Method for corroding silicon carbide ceramics
A silicon carbide ceramic and silicon carbide technology is applied in the field of microscopic morphology analysis of dense silicon carbide ceramics. The effect of high chemical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
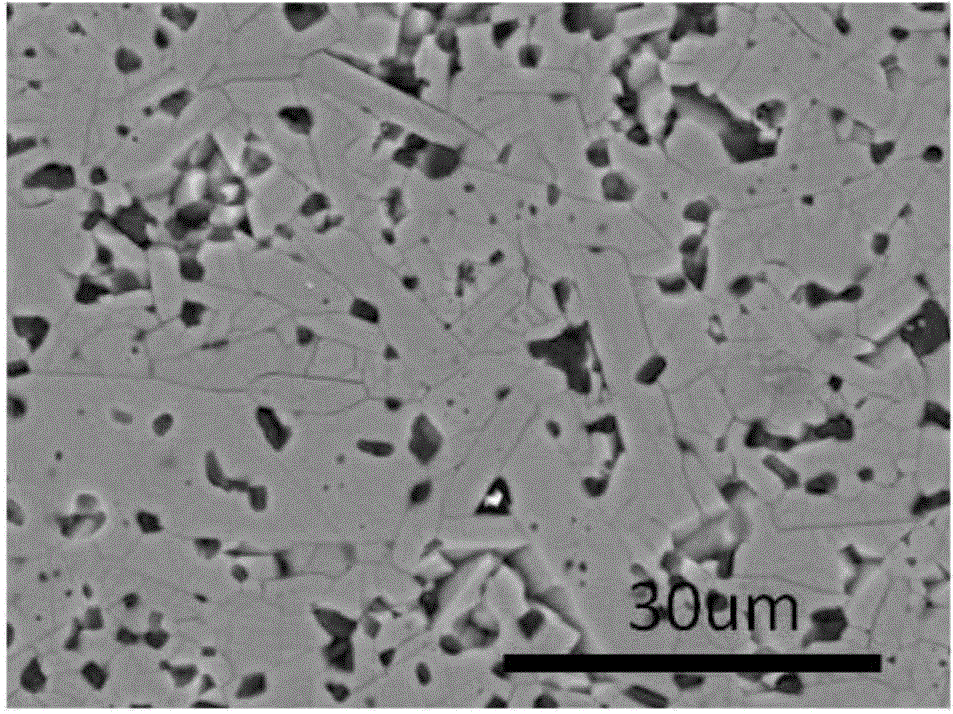
[0025] Preparation of silicon carbide samples. Due to the strong oxidation and high coordination of the etchant, it can react with silicon carbide. As an example, two different silicon carbide ceramic samples are prepared by solid-state atmospheric pressure sintering method, and the samples are processed into a test strip with a size of 4*5*40mm. Each side of the sample Chamfer.
[0026] Polishing treatment of silicon carbide specimens. As a detailed example, use a surface grinder to rough the surface of the sample to make the surface flatness less than 1°C, and then use 180 mesh, 280 mesh B 4 C abrasive is used for grinding and polishing, the speed of the polishing machine is set to 50r / min, and the grinding and polishing time is 2h, and then the silicon carbide ceramic sample is polished with 20um and 10um diamond abrasive paste, and the speed of the polishing machine is set to 40r / min. min, the polishing time is 1h, and finally the silicon carbide ceramics are polished w...
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for corroding solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramics at low temperature, the realization steps are as follows:
[0034] 1) Preparation of corrosion solution: first add 29ml of concentrated hydrofluoric acid to the container, then slowly add 23ml of concentrated nitric acid, the volume ratio of concentrated hydrofluoric acid to concentrated nitric acid is 1.261:1, stir well, pour into a closed container and let it stand 15min, set aside.
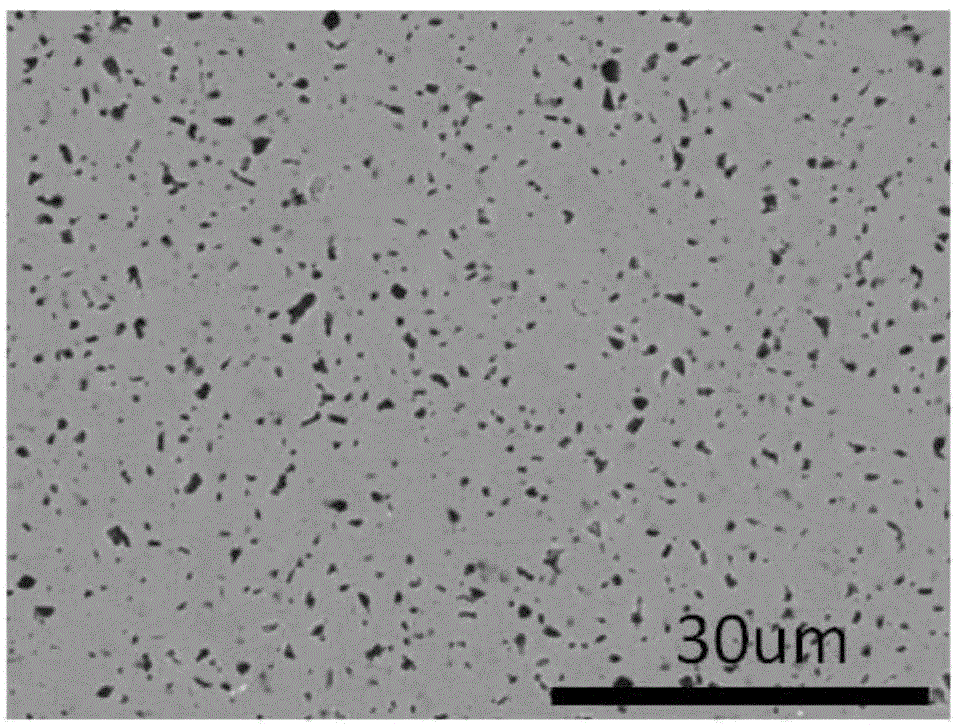
[0035] 2) Corrosion of silicon carbide ceramic samples: Pour the corrosion solution into the lining of the polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and the content of the polished sintering aid is 5wt%C and 0.6wt%B 4 C. The solid-phase sintered SiC material silicon carbide sample with a sintering temperature of 2150 ° C is completely immersed in the corrosion solution, and the polytetrafluoroethylene liner filled with the corrosion solution and the corrosion sample is put into a stainless steel reaction kettle, and the corrosion ...
Embodiment 2
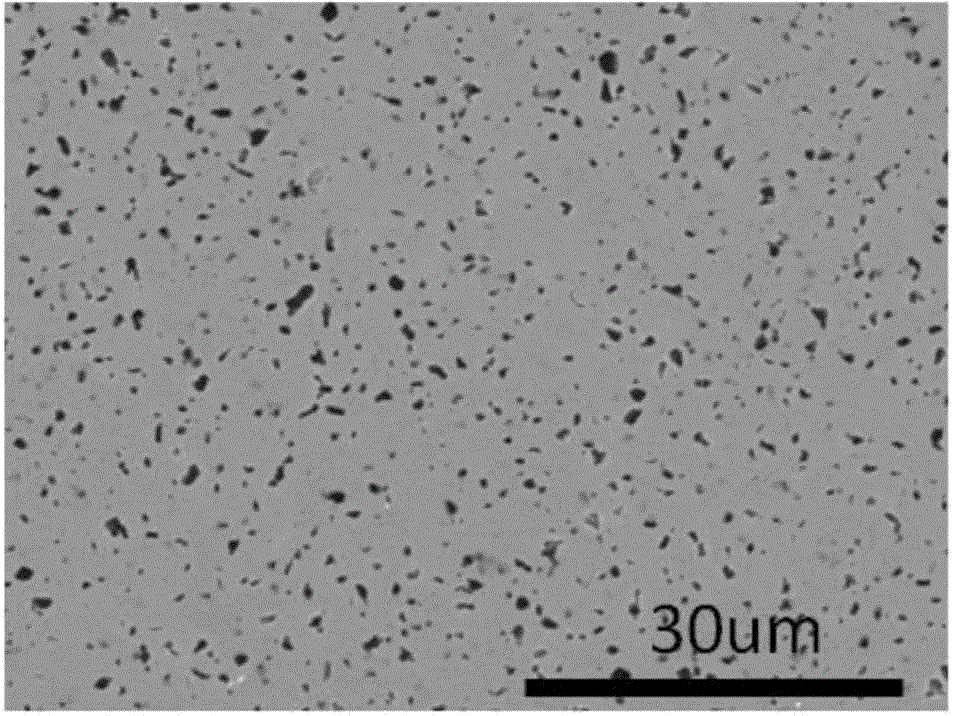
[0045] First add 29ml of concentrated hydrofluoric acid into the container, then slowly add 23ml of concentrated nitric acid, the volume ratio of concentrated hydrofluoric acid to concentrated nitric acid is 1.261:1, stir well, pour it into a closed container and let it stand for 15 minutes, then use it. Pour the corrosion solution into the reactor lining of polytetrafluoroethylene, and the content of the sintering aid after polishing is 6wt%C and 0.6wt%B 4 C. The solid-phase sintered SiC material silicon carbide sample with a sintering temperature of 2150 ° C is completely immersed in the corrosion solution, and the polytetrafluoroethylene liner filled with the corrosion solution and the corrosion sample is put into a stainless steel reaction kettle, and the corrosion temperature is 175 ℃, and the corrosion time is 24h. Rinse the surface of the sample with deionized water for 30s, then use absorbent cotton with alcohol to wipe the surface of the sample and then rinse the surf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com