InDel molecular marker for identifying watermelon fusarium wilt and primer and application thereof
A watermelon wilt and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of insufficient stability, cumbersome steps, and high cost, and achieve the effects of stable variation, low cost, and easy detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Watermelon Fusarium wilt resistance identification, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Preparation of bacteria soil: separate and cultivate the bacteria from the watermelon wilt plants cultivated in the incubator, multiply and cultivate with wheat grains before use, mix with sterilized sand in a ratio of 1:50, and set aside;
[0035] (2) Seed preparation: take 100 seeds of each variety, soak the seeds at room temperature for 24 hours, and sow seeds at 33°C for 36 hours;
[0036] (3) Inoculation identification: use the wheat grain sand fungus soil method, put the prepared fungus soil in a nutrient bowl, sow in a heated seedbed in the greenhouse, 5 seeds per nutrient bowl, repeat twice, and set a susceptible and disease-resistant control and protection lines;
[0037] (4) Disease investigation: 10 days after sowing, the disease begins, and the emergence and disease situation are recorded. After about 4 weeks, when the susceptible and disease-resistant contro...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The development method for identifying the InDel molecular marker of watermelon wilt, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048](1) Preliminary mapping of genome-wide QTL for Fusarium wilt resistance
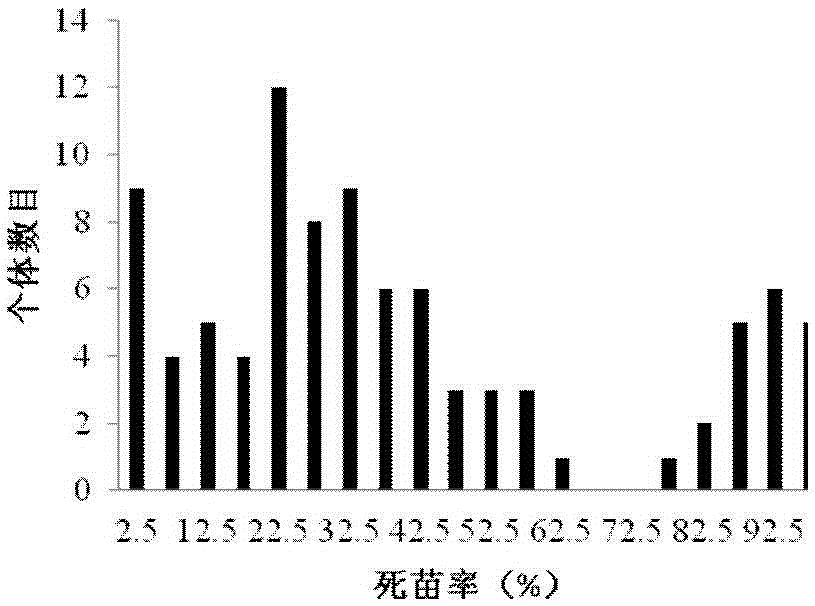
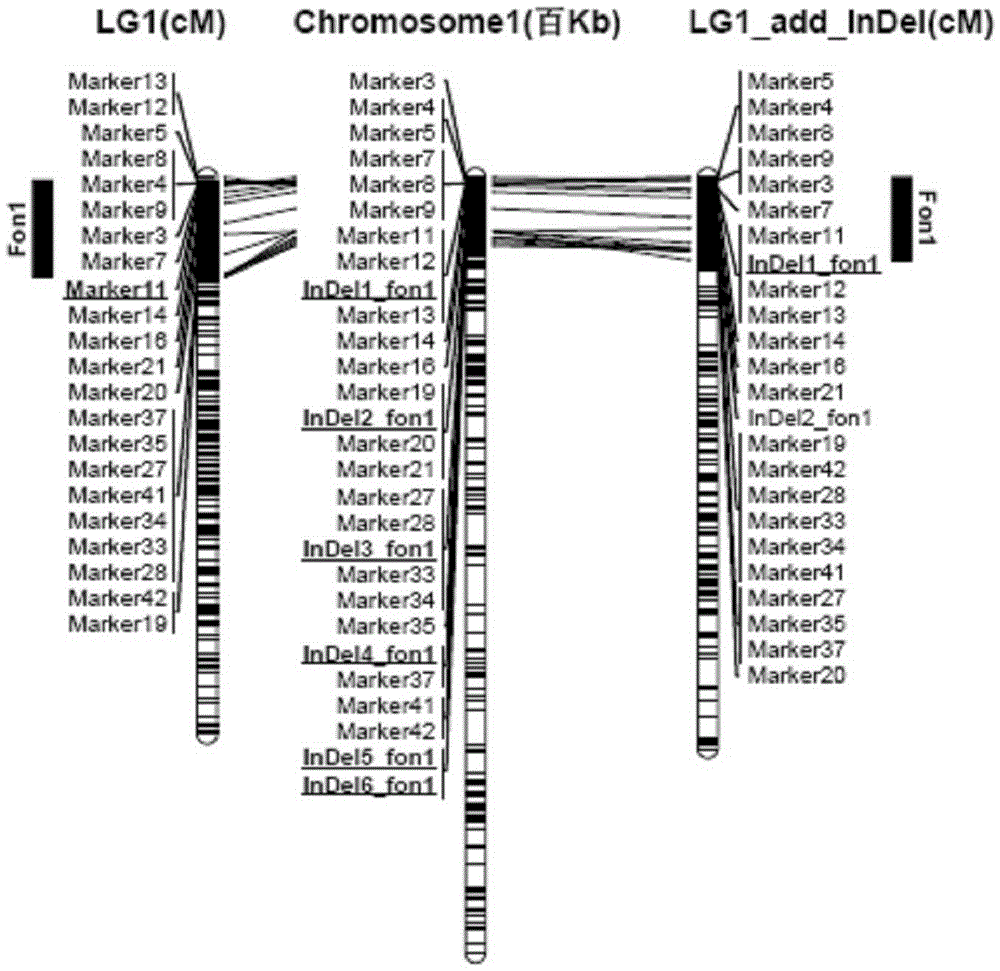
[0049] F obtained by crossing the female parent "ZXG01478" (highly resistant to Fusarium wilt) and the male parent "14CB11" (highly susceptible to Fusarium wilt) 2 The population has constructed a high-density genetic linkage map (linkage grouping was carried out through the mLOD value between molecular tags, see Table 1), and the parents, F 1 and F 2 Fusarium wilt resistance identification was carried out on 93 individual plants of the population; combined genetic linkage map and F 2 Identification results of population Fusarium wilt resistance ( figure 1 ), using WinQTLcartographer2.5software (http: / / statgen.ncsu.edu / qtlcart / WQTLCart.htm) for initial QTL mapping, a QTL site fon1 related to Fusarium wilt resistance was identified in the LG1 linkage group, and its LO...
Embodiment 3
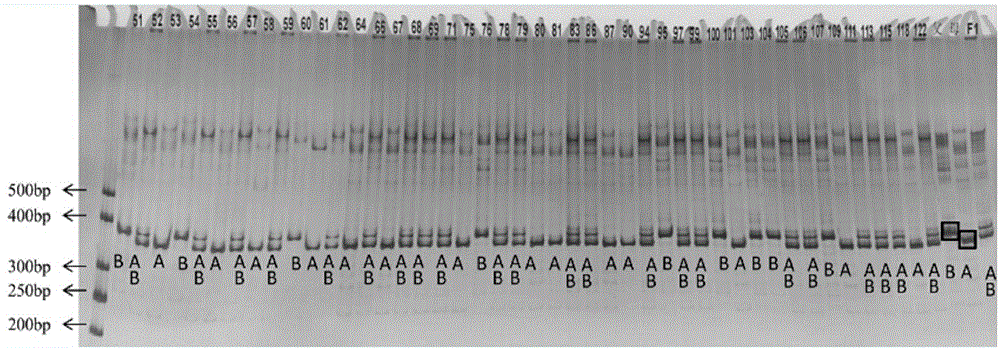
[0059] Watermelon F 2 Population molecular marker analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0060] (1) Extract the total DNA of leaves by CTAB method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0061] Take 1g of fresh leaves and put them into a mortar, add liquid nitrogen to grind them into powder, then transfer them into a centrifuge tube with 1ml of CTAB extraction solution, mix the two thoroughly, then place them in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C for 60 minutes, and mix them upside down for 2 minutes. -3 times;
[0062] After taking it out from the water bath, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 1min;
[0063] Take the supernatant and put it in another centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1, V / V), invert gently to mix well;
[0064] Centrifuge at 10000rpm for 5min, and take the supernatant (try not to get the middle sediment);
[0065] Add 0.7 times the volume of isopropanol (need to pre-cool for 30 minutes in advance), mix well...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com