A kind of synthesis method of p53-mdm2 binding inhibitor dihydroxyisoquinoline derivative
A compound and alkyl technology, applied in the field of organic synthesis, can solve the problems of high cost and increased synthesis cost, and achieve the effects of convenient post-processing, easy operation and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
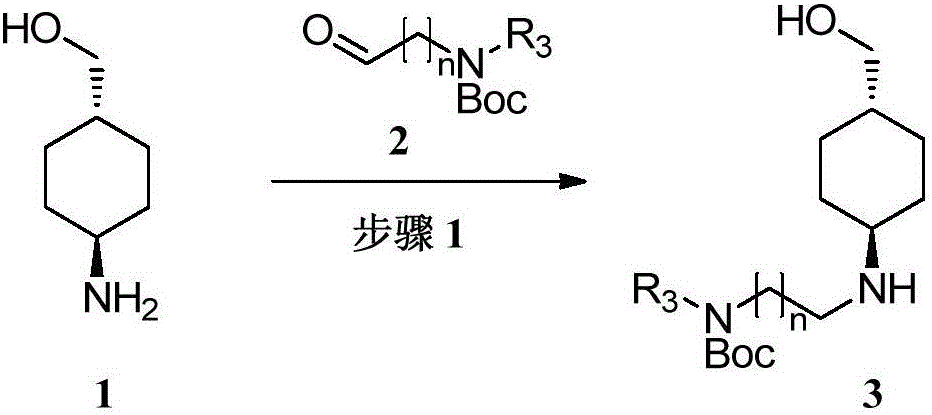
[0065] The preparation of embodiment 1 compound 13
[0066]
[0067] Dissolve compound 1 (100g, 774.0mmol) in ethanol (1.5L), add N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-(methylamino)acetaldehyde (134.06g, 774.0mmol), stir for 10 minutes, add acetic acid (14.0g, 232.2mmol), stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, cooled to 0°C and added sodium triacetoxyborohydride (328.1g, 1548.0mmol), and slowly raised to room temperature for 20 hours. Concentrate the reaction solution and dissolve it with dichloromethane (800mL), add water (800mL) and stir, separate the layers, and wash the aqueous phase with dichloromethane (800mL×2). The resulting aqueous phase was adjusted to pH=8-9 with sodium carbonate, extracted by adding dichloromethane (800mL×3), the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated to give brown oil 13 (210g, purity 85% , yield 80.5%).
[0068] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ):δ3.48-3.43(d,2H,J=6.4Hz),3.40-3.25(m,2H),2.87(s,3H),2.86-2.72(m...
Embodiment 2
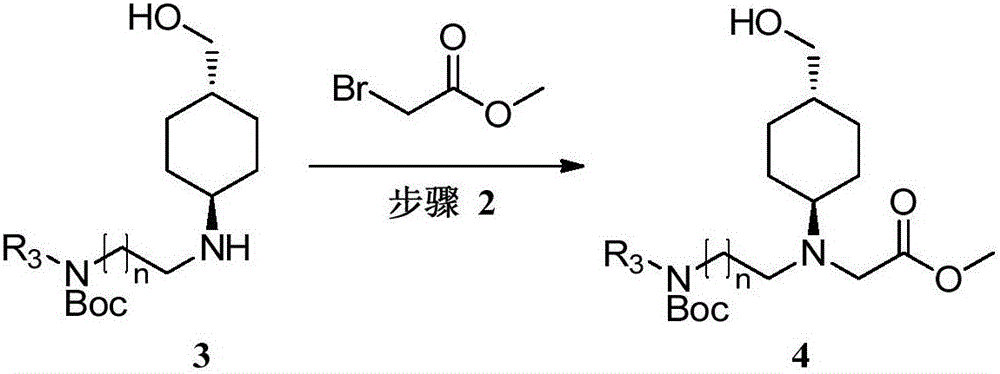
[0069] The preparation of embodiment 2 compound 14
[0070]
[0071] Potassium carbonate (171.12g, 1.24mol) was added to compound 13 (209g, 85%, 620.0mmol) in acetonitrile (1.8L) solution, after stirring for 40 minutes, methyl bromoacetate (94.84g, 620.0mmol) was added and Potassium iodide (2.06 g, 12.4 mmol), stirred overnight at room temperature until the reaction of detection compound 13 was complete. The reaction solution was filtered, concentrated, and separated by column chromatography (dichloromethane:methanol=50:1) to obtain light yellow oil 14 (206.0 g, yield 92.7%).
[0072] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ):δ3.69(s,3H),3.45-3.42(d,2H, J=6.0Hz),3.38(s,2H),3.24-3.22(m,2H),2.87(s,3H),2.73( m,2H),2.59-2.51(m,1H),1.91-1.79(m,4H),1.44(s,9H),1.36-1.32(m,1H),1.23-1.12(m,2H),1.04- 0.90(m,2H).
Embodiment 3
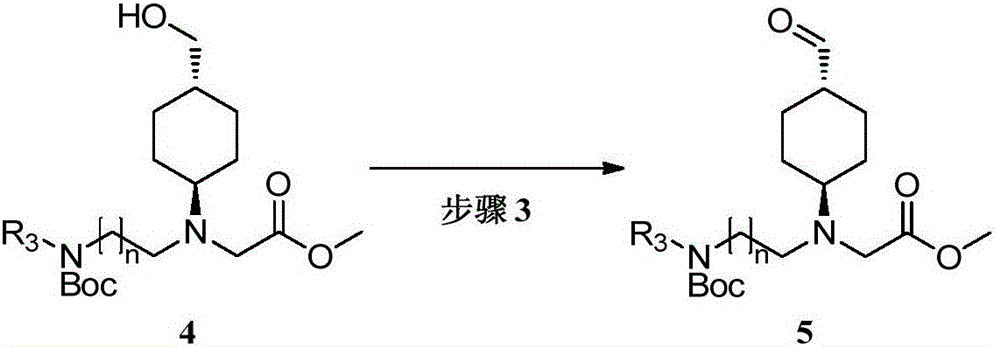
[0073] The preparation of embodiment 3 compound 15
[0074]
[0075] Dimethyl sulfoxide (8.7 g, 111.7 mmol) was slowly added dropwise to a solution of oxalyl chloride (8.66 mL, 101.5 mmol) in dichloromethane (100 mL) at -60°C. After stirring for 0.5 hours, dichloromethane (50 mL) of compound 14 (18.2 g, 50.8 mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and the temperature of the reaction system was kept at -65 ° C. After stirring for 1 hour, dichloromethane was added at -60 ° C Isopropylethylamine (39 mL, 223.4 mmol), the reaction system was slowly raised to room temperature within 5 hours, and continued to stir overnight. Wash the reaction solution with 10% citric acid, extract with dichloromethane (200 mL), combine the organic phases, and wash with saturated brine, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, concentrate, and column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate=10 : 1) Separation and concentration gave light brown oily compound 15 (17.2 g, yield 95%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com