LED (light-emitting diode) epitaxial growth method capable of improving hole injection
A light-emitting diode, epitaxial growth technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
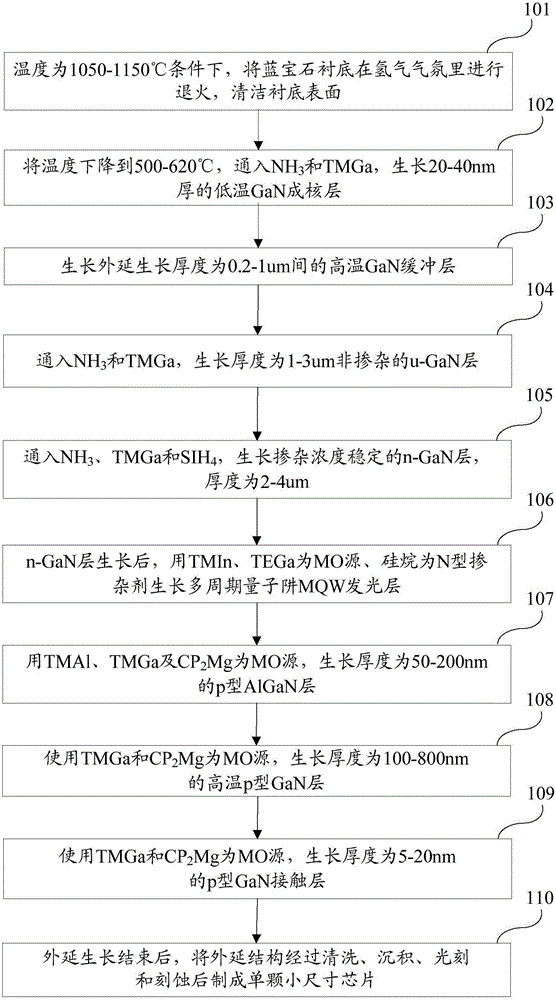
[0071] Such as image 3 As shown, is a schematic flow chart of an alternative embodiment of the epitaxial growth method of a light-emitting diode with improved hole injection according to the present invention. The invention grows Mg-doped and Mg-non-doped InGaN:Mg / InGaN superlattice layer structures in the LED epitaxial layer, improves the hole injection level of the quantum well region, reduces the working voltage of the light-emitting diode (LED) and improves the Luminous efficiency of LEDs. The light-emitting diode epitaxial growth method for improving hole injection described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0072] Step 301 , at a temperature of 1050-1150° C., anneal the sapphire substrate in a hydrogen atmosphere with a purity above 99.999%, and then clean the surface of the substrate.
[0073] Step 302, lower the temperature to 500-620°C, feed TMGa and NH with a purity of 99.999% or more 3 , grow a low-temperature GaN nucleation layer with a thickne...
Embodiment 2
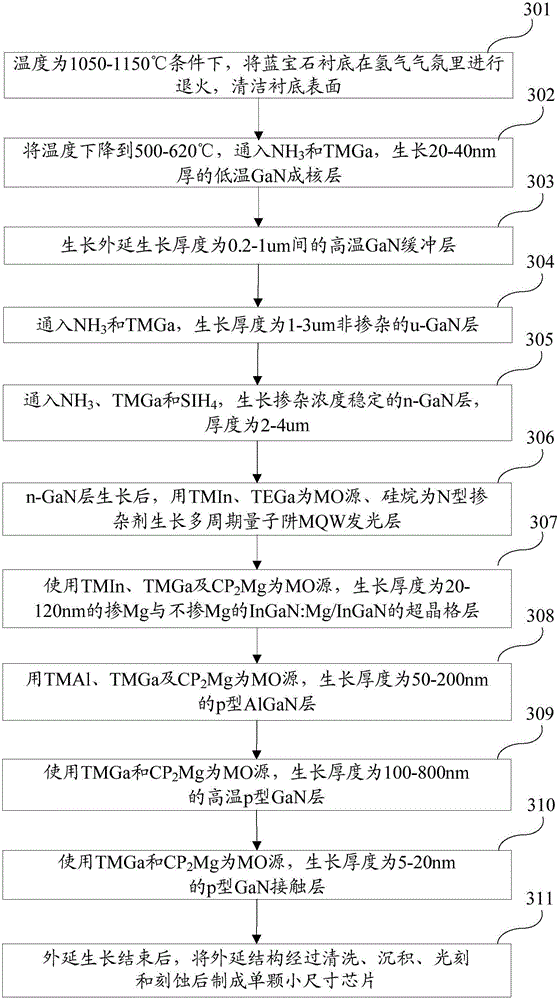
[0088] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it is a schematic flowchart of the epitaxial growth method of light-emitting diodes with improved hole injection described in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In this embodiment, a specific method for realizing each step of epitaxial growth of a light emitting diode is provided. The light-emitting diode epitaxial growth method for improving hole injection in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0089] Step 501 , after annealing the sapphire substrate in a hydrogen atmosphere with a purity above 99.999% at a temperature of 1050-1150° C., the surface of the substrate is cleaned.
[0090] Step 502, lower the temperature to 500-620°C, feed TMGa and NH with a purity of 99.999% or more 3 , under the condition that the growth pressure is 400-650 Torr and the V / III molar ratio is 500-3000, a low-temperature GaN nucleation layer with a thickness of 20-40 nm is grown.
[0091] Step 503, stop feeding TMGa, raise the temperature to 10...
Embodiment 3
[0105] In this embodiment, the LEDs prepared by the traditional method and the LEDs prepared by the solution of the present invention were used to conduct contrast tests of brightness and driving voltage. details as follows:
[0106] Sample 1 was prepared according to the traditional LED growth method, and sample 2 was prepared according to the method described in this patent; the difference between the parameters of the epitaxial growth method of sample 1 and sample 2 is that sample 2 was grown by the method of the present invention after the MQW light-emitting layer was grown. A layer of Mg-doped and non-Mg-doped InGaN:Mg / InGaN superlattice layer structure was prepared. For details, refer to sample 1 and sample 2 in Table 1. ITO (indium tin oxide, indium tin oxide, Commonly known as ITO) layer, 70nm Cr / Pt / Au electrodes are plated under the same conditions, and SiO is plated under the same conditions 2 The protective layer is 30nm, and then the sample is ground and cut into ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com