An interface infiltrated quasi-solid alkali metal cell, electrodes of the cell and a preparing method of the cell
An alkali metal battery, quasi-solid-state technology, applied in non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, battery electrodes, lithium batteries, etc., can solve the problems of battery capacity decay, limited operating temperature of polymer batteries, and decreased electrolyte conductivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
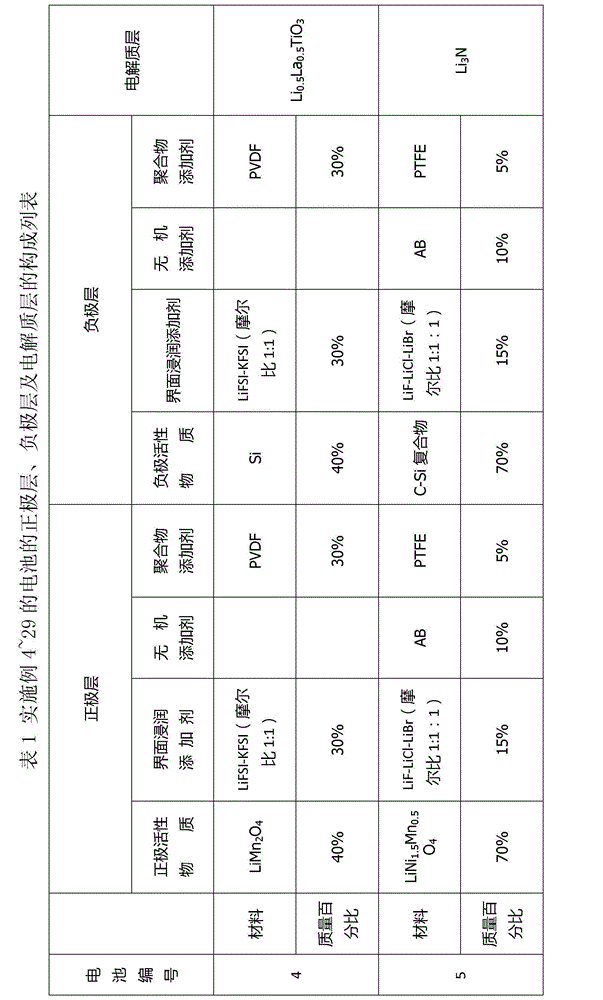
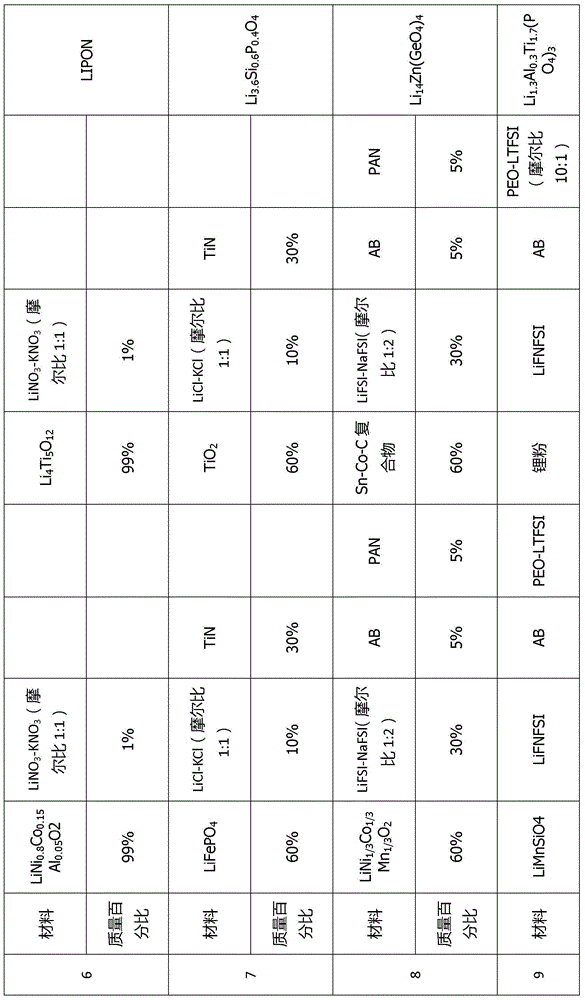
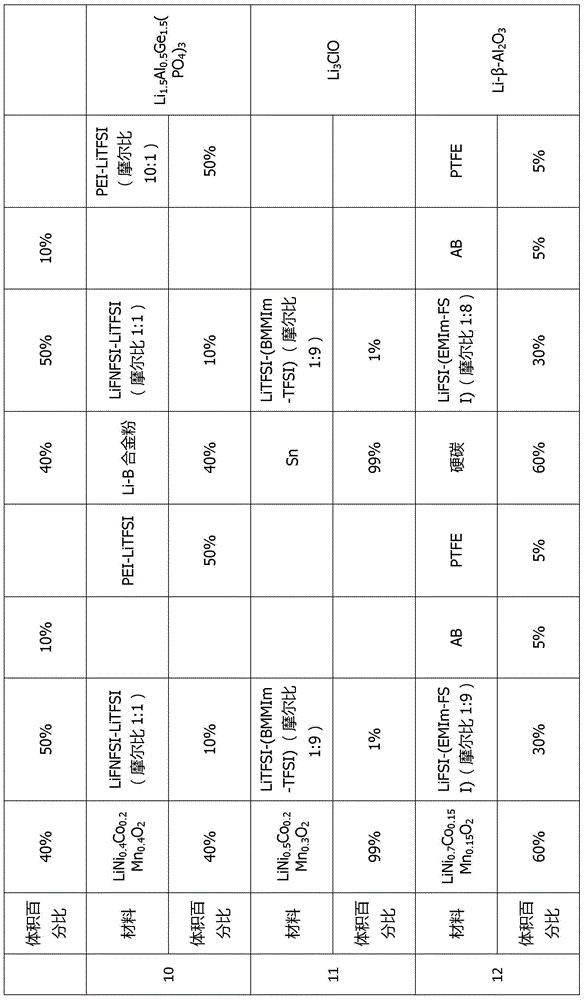
[0073] This embodiment provides a quasi-solid-state lithium battery that can be infiltrated in a wide temperature range, wide voltage window, and interface. The battery number is C1. The battery composition includes: a positive electrode layer, an electrolyte layer, and a negative electrode layer. The battery structure is a three-layer laminated structure. The positive electrode layer includes a positive electrode active material, a positive electrode inorganic additive, a positive electrode polymer additive, and a positive electrode interfacial wetting additive. The positive active material is LiCoO 2 , with a mass fraction of 85%. The positive inorganic additive is conductive carbon black with a mass fraction of 5%. The positive polymer additive is PVDF with a mass fraction of 5%. The positive electrode interfacial wetting additive is lithium (fluorosulfonyl) (perfluorobutylsulfonyl) imide (Li[N(SO 2 F)(SO 2 C 4 f 9 )], LiFNFSI) and potassium (fluorosulfonyl) (perfluo...
Embodiment 2
[0084] This embodiment provides a quasi-solid lithium battery that can be infiltrated in a wide temperature range, wide voltage window, and interface, and the battery number is C2. The difference from Example 1 is that different positive electrode interface wetting additives and negative electrode interface additives are used, and the preparation processes of the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet are also different. The positive interface wetting additive used is LiPF 6 - PC-EC-TTFP solution (where LiPF 6 The concentration is 1mol / L, the content of TTFP is 5wt%, and it is liquid at room temperature), and the negative electrode interface wetting additive used is LiPF 6 - PC-EC-TTFP solution (where LiPF 6 The concentration is 1mol / L, the content of TTFP is 5wt%, and it is liquid at room temperature).
[0085] The preparation process of the positive layer electrode sheet: using NMP as a solvent, mix the positive active material, inorganic additives, and...
Embodiment 3
[0089] This embodiment provides a quasi-solid lithium battery that can be infiltrated at the interface of a wide temperature range and a wide voltage window, and the battery number is C3. The difference from Example 1 is that the electrolyte layer uses a polymer solid electrolyte, and the composition of the polymer solid electrolyte is LiClO 4 -PEO (where PEO and LiClO 4 The molar ratio is 10:1).
[0090] Preparation process of polymer electrolyte: weighing 1molPEO and 0.1molLiClO 4 Dissolve in 50ml of NMP solution, stir for 2 hours until it is fully dissolved, pour the solution into a rectangular PVDF tank with a size of 10cm×10cm and a depth of 1mm, place it in a vacuum oven at 50°C for 48 hours, and dry to obtain a polymer solid electrolyte membrane.
[0091] The full battery C3 obtained in this embodiment can work normally at a temperature range of 65-85° C., with a cell capacity of 1 Ah, and a charging and discharging voltage range of 3-4 V.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com