorable widespread use, and achieve Effects of reducing waste output, increasing added value, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
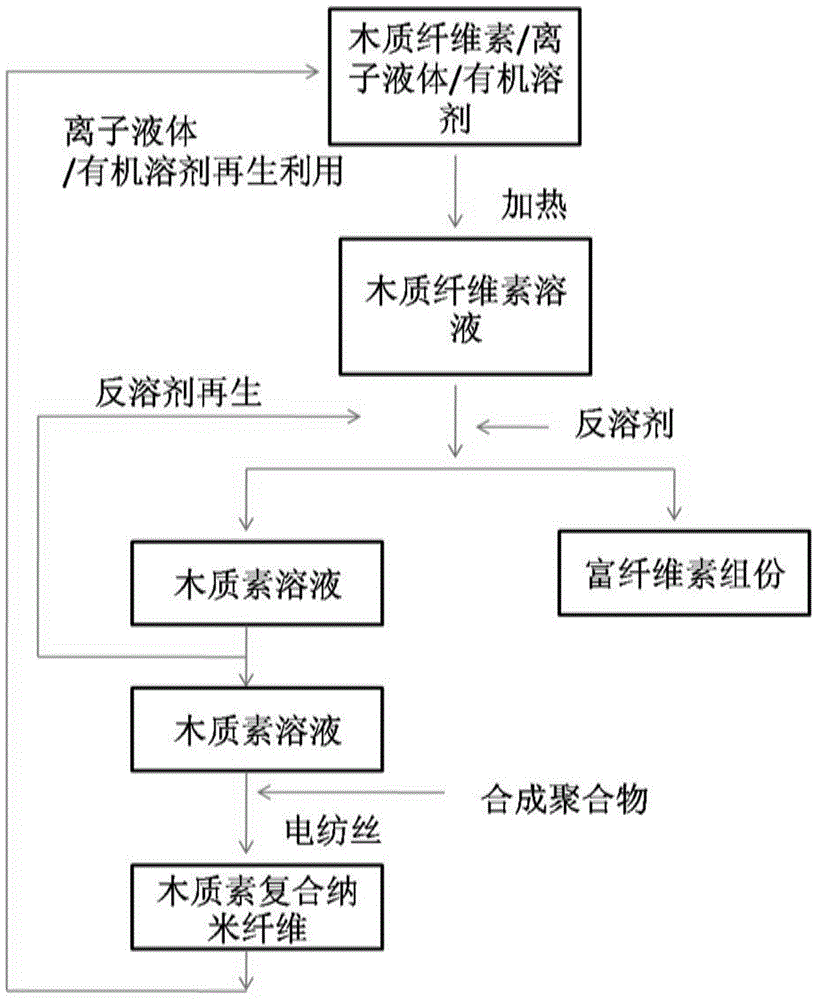
[0037] The invention provides a method for in-situ extraction and preparation of lignin / synthetic polymer composite nanofibers using natural lignocellulosic biomass as raw material, which is carried out according to the following steps:
[0038] (1) Using natural lignocellulose as raw material;
[0039] (2) Dissolving natural lignocellulose in a blended electrolyte composed of ionic liquid and organic solvent;
[0040] (3) Precipitate cellulose and hemicellulose in lignocellulose with anti-solvent, separate and concentrate to obtain lignin electrolyte solution;
[0041] (4) The synthetic polymer added in the lignin electrolyte solution to obtain the lignin-synthetic polymer electrolyte spinning stock solution;
[0042] (5) Electrospinning the obtained lignin-synthetic polymer electrolyte spinning dope by electrospinning technology to obtain lignin blended nanofibers.
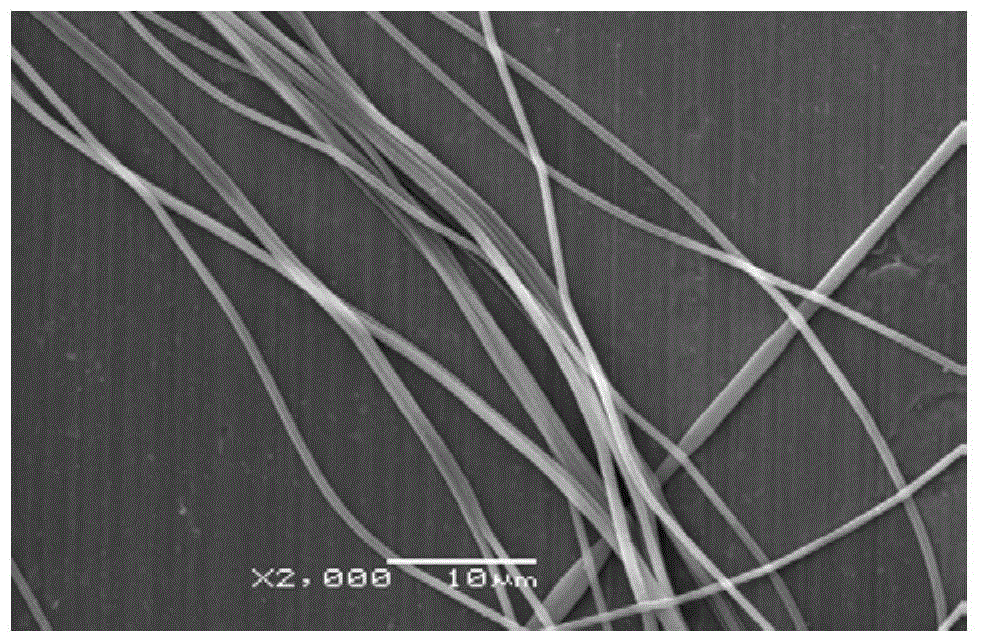
[0043] Specific technical process such as figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0045] Weigh 20 g of corn stalks with a particle size of 0.1 μm, and add them into a round-bottomed flask filled with 200 g of [Emim][Ac] / DMSO organic electrolyte solvent (the molar fraction of ionic liquid in the organic electrolyte is 20%) ([Emim] ][Ac]=1-methyl-3-ethyl-imidazole acetate), mechanically stirred and dissolved in a constant temperature oil bath at 80°C for 1h, then regenerated with 500ml of anti-solvent methanol, and filtered the filter residue with 300ml of Methanol was washed and stirred three times, so as to further remove the ionic liquid and DMSO residues in the regenerated biomass material. After removing the anti-solvent methanol in the filtrate with a rotary evaporator, a solution of extracted lignin [Emim][Ac] / DMSO with a dissolved mass concentration of 1.1 wt% was obtained. Add 7.7g PAN into this solution, dissolve and prepare lignin-PAN electrospinning stock solution. Pass the prepared corn stalk lignin / PAN spinning solution through a high-voltage e...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Weigh 20g of poplar wood powder with a particle size of 0.5 microns, and add it to a round-bottomed flask filled with 200g of [Emim][Ac] / DMF organic electrolyte solvent (the molar fraction of the ionic liquid in the organic electrolyte is 5%), 180 ℃ mechanical stirring and dissolving in a constant temperature oil bath for 3 hours, and then regenerated with 400ml of anti-solvent ethanol. After filtration, the filter residue was washed and stirred three times with 200ml of ethanol respectively, so as to further remove the ionic liquid and DMSO residue in the regenerated biomass material. After removing the anti-solvent ethanol in the filtrate with a rotary evaporator, a solution with a dissolved mass concentration of 1.9% extracted lignin [Emim][Ac] / DMF was obtained. Add 6.2g PAN into this solution, dissolve and prepare lignin-PAN electrospinning stock solution. Pass the prepared corn stalk lignin / PAN spinning solution through a high-voltage electrospinning machine, set v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com