Preparation method for compact solid-phase sintered silicon carbide by using particle-size blended powder as raw material
A technology of solid-phase sintering and nano-scale silicon carbide, which is applied in the field of preparing dense solid-phase sintered silicon carbide, to achieve the effects of reducing slurry viscosity, consistent size, and inhibiting abnormal grain growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
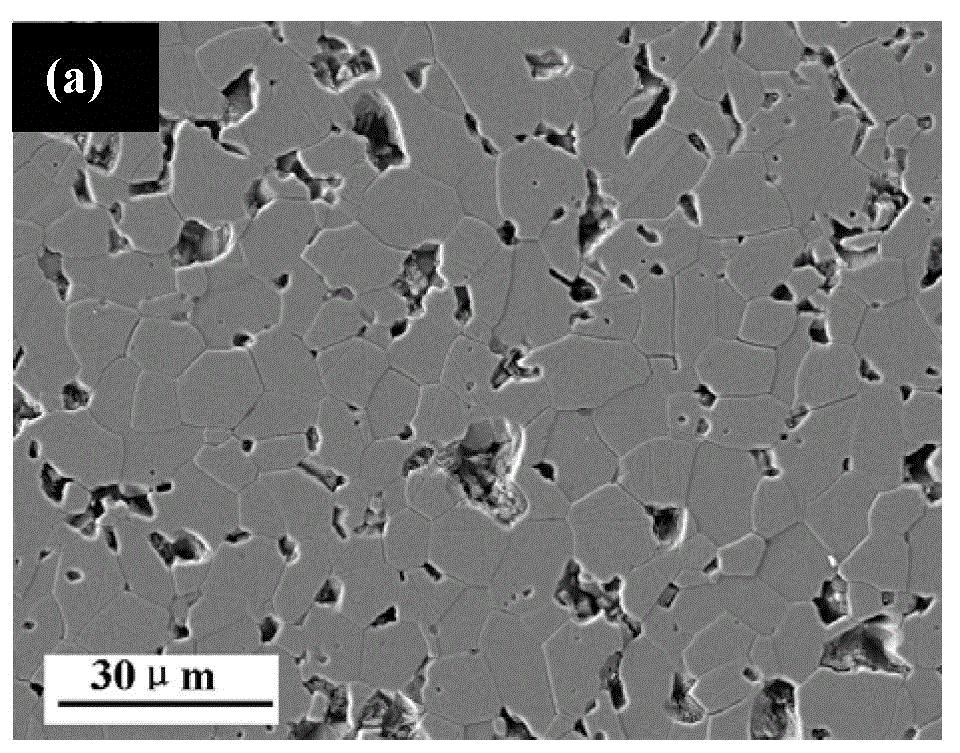
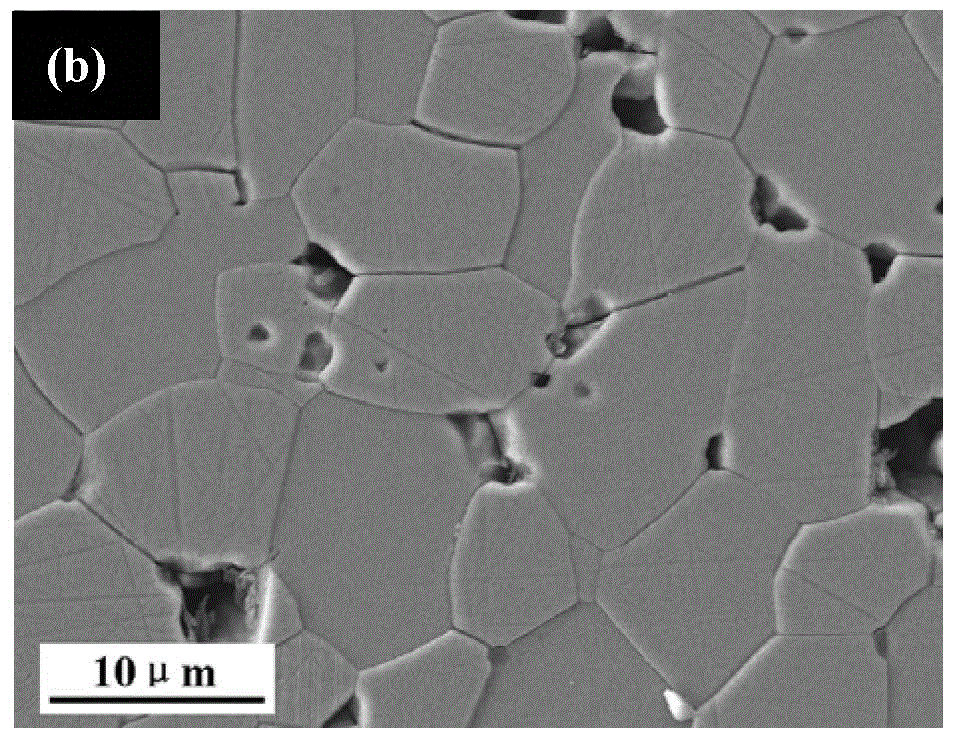
[0040] The 5 μm and 0.5 μm SiC powders are mixed according to the mass ratio of 2:1 by roller milling to obtain particle-graded powders. Next, add 0.1wt.% of B that accounts for the total mass of the particle-graded powder 4 C, 5wt.% carbon powder to obtain a composite powder. Afterwards, hydroxymethyl cellulose was added to the composite powder as a binder, and dry-pressed at 200 MPa to obtain a green body. Finally, put the green body into the graphite furnace, under Ar atmosphere, heat up to 2100°C for sintering to obtain dense solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramics. The microstructure photos are shown in Figure 1(a) and Figure 1(b). and performance parameters are listed in Table 1:
[0041] The structure and performance parameters of the dense solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramics obtained in Table 1 Example 1
[0042] .
Embodiment 2
[0044] The 1 μm and 0.1 μm SiC powders are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:1 by roller milling to obtain particle-graded powders. Next, add 1wt.% of B 4 C. 7wt.% carbon powder to obtain a composite powder. Afterwards, phenolic resin was added to the composite powder as a binder, and dry-pressed at 200 MPa to obtain a green body. Finally, the green body is put into a graphite furnace, and heated up to 2000°C for sintering under an Ar atmosphere to obtain a dense solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramic.
Embodiment 3
[0046] The 50 μm and 1 μm SiC powders are mixed according to the mass ratio of 0.5:1 by roller milling to obtain particle-graded powders. Add 3wt.% of B to the particle grading powder to account for its total mass 4 C. 0.5wt.% carbon powder to obtain a composite powder. Next, using tetramethylammonium hydroxide as a dispersant, the composite powder was added into an aqueous solution containing polyvinyl alcohol and stirred to obtain a stable SiC-B 4 C-C slurry. After testing, the slurry has a viscosity of 1 Pa·s and a volume solid content of 54 vol%. Afterwards, the slurry is poured into a plaster mold of a specific shape, cast into a mold, demoulded, and dried to obtain a green body. Finally, put the green body into a graphite furnace, and heat it up to 2100°C for sintering under an Ar atmosphere to obtain a dense solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramic.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com