Low-weight loss neodymium-iron-boron magnet and preparation method thereof
A technology of NdFeB and magnets, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of accelerated intergranular corrosion, accelerated oxidation, high corrosion current density, etc., to improve corrosion resistance, Improve corrosion resistance and improve the effect of corrosion weight loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
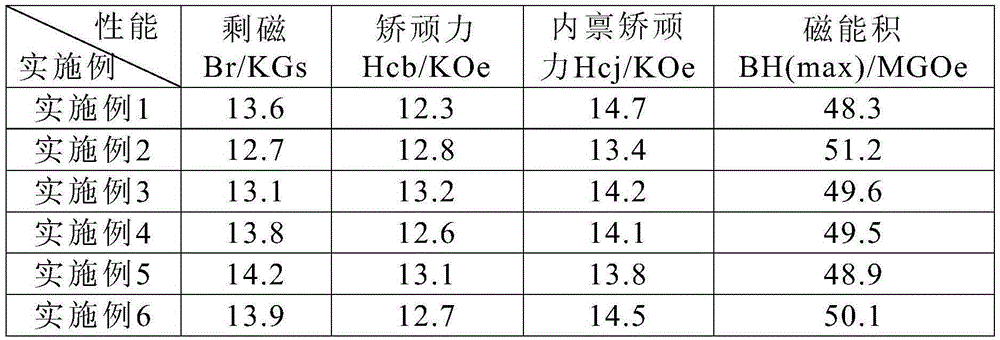
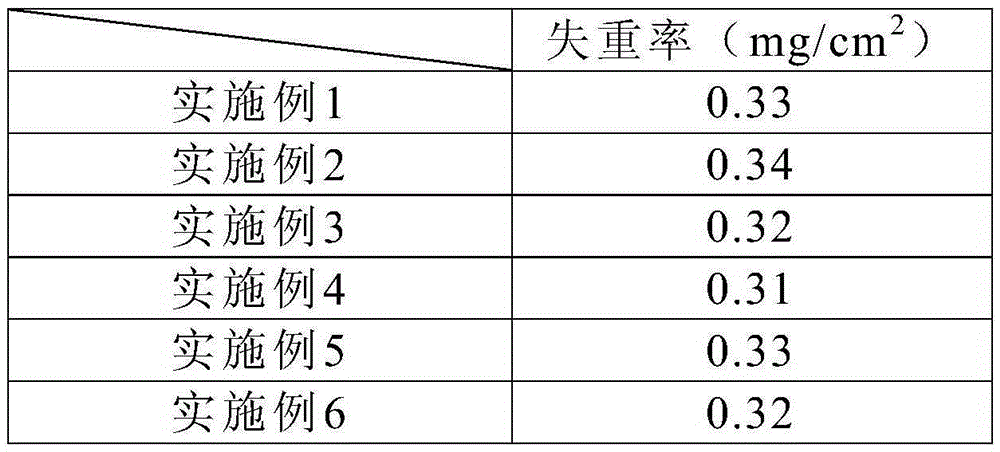
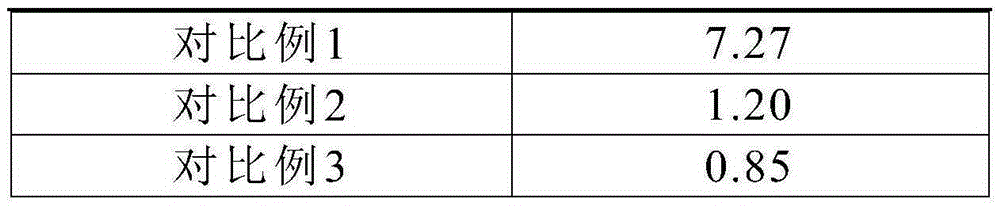
[0035]First of all, according to the composition and mass percentage of the NdFeB magnet in Table 1, the raw materials are mixed and smelted. After the smelting is complete, it is cast into a strip. Swing the belt for hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make a powder with a particle size of 3-5 μm. Under the protection of inert gas, put the powder into the molding press mold and apply a magnetic field for orientation. After orientation, press molding, demagnetization and vacuum packaging. Put the vacuum-packed green body into the isostatic press to pressurize at 10MPa and hold the pressure for 6 minutes. Then take it out. The green body obtained after molding is put into a sintering furnace for sintering at a high temperature of 1050° C., and the sintering time is controlled at 5 hours. Then perform primary tempering at 850°C for 3 hours, then air-cool, and after air-cooling, perform secondary tempering at 550°C for 5 hours and take it out to obtain a low weight loss NdFeB m...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Firstly, according to the composition and mass percentage of the NdFeB magnet in Table 2, the raw materials are mixed and smelted. After the smelting is complete, it is cast into a strip. Swing the belt for hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make a powder with a particle size of 3-5 μm. Under the protection of inert gas, put the powder into the mold of the forming press and apply a magnetic field for orientation. After orientation, press molding, demagnetization and vacuum packaging. Put the vacuum-packed green body into the isostatic press to pressurize at 15 MPa and hold the pressure for 5 minutes. Then take it out. The green body obtained after molding is put into a sintering furnace for sintering at a high temperature of 1080° C., and the sintering time is controlled at 4 hours. Then temper once at 880°C for 3h, then air-cool, and then temper twice at 560°C for 5h after air-cooling, and then take it out to obtain a low weight loss NdFeB magnet body. Finally, the...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Firstly, according to the composition and mass percentage of the NdFeB magnet in Table 3, the raw materials are mixed and smelted. After the smelting is complete, it is cast into a strip. Swing the belt for hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make a powder with a particle size of 3-5 μm. Under the protection of inert gas, put the powder into the molding press mold and apply a magnetic field for orientation. After orientation, press molding, demagnetization and vacuum packaging. Put the vacuum-packed green body into the isostatic press and pressurize it for 5 minutes. Then take it out. The green body obtained after molding is put into a sintering furnace for sintering at a high temperature of 1100° C., and the sintering time is controlled at 4 hours. Then perform primary tempering at 900°C for 3 hours, then air cooling, and then perform secondary tempering at 560°C for 4 hours before taking out to obtain a low weight loss NdFeB magnet body. Finally, Zn metal electropl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com