Thermally activated secondary battery using low-temperature molten salt electrolyte
A low-temperature molten salt, secondary battery technology, applied in secondary batteries, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced energy utilization efficiency, high battery operating temperature, only one-time use, etc. The effect of high discharge voltage and improved safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
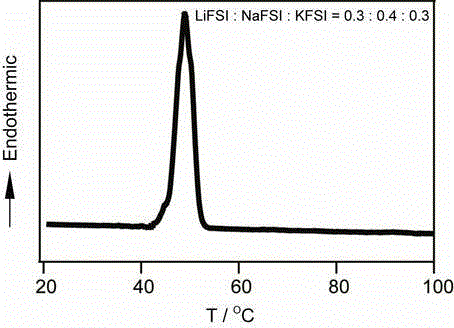
[0025] Determination of Phase Transition Temperature of Low Temperature Molten Salt Electrolyte : In a glove box filled with argon gas, weigh a certain amount of LiFSI, NaFSI and KFSI respectively according to the molar ratio of 3:4:3, grind them evenly, and carry out differential scanning calorimetry test on the above mixture, the obtained curve is as follows figure 1 , it can be found that the molten salt system has a definite phase transition temperature of 45 °C.
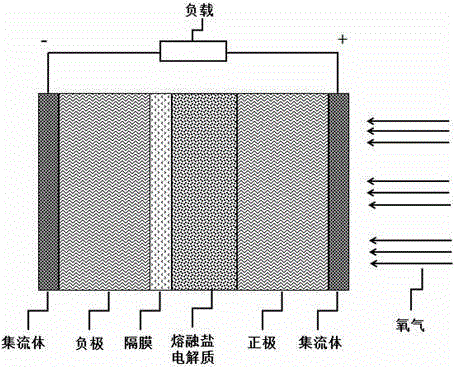
[0026] Assembly of thermally activated secondary batteries using low temperature molten salt electrolyte: The structure of the assembled thermally activated secondary battery is as figure 2 shown. A metal lithium sheet with a diameter of 1.2 cm and a thickness of 200 μm was used as the negative electrode of the battery. The carbon material SuperP and the binder polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are mixed in a mass ratio of 90:10, stirred evenly to form a slurry, the slurry is evenly coated and compacted on t...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The low-temperature molten salt electrolyte used in Example 1 was changed to LiFSI-KFSI with a molar ratio of 0.41:0.59, and the manufacturing process of the secondary battery activated by residual heat was the same as that of Example 1.
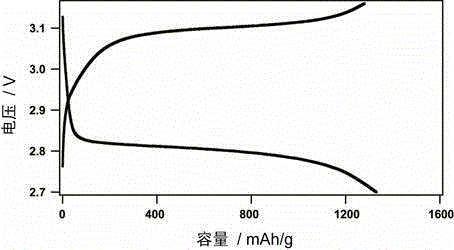
[0030] Test of thermally activated secondary battery using low temperature molten salt electrolyte : According to the differential scanning calorimetry test, the melting temperature of the LiFSI-KFSI molten salt electrolyte with a molar ratio of 0.41:0.59 is 68°C. The positive electrode and negative electrode of the thermally activated secondary battery using low-temperature molten salt electrolyte constitute a circuit, and the charge and discharge test is carried out at a current density of 50mA / g (supreP), an oxygen pressure of 1atm, and a battery temperature of 70°C. Thermally activated secondary batteries can reach about 1200mAh / g in discharge and charge specific capacity based on the quality of superP carbon material at this cur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Discharge specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com