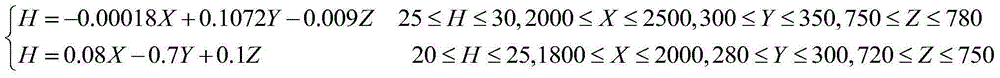Method for performing in-situ activation on greenhouse soil heavy metal through coordination of corn stalks and decomposed coal
A technology of corn stalks and weathered coal, which is applied in the field of agricultural production, can solve the problems of many limiting factors in application, and achieve the effects of low cost, reduced content, and environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
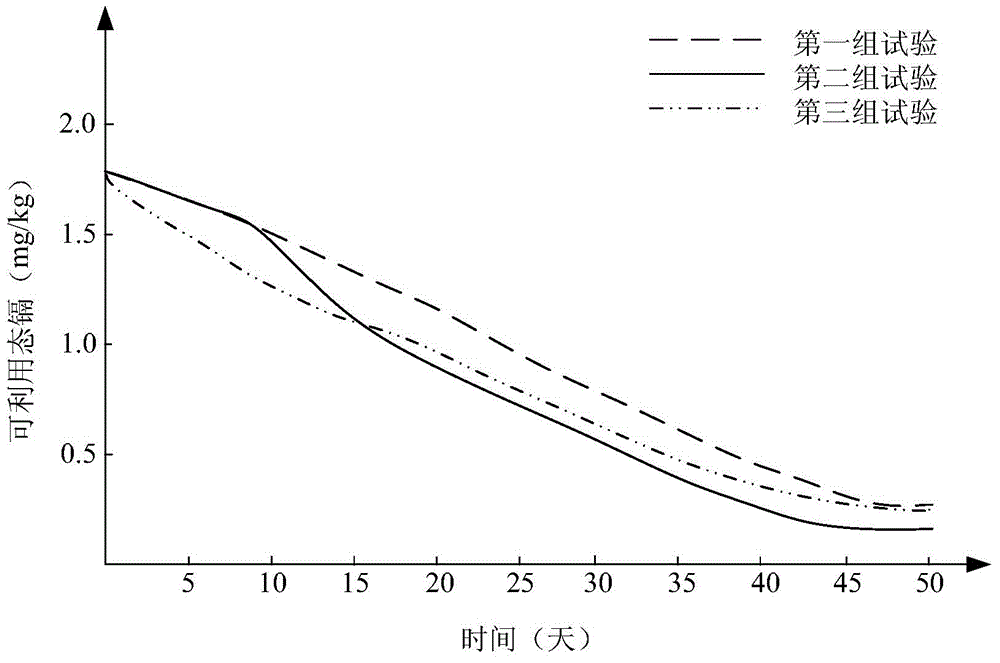
Embodiment 1
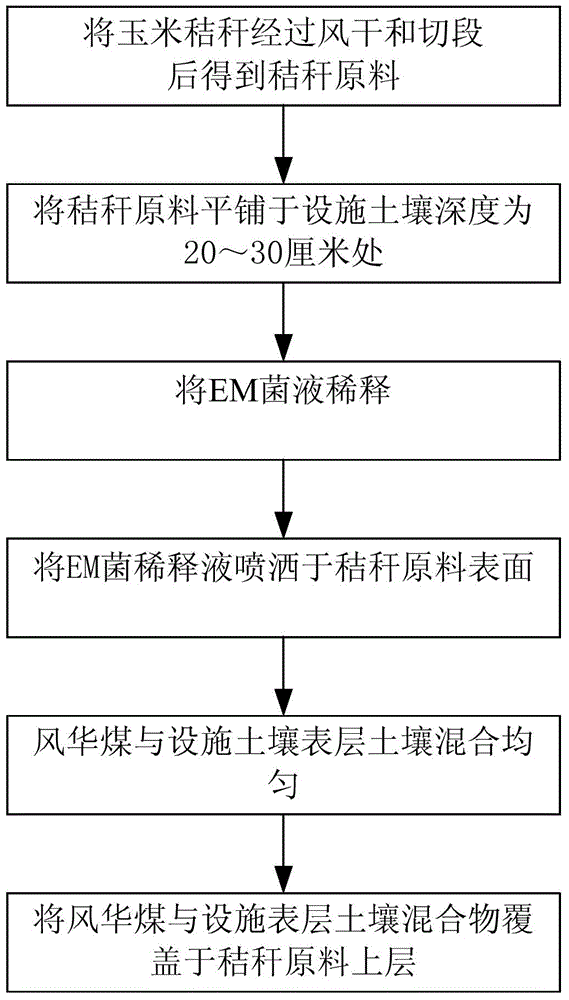
[0033] Example 1: A method for corn stalks to synergize weathered coal and in-situ passivation facility soil heavy metals,
[0034] (1) Air-drying: The harvested corn stalks are naturally air-dried indoors for more than 10 days, and the cellulose content is 320-400g / kg;
[0035] (2) Cut sections: Cut the corn stalks of step (1) to a length of 5cm, which is straw raw material;
[0036] (3) Flat-laying: dig out the surface facility soil with a thickness of 20cm, and press the straw material at 1800kg / hm 2 The amount is applied flatly at a depth of 20cm from the soil surface of the facility;
[0037] (4) EM bacteria dilution: Dilute EM bacteria liquid and distilled water in a volume ratio of 1:100;
[0038] (5) Spraying: use a sprayer or watering can to press 280L / hm for the diluted EM bacterial liquid 2 Spray evenly on the surface of straw materials;
[0039] (6) Mixing: Mix uniformly the surface facility soil with a thickness of 20cm excavated in step (3) with weathered coal, the humic ac...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A method for in-situ passivation facility soil heavy metals with corn stalks and weathered coal,
[0043] (1) Air-drying: The harvested corn stalks are naturally air-dried indoors for more than 10 days, and the cellulose content is 320-400g / kg;
[0044] (2) Cut sections: Cut the corn stalks of step (1) to a length of 10 cm, which is straw raw material;
[0045] (3) Flat paving: dig out the surface facility soil with a thickness of 20cm, and press the straw raw materials at 2000kg / hm 2 The amount is applied flatly at a depth of 20cm from the soil surface of the facility;
[0046] (4) EM bacteria dilution: Dilute the EM bacteria liquid and distilled water in a volume ratio of 1:150;
[0047] (5) Spraying: use a sprayer or watering can to press 300L / hm for the diluted EM bacterial liquid 2 Spray evenly on the surface of straw materials;
[0048] (6) Mixing: The surface facility soil with a thickness of 20cm excavated in step (3) is uniformly mixed with weathered coal, the humic acid ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for in-situ passivation facility soil heavy metals with corn stalks and weathered coal,
[0052] (1) Air-drying: The harvested corn stalks are naturally air-dried indoors for more than 10 days, and the cellulose content is 320-400g / kg;
[0053] (2) Cut sections: Cut the corn stalks of step (1) to a length of 15cm, which is straw raw material;
[0054] (3) Flat-laying: dig out the surface facility soil with a thickness of 30cm, and press 2500kg / hm of straw raw materials 2 The amount is applied flatly at a depth of 30cm from the soil surface of the facility;
[0055] (4) EM bacteria dilution: Dilute EM bacteria liquid and distilled water in a volume ratio of 1:200;
[0056] (5) Spraying: use a sprayer or watering can to press the diluted EM bacteria liquid to 350L / hm 2 Spray evenly on the surface of straw materials;
[0057] (6) Mixing: The surface facility soil with a thickness of 30cm excavated in step (3) is uniformly mixed with weathered coal. The humic acid content of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com