Thermal conductive plastic alloy, radiator based on alloy and preparation method
A heat-conducting plastic and heat sink technology, applied in the field of heat-conducting alloy materials and a heat sink, can solve the problems that affect the service life of the product, the heat dissipation area is limited, the heat dissipation is not large enough, etc., and it is not easy to decay, the heating time is long, and the thermal engineering good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Thermally conductive plastic alloys for radiators, in parts by weight, include 70 parts of polyisobutylene, 5 parts of polyethylene, 70 parts of graphite powder with a particle size of 7 μm and 18 μm, 9 parts of carbon fiber, 12 parts of thermally conductive carbon black, and thermal conductivity enhancer 2 parts of nanometer aluminum oxide, 2 parts of titanate coupling agent 101 type, 0.5 part of stearic acid.
[0029] The graphite powder is a thermally conductive graphite sheet.
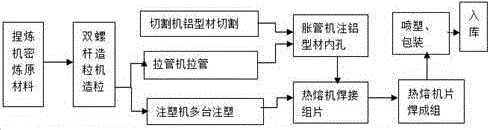
[0030] The preparation process of the radiator is as follows: the heat-conducting plastic alloy is granulated, then drawn and injected to make the inner water pipe and connectors of the radiator, and the inner water pipe is first expanded into the inner hole of the aluminum wing pipe of the radiator The radiator column or sheet is obtained, and then the column or sheet is thermally welded with the connecting piece to form a single radiator; then, the radiator is thermally welded between the ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Thermally conductive plastic alloys for heat sinks, in parts by weight, include 110 parts of polybutene, 3 parts of polyethylene, 100 parts of graphite powder with a particle size of 7 μm, 8 parts of carbon fiber, 15 parts of F900A thermal conductive carbon black, and thermal conductivity enhancer 3 parts of nanometer aluminum oxide, 5 parts of titanate coupling agent, and 0.5 part of stearic acid.
[0034] The graphite powder is a thermally conductive graphite sheet.
[0035] The heat-conducting plastic alloy is granulated and then drawn and injected to make the inner water pipe and connectors of the radiator. First, the inner water pipe is expanded into the inner hole of the aluminum wing pipe of the radiator to obtain the radiator column or sheet. material, and then thermally weld the column or sheet and the connecting piece to form a single radiator; then, thermally weld the radiator monoliths to form a radiator.
Embodiment 3
[0037]The thermally conductive plastic alloy used for radiators is characterized in that, in parts by weight, it includes 100 parts of polyisobutylene, 3 parts of polyethylene, 90 parts of graphite powder with a particle size of 7 μm, 8 parts of carbon fiber, and 8 parts of F900B type thermally conductive carbon black, 4 parts of nano-scale aluminum oxide as thermal conductivity enhancer, 3 parts of titanate coupling agent, and 1 part of stearic acid.
[0038] The graphite powder is a thermally conductive graphite sheet.
[0039] After the heat-conducting plastic alloy is granulated, it is drawn and injected to make the inner water pipe and connectors of the radiator. First, the inner water pipe is expanded into the inner hole of the aluminum wing pipe of the radiator to obtain the radiator column or sheet. material, and then thermally weld the column or sheet and the connecting piece to form a single radiator; then, thermally weld the radiator monoliths to form a radiator.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com