Biodegradable heat shrinking film
A heat-shrinkable film and biodegradable technology, applied in the field of heat-shrinkable film, can solve the problem of difficult biodegradation of heat-shrinkable film, and achieve the effect of good physical properties and good biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
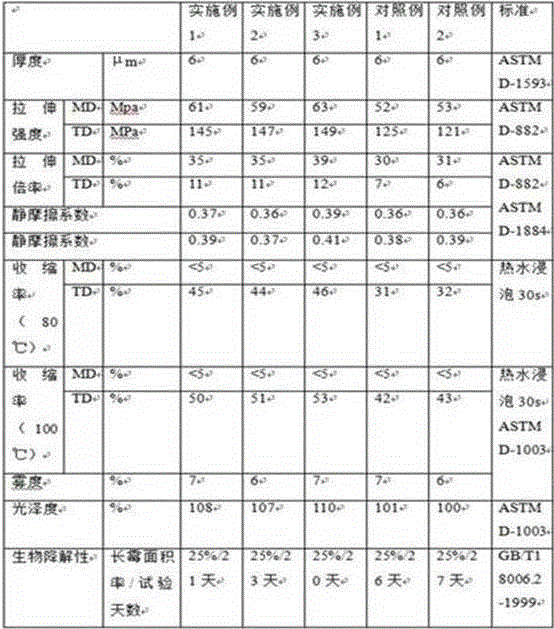
Embodiment 1
[0034] A biodegradable heat-shrinkable film, which is prepared through the following steps:
[0035] In the first step, by weight, 10 parts of dialdehyde starch, 4 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 3 parts of chitosan and 1 part of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose are added to the reactor, and after reacting under sealed conditions, the improved Reactive dialdehyde starch, reaction time 40min, reaction temperature 80°C;
[0036] In the second step, using a stirring mixer, 150 parts of polylactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 3 to 300,000, 15 parts of high density polyethylene with a weight average molecular weight of 4 to 500,000, and a weight average molecular weight of 6,000 to 100,000 15 parts of polybutylene adipate, 10 parts of modified dialdehyde starch, 5 parts of polypropylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1000-2000, 1 part of plasticizer ethylene glycol, 1 part of crosslinking agent acetaldehyde, compatibilizer Agent ethylene acrylic acid copolymer 1 par...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A biodegradable heat-shrinkable film, which is prepared through the following steps:
[0040] In the first step, by weight, 20 parts of dialdehyde starch, 7 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 5 parts of chitosan and 3 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose are added to the reactor, and after reacting under sealed conditions, the improved Reactive dialdehyde starch, reaction time 60min, reaction temperature 90°C;
[0041] In the second step, using a stirring mixer, 200 parts of polylactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 3 to 300,000, 25 parts of high density polyethylene with a weight average molecular weight of 4 to 500,000, and a weight average molecular weight of 6,000 to 100,000 25 parts of polybutylene adipate, 30 parts of modified dialdehyde starch, 15 parts of polypropylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1000-2000, 4 parts of plasticizer ethylene glycol, 4 parts of crosslinking agent acetaldehyde, compatibilizer Agent ethylene acrylic acid copolymer 4 p...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A biodegradable heat-shrinkable film, which is prepared through the following steps:
[0045] In the first step, by weight, 15 parts of dialdehyde starch, 5 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 4 parts of chitosan and 2 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose are added to the reactor, and after reacting under sealed conditions, the improved Reactive dialdehyde starch, reaction time 50min, reaction temperature 85°C;
[0046] In the second step, using a stirring mixer, 170 parts by weight of polylactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 3 to 300,000, 20 parts of high density polyethylene with a weight average molecular weight of 4 to 500,000, and 6,000 to 100,000 weight average molecular weight 20 parts of polybutylene adipate, 20 parts of modified dialdehyde starch, 10 parts of polypropylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1000-2000, 2 parts of plasticizer ethylene glycol, 2 parts of crosslinking agent acetaldehyde, compatibilizer 2 parts of ethylene acrylic acid c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com