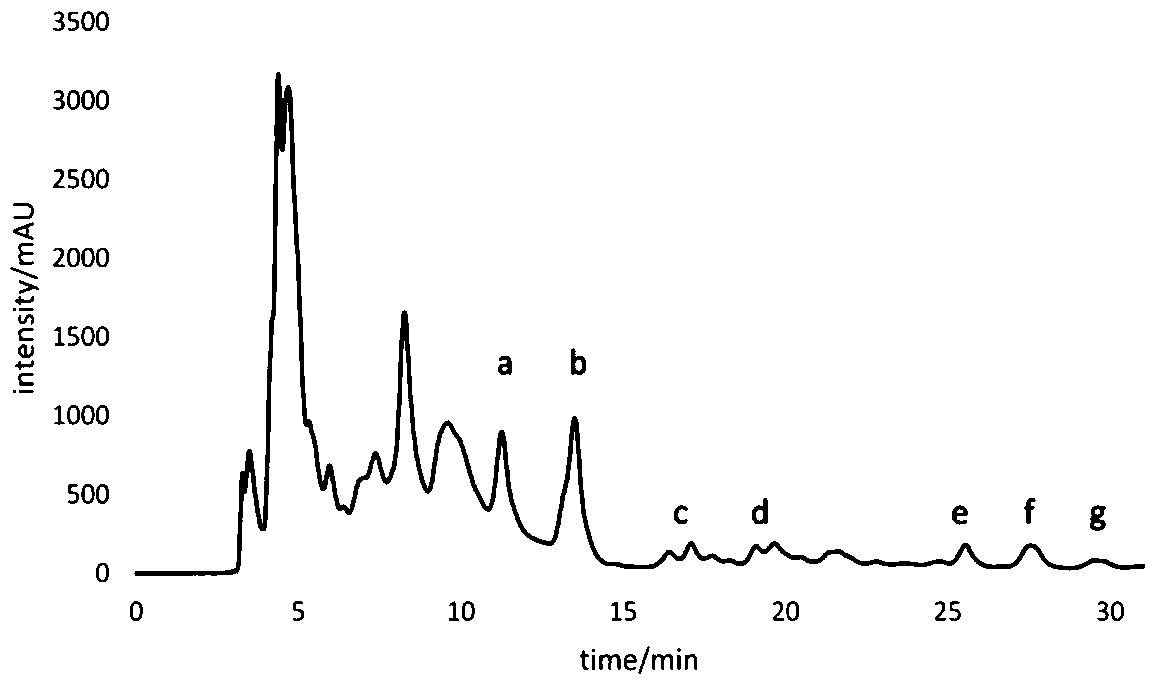
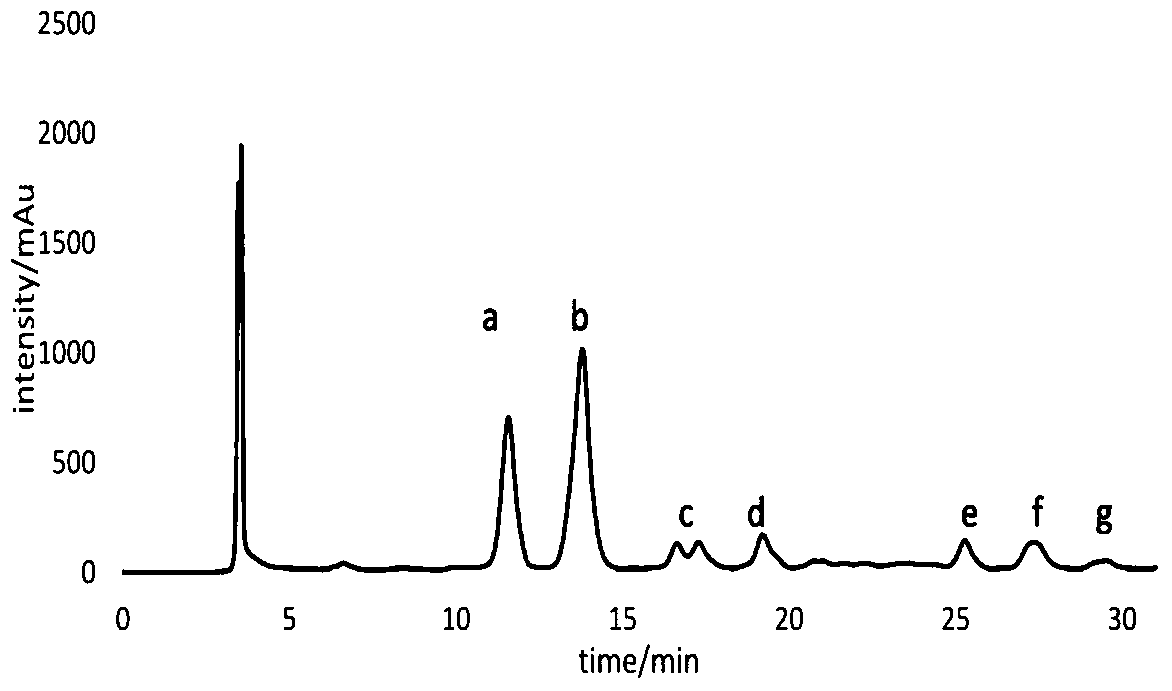
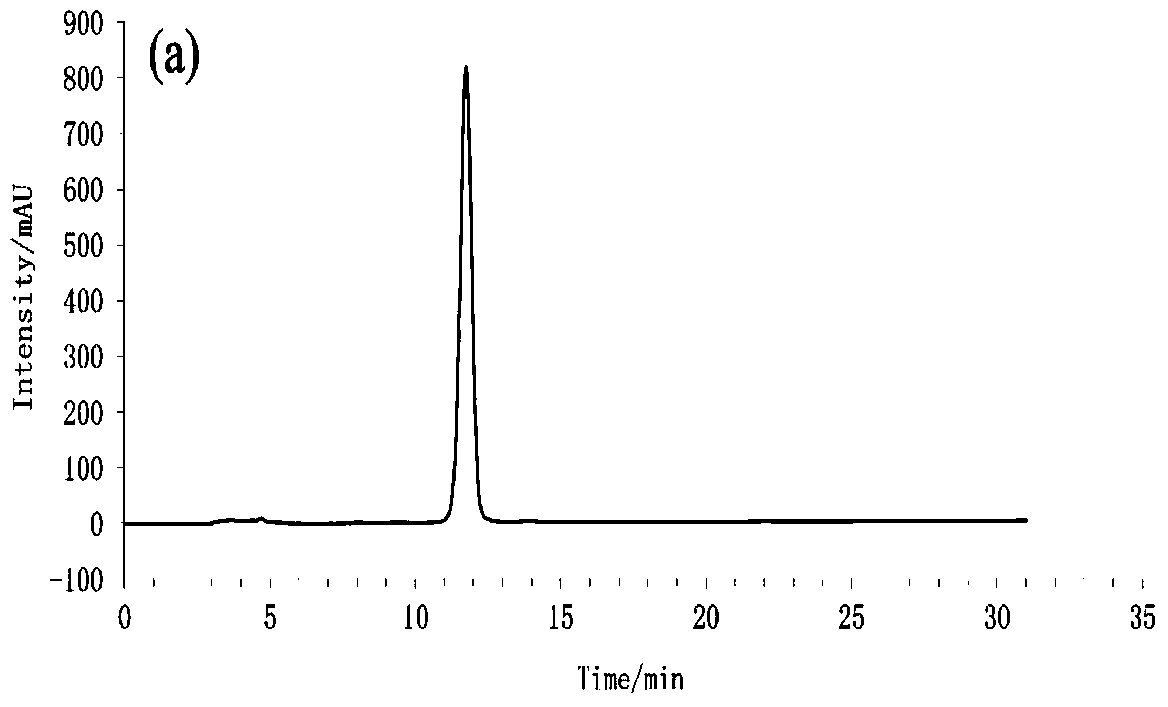
A kind of separation method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens q-426 and lipopeptide thereof
A technology for the separation of amyloliquefaciens spores and methods, which is applied in the field of separation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 and its lipopeptides, which can solve problems such as inability to separate various lipopeptide components, and achieve broad-spectrum antifungal activity and nutritional requirements Not high, improve the effect of solvent utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] (1) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 from China Type Culture Collection Center (CCTCC NO.M 2010237) was sequentially activated, first-level seed fermentation, and fermentation culture to obtain a fermentation liquid;
[0057] (2) Acid precipitation: Centrifuge 100 mL of the fermentation broth to remove bacteria, take the supernatant, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 2.5 for acid precipitation, and centrifuge (6000 rpm, 15 min) to remove the supernatant to obtain a precipitate;
[0058] (3) Cleaning: Use 20 mL of ultrapure water with a pH of 1.8 to wash the precipitate obtained in step (1), and wash twice;
[0059] (4) Extraction: use 40mL 100wt% methanol to resuspend the precipitate washed in step (2), shake it for 3h, centrifuge (12000rpm, 5min) to leave the supernatant, repeat the vibration of the precipitate 3 times with 100wt% methanol, and combine centrifuged supernatant after 3 extractions;
[0060] (5) Concentration: Concentrate the supernatant obtained in st...
Embodiment 2
[0065] (1) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 from China Type Culture Collection Center (CCTCC NO.M 2010237) was sequentially activated, first-level seed fermentation, and fermentation culture to obtain a fermentation liquid;
[0066] (2) Acid precipitation: Centrifuge 100 mL of the fermentation broth to remove bacteria, take the supernatant, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 3.0 for acid precipitation, and centrifuge (6000 rpm, 15 min) to remove the supernatant to obtain a precipitate;
[0067] (3) Cleaning: Use 20 mL of ultrapure water with a pH of 1.8 to wash the precipitate obtained in step (1), and wash twice;
[0068] (4) Extraction: use 40mL 100wt% methanol to resuspend the precipitate washed in step (2), shake it for 3h, centrifuge (12000rpm, 5min) to leave the supernatant, repeat the vibration of the precipitate 3 times with 100wt% methanol, and combine centrifuged supernatant after 3 extractions;
[0069] (5) Concentration: Concentrate the supernatant obtained in st...
Embodiment 3
[0074] (1) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 from China Type Culture Collection Center (CCTCC NO.M 2010237) was sequentially activated, first-level seed fermentation, and fermentation culture to obtain a fermentation liquid;
[0075] (2) Acid precipitation: Centrifuge 100 mL of the fermentation broth to remove bacteria, take the supernatant, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 2.0 for acid precipitation, and centrifuge (6000 rpm, 15 min) to remove the supernatant to obtain a precipitate;
[0076] (3) Cleaning: Use 20 mL of ultrapure water with a pH of 1.8 to wash the precipitate obtained in step (1), and wash twice;
[0077] (4) Extraction: use 40mL 100wt% methanol to resuspend the precipitate washed in step (2), shake it for 3h, centrifuge (12000rpm, 5min) to leave the supernatant, repeat the vibration of the precipitate 3 times with 100wt% methanol, and combine centrifuged supernatant after 3 extractions;
[0078] (5) Concentration: Concentrate the supernatant obtained in st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com