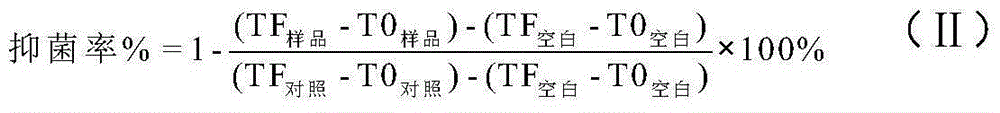Application of chitosan derivative in bacterial wilt prevention and treatment
A technology for chitosan derivatives and bacterial wilt disease, which is applied in the application field of chitosan derivatives in the prevention and control of bacterial wilt disease, can solve problems such as large environmental impact, and achieve the effect of no pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] The preparation method of chitosan derivative solution comprises the following steps:
[0024] Weigh a small amount of chitosan derivatives, dissolve them in dilute acid solution, and prepare mother liquor. The dosage and concentration can be diluted as required.
[0025] The antibacterial effect of chitosan derivatives was determined by spectrophotometry.
[0026] Spectrophotometric method: use a microplate reader to measure the absorbance of the bacterial solution added with different concentrations of chitosan derivatives, and accurately determine its inhibitory rate and half-inhibitory concentration on R. solanacearum. The formula for calculating the antibacterial rate is formula (II):
[0027]
[0028] Among them, the T0 sample and the TF sample are the absorbance of the bacterial solution adding chitosan derivatives before and after cultivation; the T0 blank and the TF blank are the absorbance of only adding the culture medium before and after cultivation; the...
Embodiment 1
[0030] In this example, spectrophotometry is used to detect the inhibitory effect of chitosan derivatives in the lowest concentration range on the pathogenic bacteria of mulberry wilt.
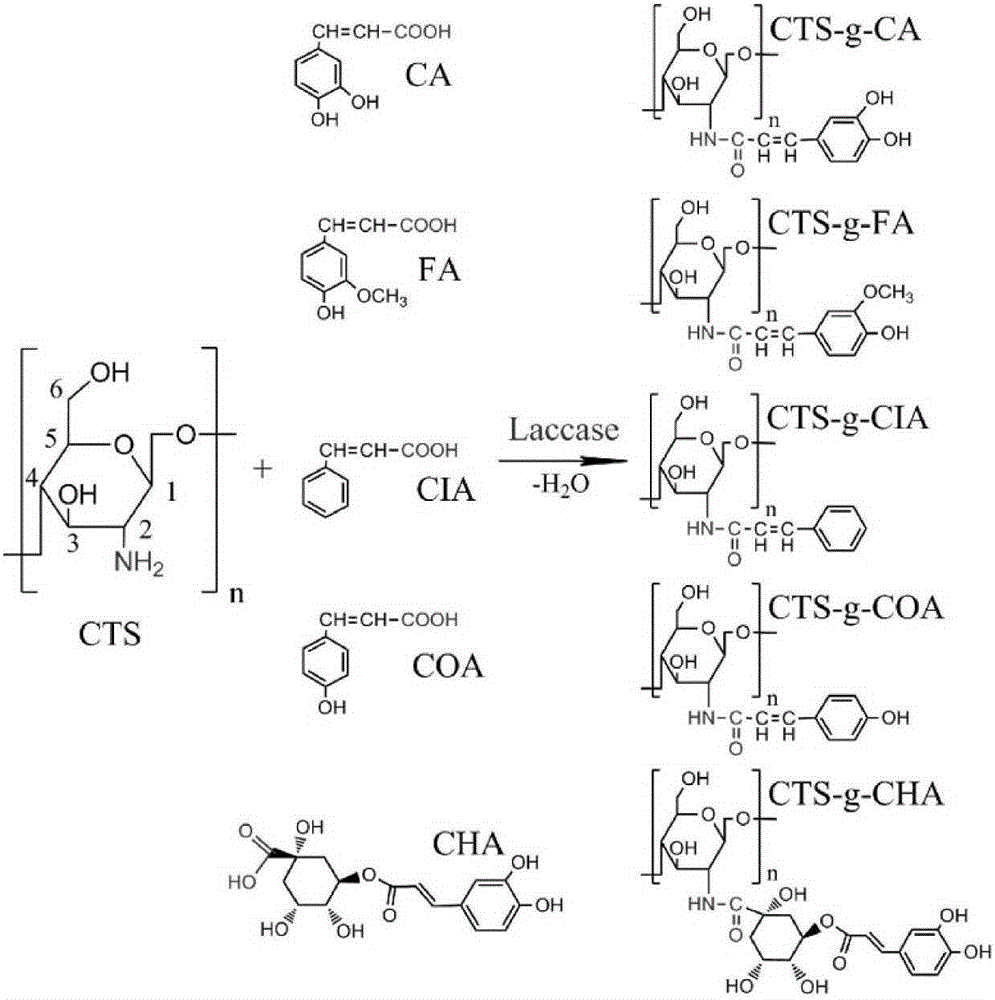
[0031] Mulberry wilt pathogen RS-5 was cultured with shaking at 28° C. for 24 hours in TM liquid medium (10 g of peptone, 5 g of glucose, 1 g of casein, and 1 L of distilled water) to obtain a bacterial suspension. Dissolve chitosan derivatives in dilute acid, prepare a 20g / L solution, and filter with a 0.22μm microporous membrane to remove the influence of bacteria. Add 5mLTM liquid medium to each test tube to set different concentrations of chitosan derivatives (CTS-g-CA, CTS-g-FA, CTS-g-CIA, CTS-g-COA and CTS-g-CHA) , with a structure such as figure 1 shown. Mulberry wilt pathogen RS-5 was inserted into the test tube, and three replicates were done, and cultured overnight. Finally, 200 μL of the bacterial suspension in the test tube was added to a 96-well plate, read at 600 nm with a mic...
Embodiment 2
[0034] In this example, spectrophotometry was used to detect the inhibitory effect of chitosan derivatives in the highest concentration range on the pathogenic bacteria of mulberry wilt.
[0035]The pathogen RS-5 of mulberry wilt was cultured with shaking in TM liquid medium at 28°C for 24 hours to obtain a bacterial suspension. Dissolve chitosan and its derivatives in dilute acid, prepare a 20g / L solution, and filter with a 0.22μm microporous membrane to remove the influence of bacteria. Add 5mLTM liquid medium to each test tube to set different concentrations of chitosan derivatives (CTS-g-CA, CTS-g-FA, CTS-g-CIA, CTS-g-COA and CTS-g-CHA) , with a structure such as figure 1 shown. Mulberry wilt pathogen RS-5 was inserted into the test tube, and three replicates were done, and cultured overnight. Finally, 200 μL of the bacterial suspension in the test tube was added to a 96-well plate, read at 600 nm with a microplate reader, and the bacteriostatic rate was calculated acco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com