Zero-discharge salt separation purification method for industrial high-salt wastewater
A technology of high-salt wastewater and purification methods, applied in the chemical industry, chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal sulfite/sulfite, etc., can solve the problems of high impurities in coarse salt, non-recyclable, high operating costs, etc., to achieve High purity, low investment and operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
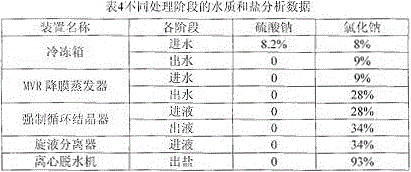
[0032] The first step, freezing and recovering sodium sulfate
[0033] After the wastewater is concentrated and treated by the membrane, the discharged concentrated brine enters the freezer, and the temperature is controlled to 1°C to cool down and precipitate sodium sulfate;
[0034] The second step, evaporation
[0035] After the concentrated brine is frozen to separate sodium sulfate, it exchanges heat with distilled water in a plate heat exchanger. After the heat exchange, the temperature is raised to 91°C, and then enters the steam preheater. After preheating, the temperature reaches 100°C. The suction port of the pump is sent to the MVR falling film evaporator, and evenly enters the tube side of the MVR falling film heat exchanger through the liquid distributor, and exchanges heat with the secondary steam from the compressor to make it evaporate, and the concentration of sodium chloride salt is concentrated to 25%;
[0036] The third step, crystallization
[0037] The...
Embodiment 2
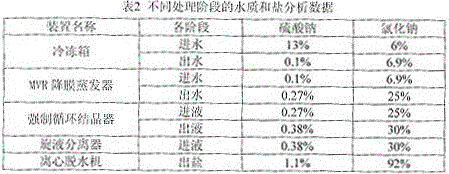
[0041] The first step, freezing and recovering sodium sulfate
[0042] After the wastewater is concentrated and treated by the membrane, the discharged concentrated brine enters the freezer, and the temperature is controlled to 3°C to cool down and precipitate sodium sulfate;
[0043] The second step, evaporation
[0044] After the concentrated brine is frozen to separate sodium sulfate, it exchanges heat with distilled water in a plate heat exchanger. After the heat exchange, the temperature is raised to 96°C, and then enters the steam preheater. After preheating, the temperature reaches 105°C. The suction port of the pump is sent to the MVR falling film evaporator, and evenly enters the tube side of the MVR falling film heat exchanger through the liquid distributor, and exchanges heat with the secondary steam from the compressor to make it evaporate, and the concentration of sodium chloride salt is concentrated to 25%;
[0045] The third step, crystallization
[0046] The...
Embodiment 3
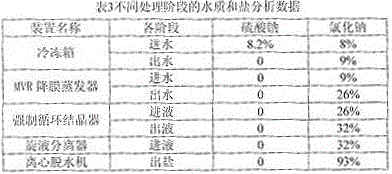
[0050] The first step, freezing and recovering sodium sulfate
[0051] After the wastewater is concentrated and treated by the membrane, the discharged concentrated brine enters the freezer, and the temperature is controlled to 1.2°C to cool down and precipitate sodium sulfate;
[0052] The second step, evaporation
[0053]After the concentrated brine is frozen to separate sodium sulfate, it exchanges heat with distilled water in a plate heat exchanger. After the heat exchange, the temperature is raised to 93°C, and then enters the steam preheater. After preheating, the temperature reaches 102°C. The suction port of the pump is sent to the MVR falling film evaporator, and evenly enters the tube side of the MVR falling film heat exchanger through the liquid distributor, and exchanges heat with the secondary steam from the compressor to make it evaporate, and the concentration of sodium chloride salt is concentrated to 26%;
[0054] The third step, crystallization
[0055] Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com