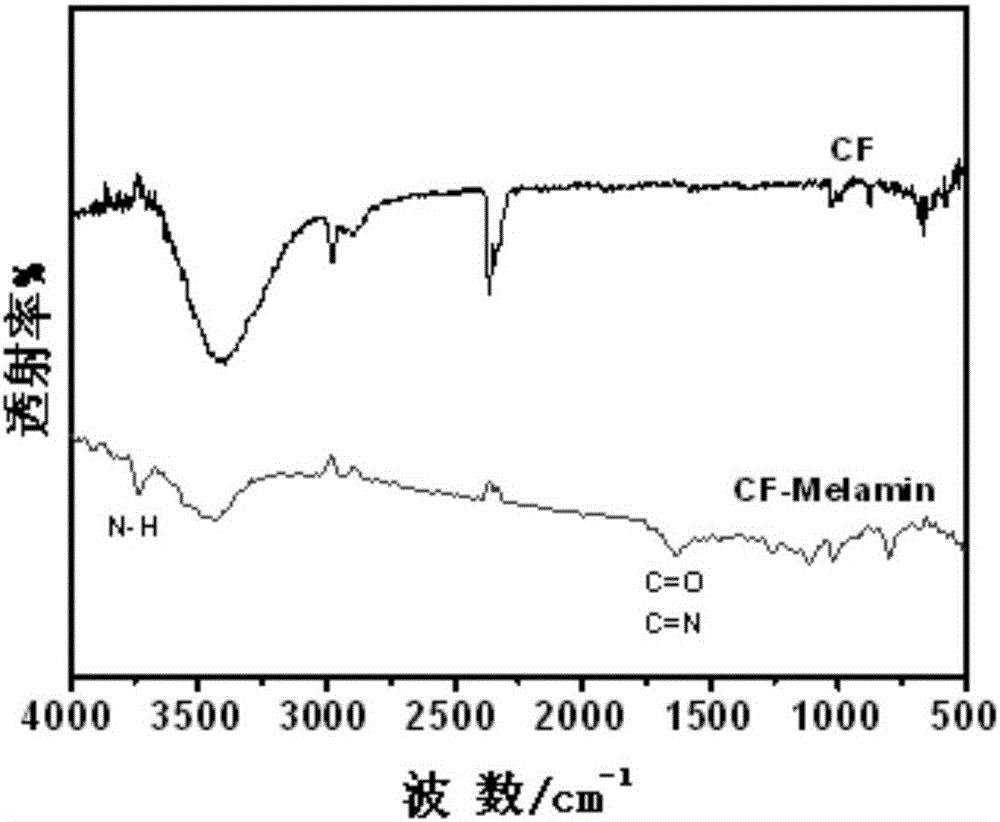
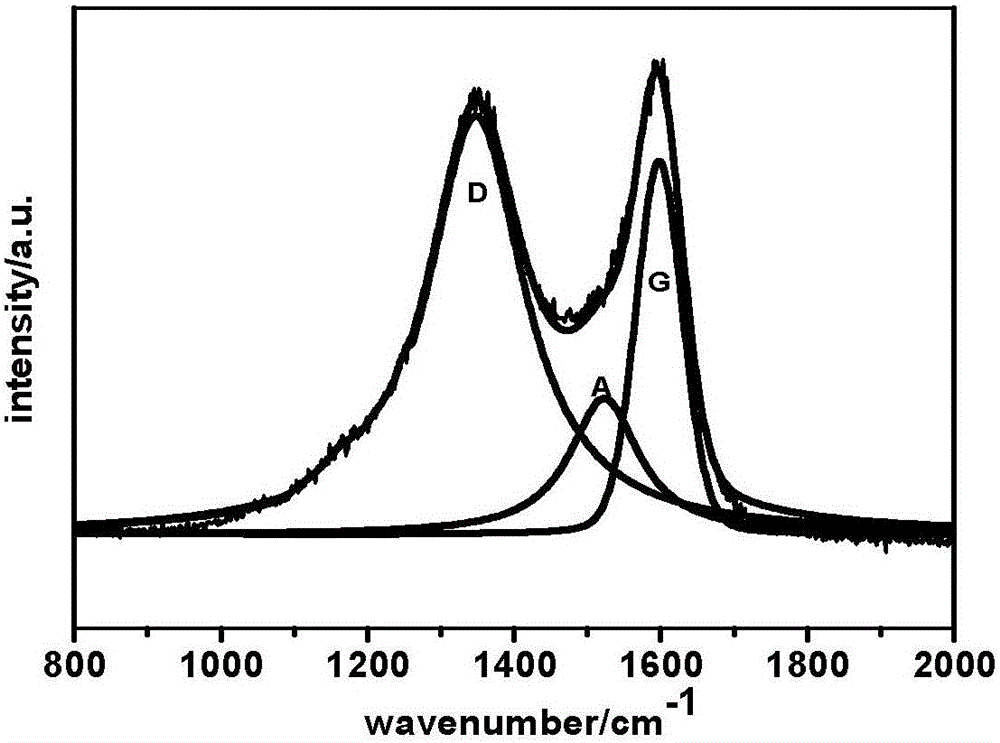
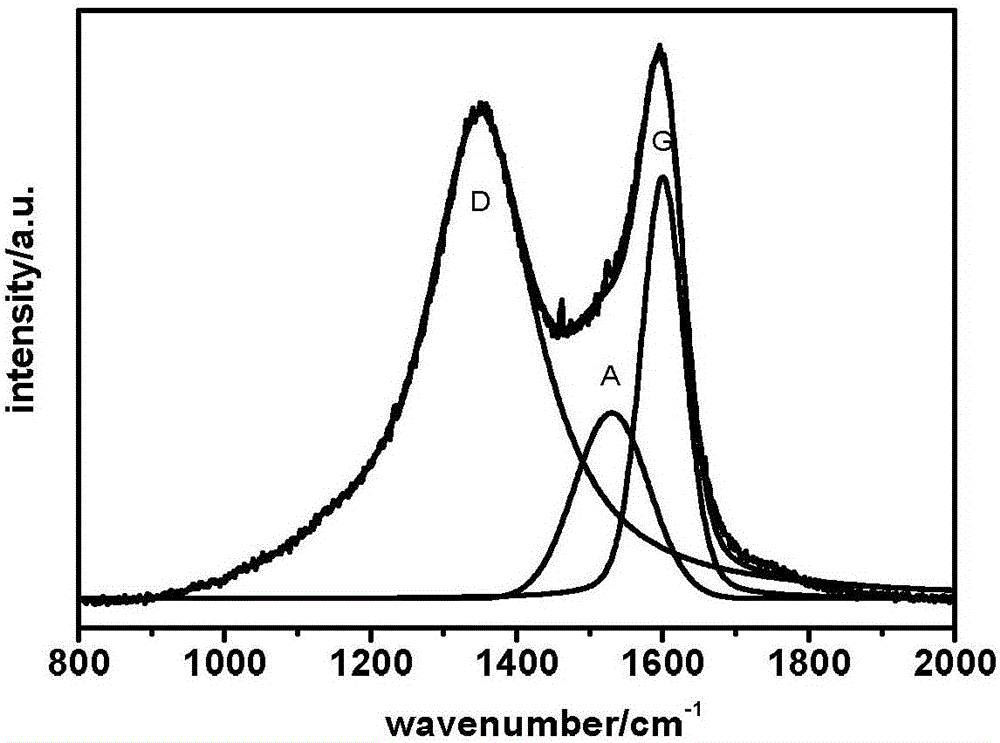
Supercritical fluid technology-based carbon fiber surface grafting method
A supercritical fluid and surface grafting technology, applied in the production of bulk chemicals, etc., can solve the problems of less reaction sites, low bonding strength between carbon fiber and resin, and easy cross-linking of grafted polymers, achieving short time consumption, Improving interface performance and improving the effect of interface structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0028] Specific embodiment one: this embodiment is based on the carbon fiber surface grafting method of supercritical fluid technology, and carries out according to the following steps:
[0029] 1. Removal of epoxy coating on carbon fiber surface:
[0030] Put the carbon fiber bundle into a Soxhlet extractor, use acetone as a solvent, heat the acetone to 75-85°C, and maintain at this temperature for 40-50h; then take out the carbon fiber and dry it;
[0031] 2. Oxidation of carbon fiber:
[0032] A. Configure a mixed solution of 30-50mL potassium persulfate and silver nitrate at normal temperature;
[0033] B. Put 0.1-0.3g of carbon fiber bundles treated in step 1 into a mixed solution of potassium persulfate and silver nitrate, heat to 60-80°C, and place at a constant temperature for 1-2h;
[0034] C. Then take the carbon fiber out of the mixed solution, soak it in 300-500mL distilled water for 5-10min, repeat this step 3-5 times;
[0035] D. Take out the carbon fibers tre...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the drying described in Step 1 is to dry in an oven at 70-80° C. for 2-4 hours. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044]Specific embodiment three: what this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two is: the concentration of potassium persulfate in the mixed solution of potassium persulfate and silver nitrate described in step 2 is 0.1-0.2mol / L, the concentration of silver nitrate 0.001-0.005mol / L. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com