High-speed fully-differential noise reduction device for CMOS optical receivers
A noise reduction, optical receiver technology, applied in electromagnetic receivers, electromagnetic wave transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to meet the requirements of sensitivity, reduce the equivalent input noise current, maintain bandwidth, reduce The effect of chip area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
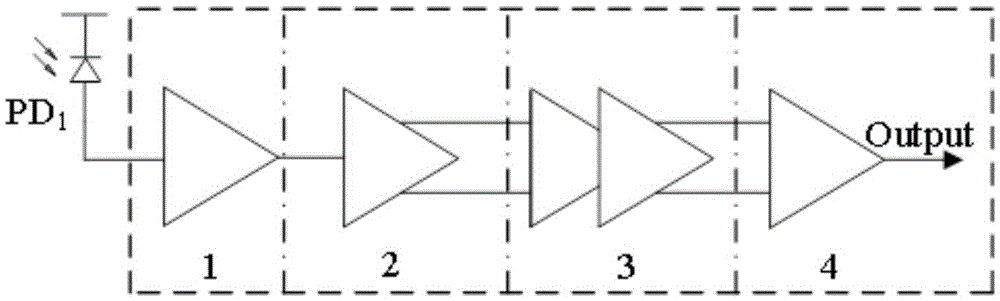
[0037] High-speed fully differential noise reduction device for CMOS optical receivers, see figure 1 , the noise reduction device includes:
[0038] A low-noise transimpedance amplifier 1 (TIA), which is used to convert the current signal output by the photodetector into a voltage signal, and perform preliminary amplification, and the transimpedance amplifier has a lower equivalent input noise current;
[0039] A single-ended to differential circuit 2 is used to realize single-ended to differential output conversion. While improving the circuit bandwidth and amplifying the voltage signal, this structure can effectively reduce the equivalent input noise current introduced by the back-end circuit;
[0040] A two-stage third-order differential limiting amplifier 3, which uses an interleaved active feedback and capacitive degeneracy circuit, for amplifying the voltage signal to the voltage level required by the digital processing unit;
[0041] An output buffer stage 4 is used to...
Embodiment 2
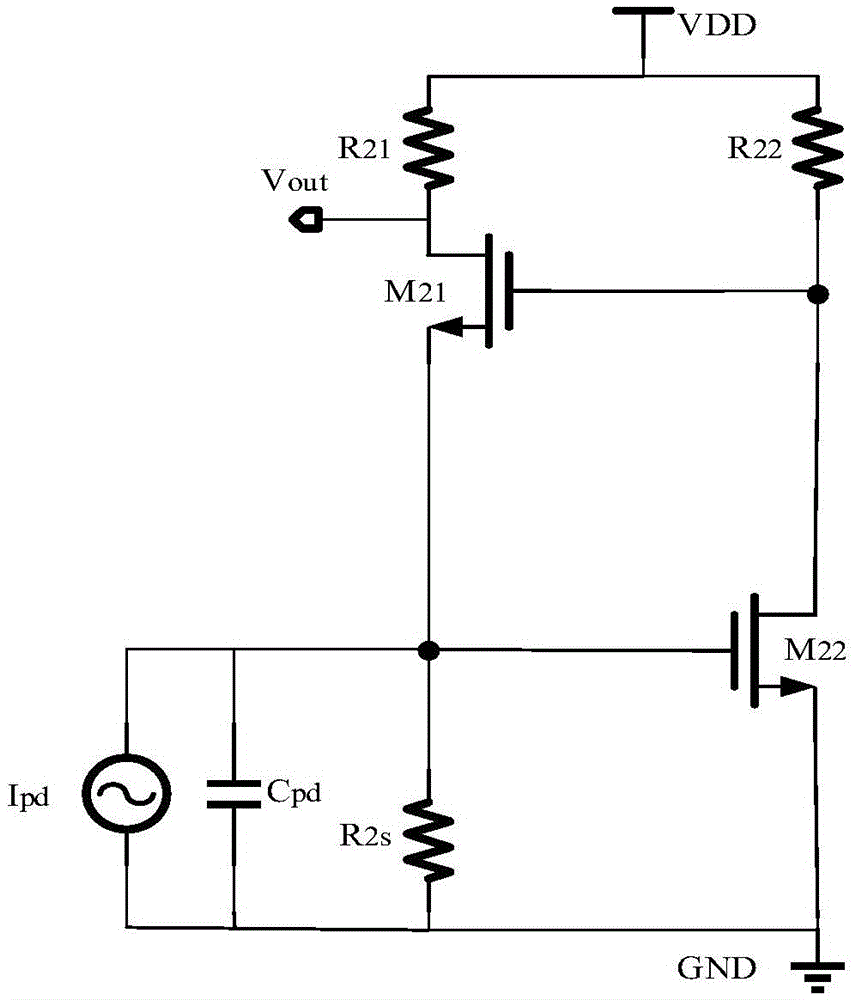
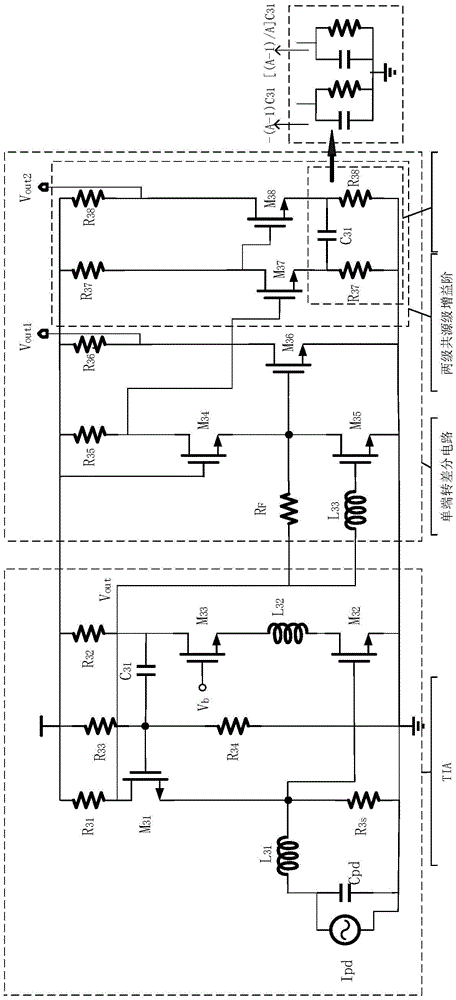
[0049] The following is a simple analysis of the noise of the traditional RGC transimpedance amplifier, and then a detailed description of the working principle of the new RGC transimpedance amplifier from the aspects of expanding bandwidth and reducing noise. As mentioned above, the main purpose of the embodiments of the present invention is to reduce noise. Therefore, the main purpose of expanding bandwidth and single-ended to differential technology is also to reduce noise.
[0050] The embodiment of the present invention comprehensively utilizes the following three technologies to expand the bandwidth, that is, cascode feedback channel reduces input impedance, Miller capacitor "shielding" effect and π-type broadband matching network. And three techniques to reduce noise, that is, a high-pass filter is introduced in the RGC structure, and the inductance L introduced at the input 31 , and introducing an inductance L at the output of the transimpedance amplifier 33 . The p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com