Mechanized hybrid rice seed production using inducible female sterility
An induced and hybrid rice technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve problems such as large-scale commercial application, and achieve the effects of reducing seed production procedures, improving efficiency, and reducing seed production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Construction of rice expression vectors carrying gene expression cassettes of rice female fertility genes driven by inducible promoters
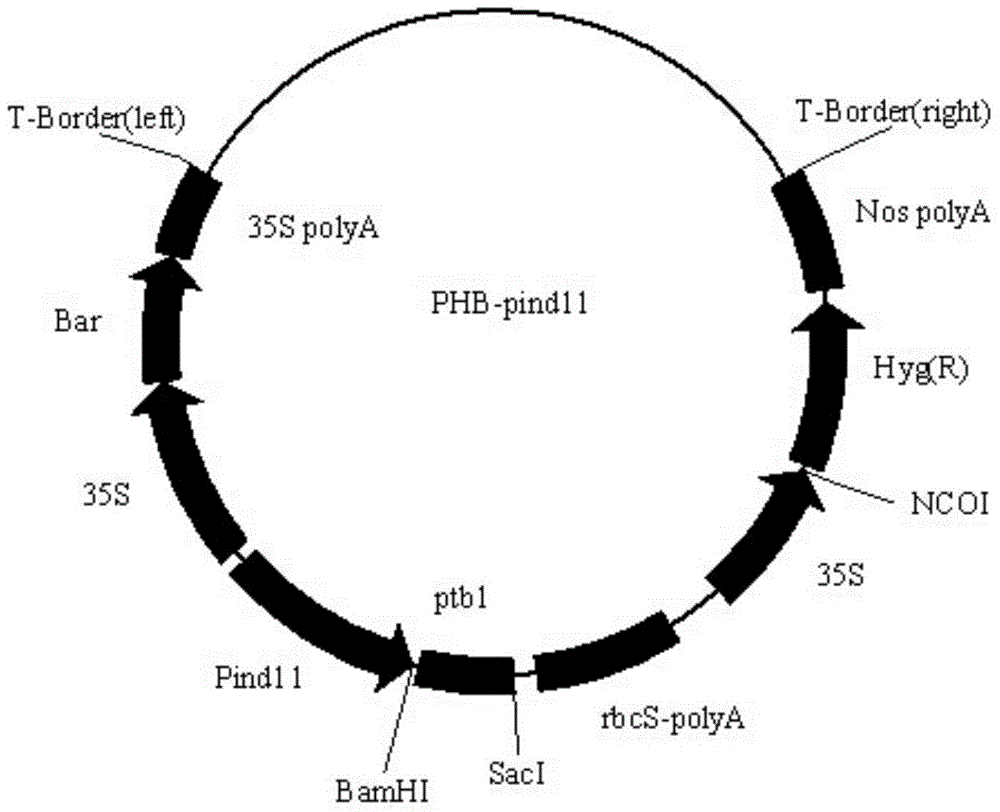
[0029] An expression cassette was inserted into the plant expression vector pHB: inducible promoter (SEQ ID NO.4), wild-type PTB1 (rice female fertility gene) coding region (SEQ ID NO.2), rbcSPolyA terminator (SEQ ID NO.5). The complete expression cassette sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6. See attached for complete construction vector map figure 1 .
[0030] The constructed vector plasmid was introduced into Agrobacterium strain EHA105 for genetic transformation of rice. The introduction method adopts the electric shock transformation method, mainly referring to the instruction manual of the electric shock instrument of bio-rad company, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) Take out the DH10B competent cells stored at -80°C and freeze and thaw them on ice, place the 1mm electric shock cup on ice for pre-coo...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: Transgenic rice obtains
[0037] 2.1 Plant material selection
[0038] The rice (Oryzasativa L.) variety used for genetic transformation was selected as the corresponding rice female sterile line carrying the PTB1 gene (SEQ ID NO.1).
[0039] 2.2 Induction of rice embryogenic callus
[0040] Take the immature rice seeds 10-15 days after pollination, peel off the seed coat, soak in 70% alcohol for 3 minutes, then soak in 0.1% mercury chloride for 15 minutes (or transfer to 20% sodium hypochlorite solution and sterilize on a shaking table for 25 minutes ), wash 3-5 times with sterile water in the ultra-clean workbench, squeeze out the sterilized immature embryos with tweezers, inoculate them on the induction medium, put about 35 seeds in each dish, and culture them in dark at 28°C for 4-5 days. Cut off the radicle, continue to culture for 12-15 days, and subculture after the callus grows up, once every two weeks, for a total of 2-3 times.
[0041]The matu...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Molecular detection of transgenic plants
[0054] 3.1 DNA large-scale extraction
[0055] T 0 Transgenic rice DNA was extracted using the CTAB method (Murry and Thompson, 1980). Weigh 2-4 grams of fresh leaves, cut them into pieces, put them into a pre-cooled mortar at -20°C, grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen, transfer them to a pre-cooled grinding bottle and store them at -20°C for later use. When extracting, add 10ml of 1.5XCTAB preheated to 100°C, stir quickly, shake in a water bath at 56°C for 20 minutes, and then extract with an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1). After centrifugation, the supernatant was extracted once with 1 / 10 volume of 10% CTAB buffer preheated to 56°C and an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and then 1% CTAB was added to the supernatant to precipitate DNA After centrifugation, add 1mol / L NaCl added with RNaseA to dissolve the DNA, completely dissolve the alcohol precipitate at 56°C overni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com