Method for mechanically producing seed by using female sterile hybrid rice
A hybrid rice and female technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve problems such as large-scale commercial application, and achieve the effects of reducing seed production procedures, improving efficiency, and easy isolation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
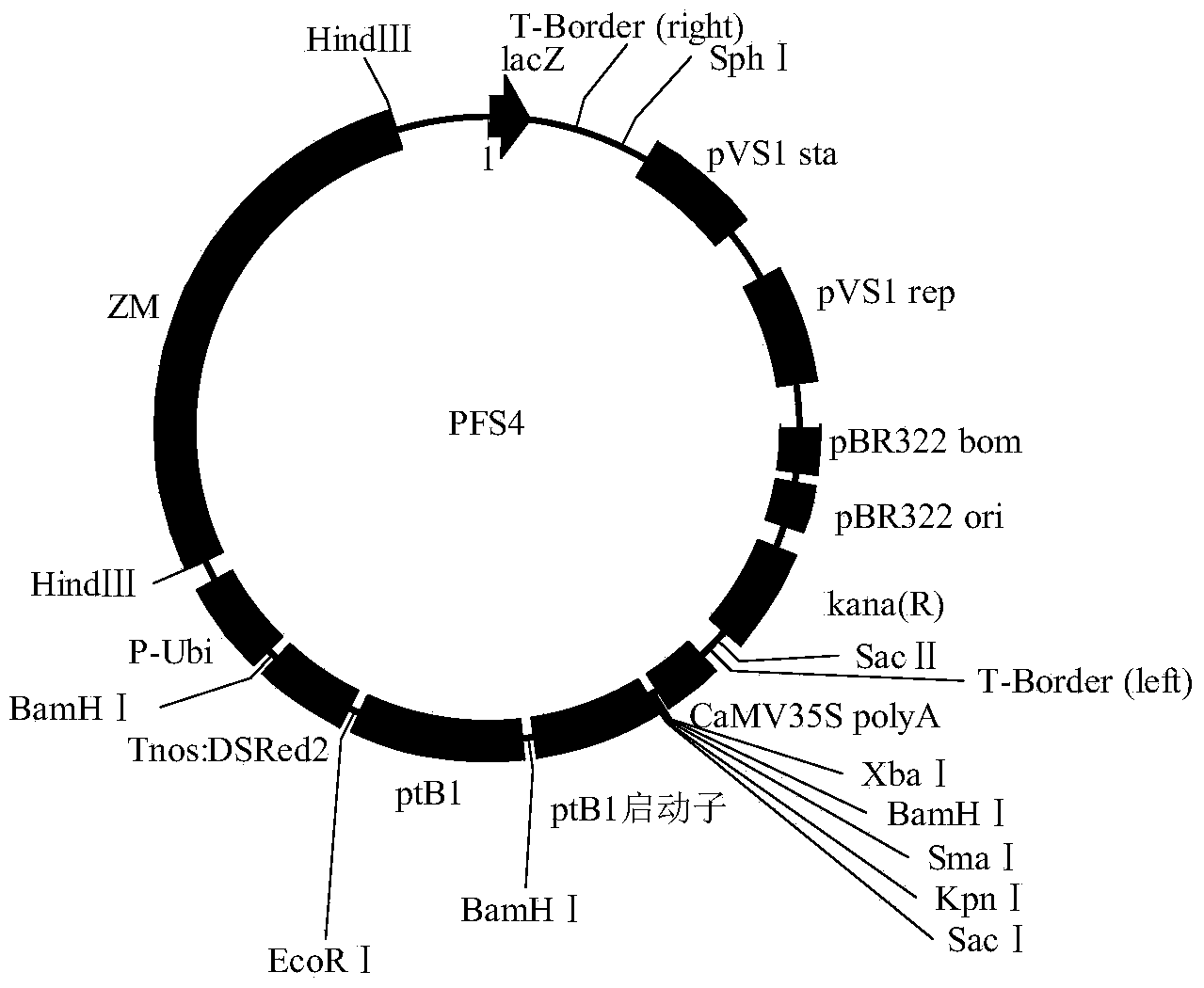
[0028] Example 1: Construction of rice expression vector carrying three gene expression cassettes of rice female fertility gene, pollen lethal gene and fluorescent selection marker gene
[0029] On the expression vector pCAMBIA1300, three expression cassettes were inserted: wild-type PTB1 expression cassette, pollen lethal amylase gene ZM-AA1 expression cassette, fluorescent screening marker gene RP expression cassette. Wild-type PTB1 carries its own promoter and terminator (see SEQ ID NO.2 for its nucleotide sequence); the amylase gene ZM-AA1 expression cassette elements include: maize pollen development late specific promoter PG47 (its nuclear See SEQ ID NO.3 for the nucleotide sequence), corn transit peptide ZM-BT1 (see SEQ ID NO.4 for its nucleotide sequence), ZM-AA1 for the amylase gene coding sequence of corn (see SEQ ID NO.4 for its nucleotide sequence) ID NO.5), corn terminator IN2-1 (see SEQ ID NO.6 for its nucleotide sequence); red fluorescent protein gene RP express...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: Transgenic rice obtains
[0037] 2.1 Plant material selection
[0038] The rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety used for genetic transformation was selected as the corresponding rice female sterile line carrying the PTB1 gene (SEQ ID NO.1).
[0039] 2.2 Induction of rice embryogenic callus
[0040] Take immature rice seeds 10-15 days after pollination, peel off the seed coat, soak in 70% alcohol for 3 minutes, then soak in 0.1% mercury chloride for 15 minutes (or transfer to 20% sodium hypochlorite solution and sterilize on a shaking table for 25 minutes ), washed 3-5 times with sterile water in the ultra-clean workbench, extruded the sterilized immature embryos with tweezers, inoculated them on the induction medium, put about 35 seeds in each dish, cultured in dark at 28°C for 4-5 days, Cut off the radicle, continue to culture for 12-15 days, and subculture after the callus grows up, once every two weeks, for a total of 2-3 times.
[0041] The mature embryos...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Molecular detection of transgenic plants
[0054] 3.1 DNA large-scale extraction
[0055] T 0 Transgenic rice DNA was extracted using the CTAB method (Murry and Thompson, 1980). Weigh 2-4 grams of fresh leaves, cut them into pieces, put them into a pre-cooled mortar at -20°C, grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen, transfer them to a pre-cooled grinding bottle and store them at -20°C for later use. When extracting, add 10ml of 1.5X CTAB preheated to 100°C, stir quickly, shake in a water bath at 56°C for 20 minutes, and then extract with an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1). After centrifugation, the supernatant was extracted once with 1 / 10 volume of 10% CTAB buffer preheated to 56°C and an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and then 1% CTAB was added to the supernatant to precipitate DNA , after centrifugation, add 1mol / L NaCl with RNase A to dissolve the DNA, completely dissolve the alcohol precipitate at 56°C overnigh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com