Monascus ruber strain with high extracellular yellow pigment yields, method for breeding monascus ruber strain and application thereof
A technology of Monascus and Monascus red, which is applied in the field of microbial strain breeding, can solve the problems of complicated production process, limited use, unfavorable water-soluble occasions, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation, mild cultivation conditions and less investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 Obtaining of Monascus strains with high production of extracellular yellow pigment
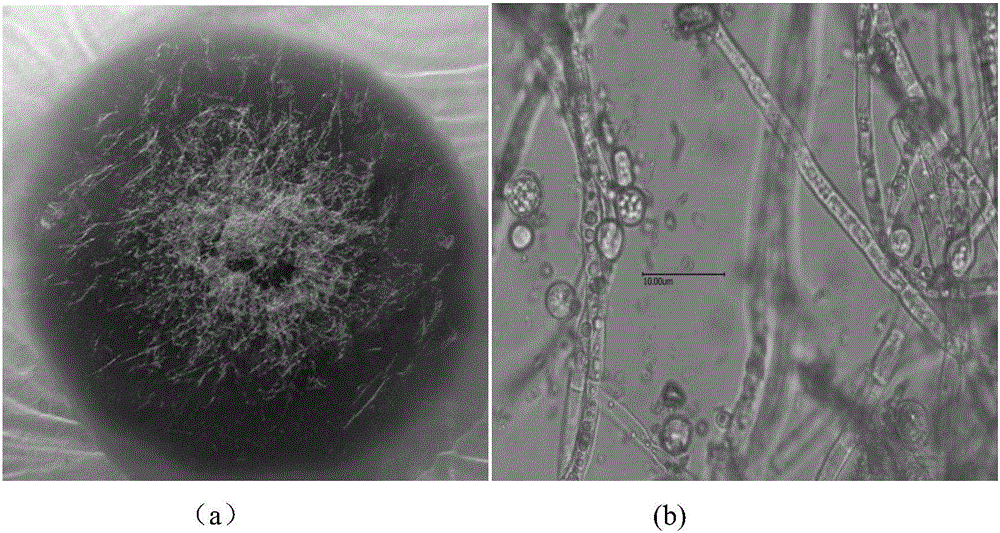
[0051] (1) Preparation of spore suspension: inoculate the original Monascus ruber strain (Monascus ruber GIM3.240, purchased from Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center) on a PDA slant, and after culturing at 30°C for 3 days, wash the slant of the strain with 5 mL of normal saline. Disperse with glass beads, filter out mycelium with 4 layers of sterile lens tissue, and make 1×10 spore-containing 5 individual / mL suspension.
[0052] (2) Ultraviolet mutagenesis: each petri dish with a diameter of 7 cm is loaded with 3 mL of the suspension prepared in step (1); the petri dish is placed at a vertical distance of 30 cm from a 15W ultraviolet lamp, and irradiated for 5 min under magnetic stirring to carry out UV radiation mutagenesis.
[0053] (3) Plate separation and screening: Take 0.5 mL of the bacterium solution after the mutagenesis, add 4.5 mL of sterile water to dilu...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Utilize the Monascus strain of high-yield extracellular yellow pigment to prepare Monascus yellow pigment by conventional method
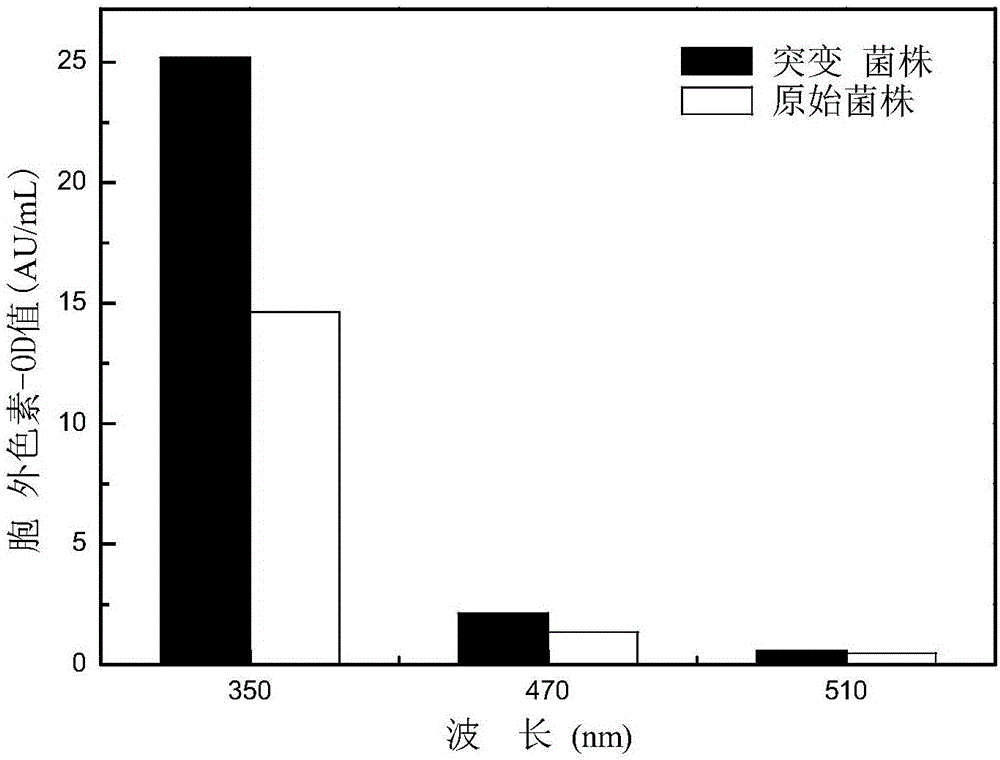
[0057] (1) Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate the plate seeds of the original strain (MonascusruberGIM3.240) and mutant strain (MonascusruberWQ15) streaked on the PDA plate into sterilized 50mL seed medium (glucose 1g, yeast extract powder 0.15g) , fish meal peptone 0.5g, KCl 0.025g, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 (00.5mg, be fixed to 50mL with distilled water, pH is natural) in carrying out culture proliferation, inoculum size is 5 single bacterium colony of cultivating 6 days, is placed in shaker control 180rpm and cultivates 30h, makes seed culture medium have mature spore, obtains seed liquid.
[0058] (2) Fermentation culture: inoculate the seed liquid into 25mL basic fermentation culture liquid (glucose 1.25g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.125g, KH 2 PO 4 0.125g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.0125g, KCl0.0125g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.25mg, ZnSO ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 Preparation of Monascus Yellow Pigment by Feeding Method Using Monascus Strain with High Production of Extracellular Yellow Pigment
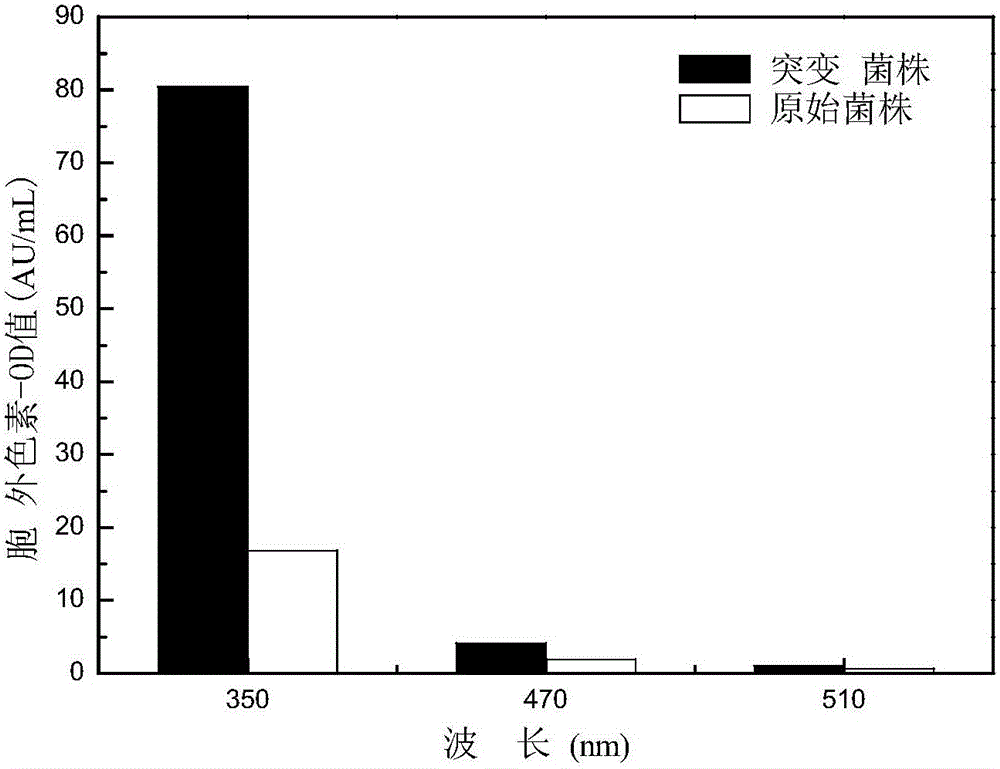
[0062] The high-yield extracellular yellow pigment MonascusruberWQ15 and the original strain MonascusruberGIM3.240 were fermented and cultivated according to the method of Example 2. The difference from Example 2 was that after the third day of fermentation, 1.25g of glucose was added to make the fermentation culture Glucose concentration in the base rises to about 60g / L, and the fermentation is continued to 6 days, and the color value and hue of the extracellular fermentation liquid are measured according to the method in Example 2.
[0063] The result is as image 3 As shown, the absorbance at 350, 470, and 510nm of the mutant strain's fermented extracellular liquid was measured by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer to be 80.40, 4.14, and 1.00 AU / mL, respectively, and the yellow hue of the fermented extracellular red yeast rice ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com