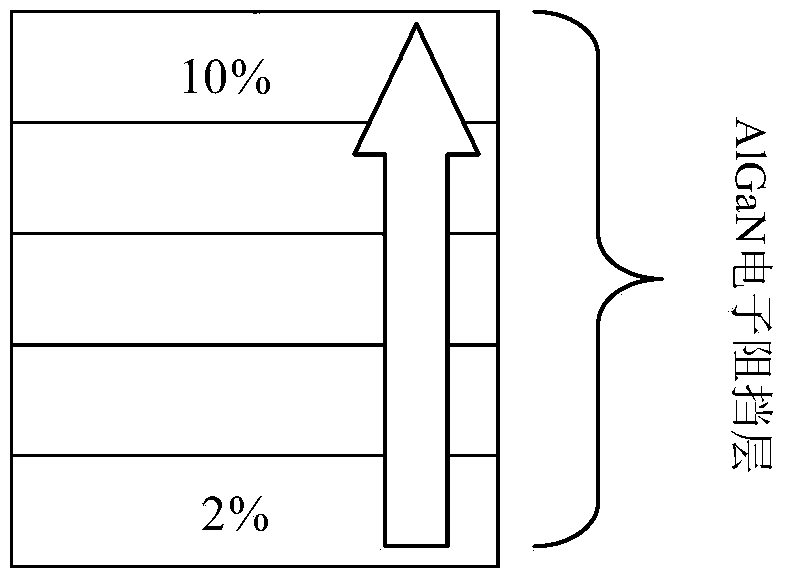
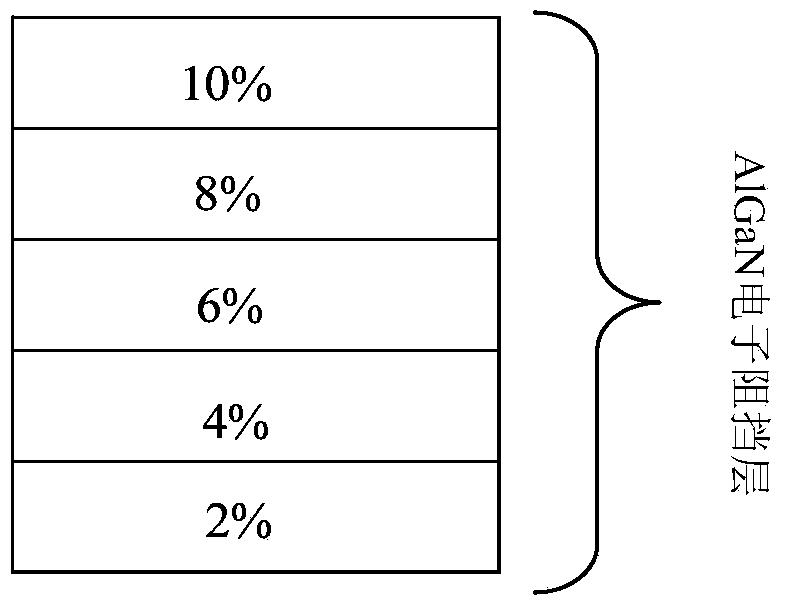
Patents
Literature
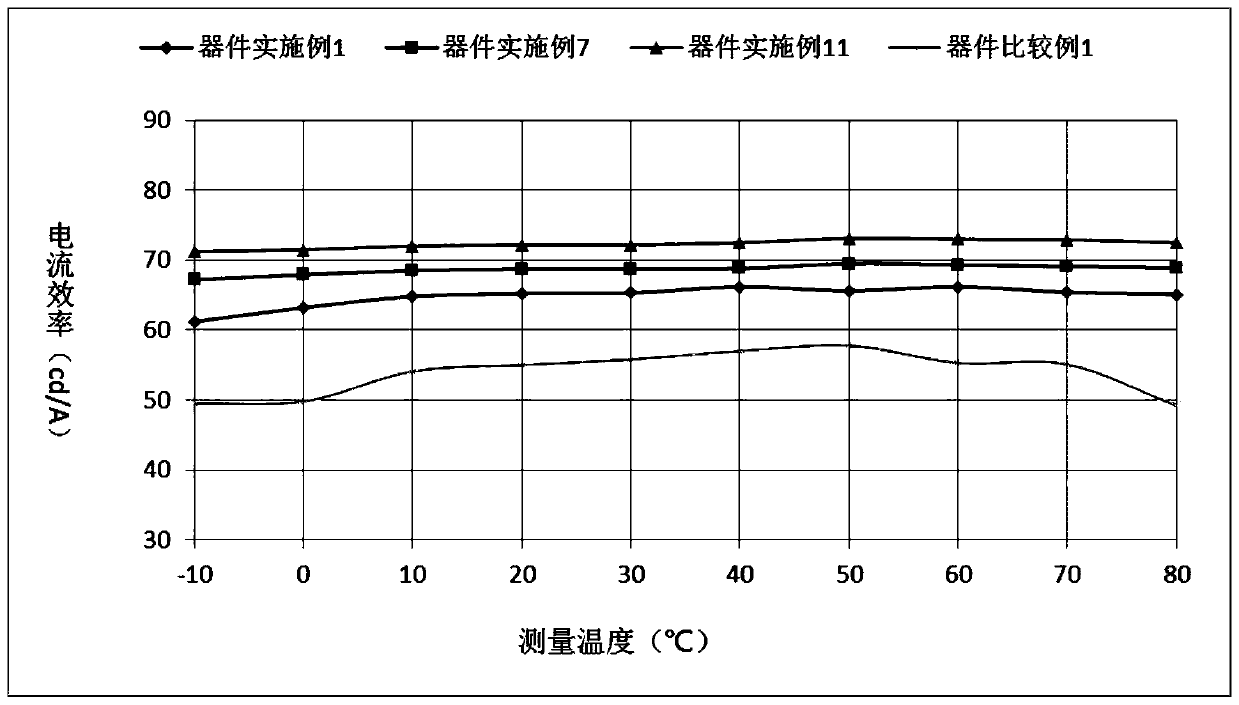
712results about How to "Improve compound efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
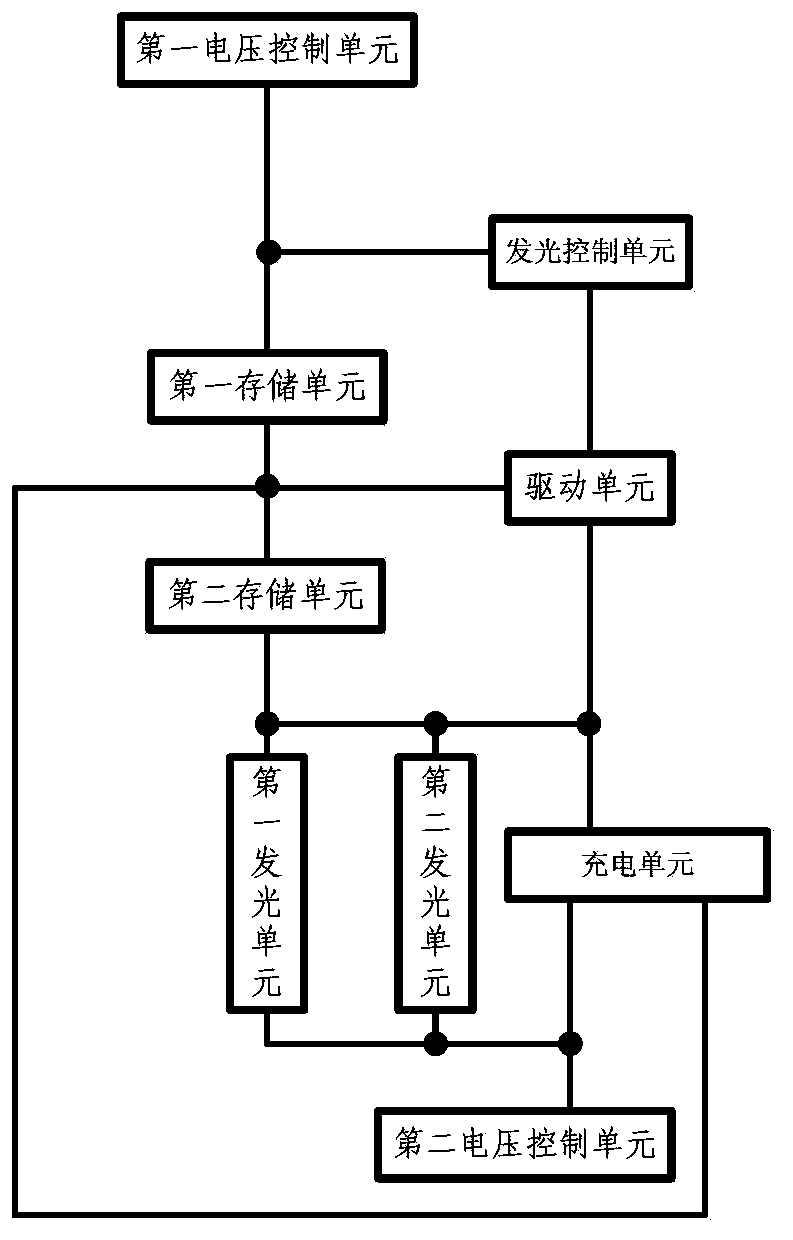
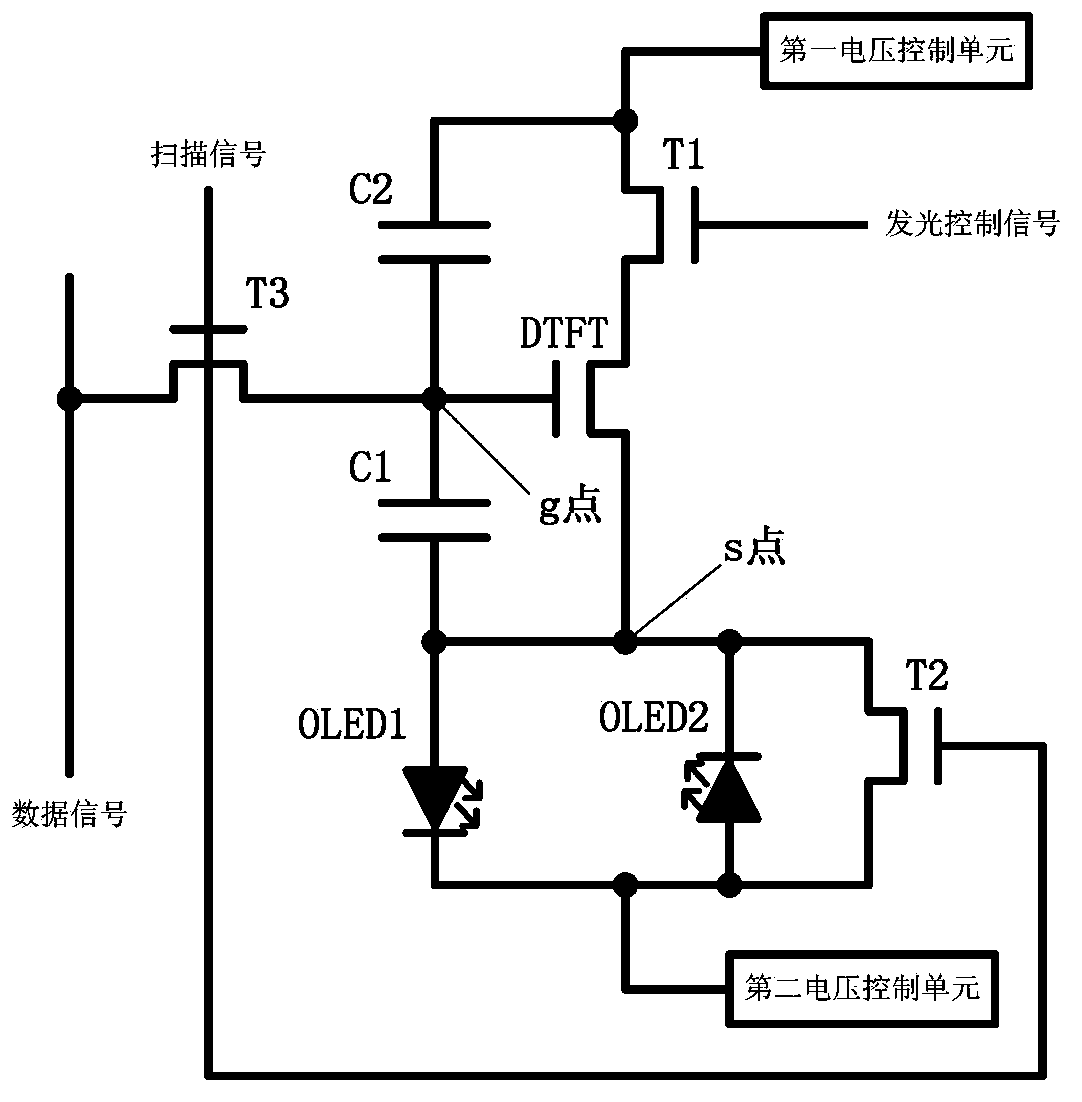
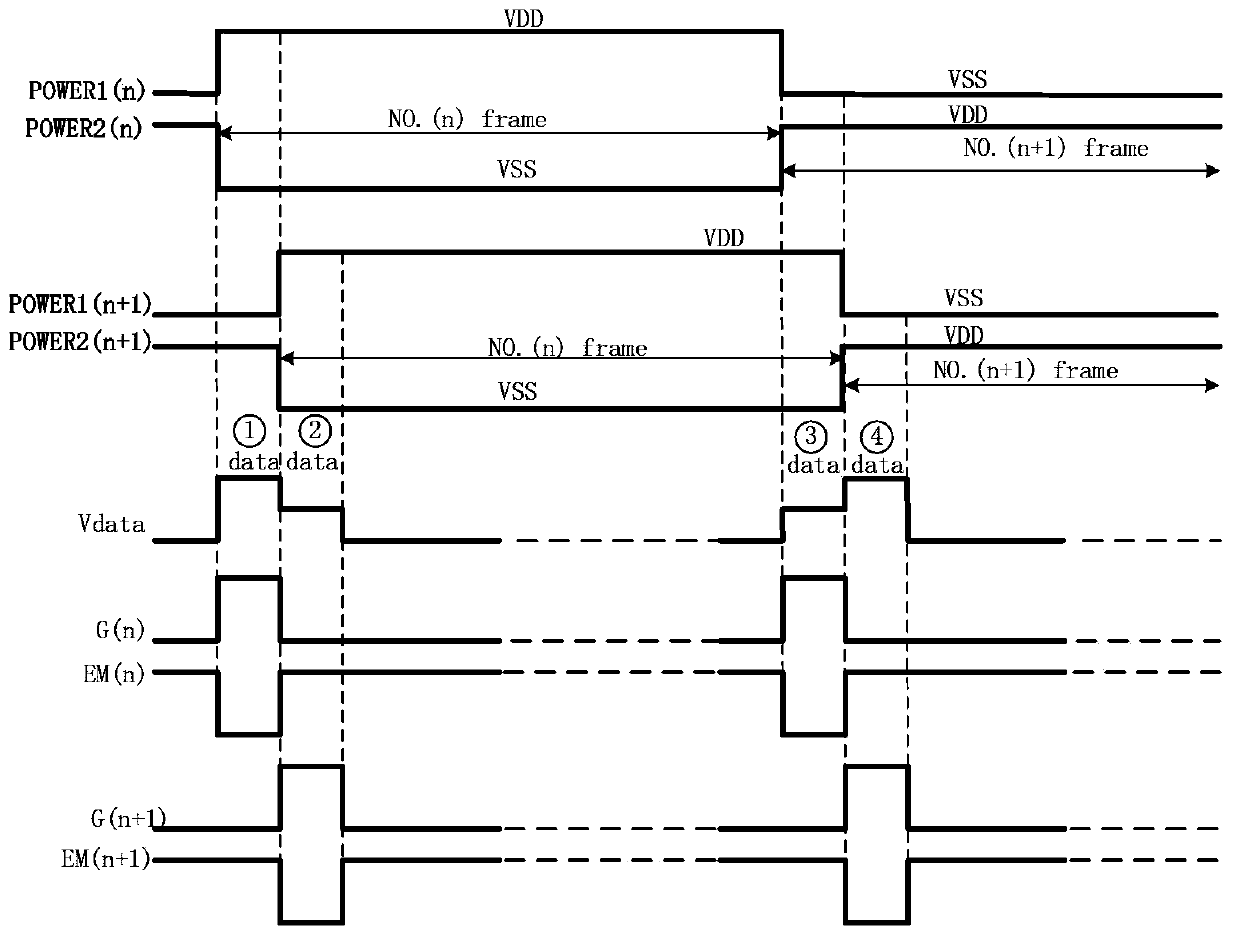
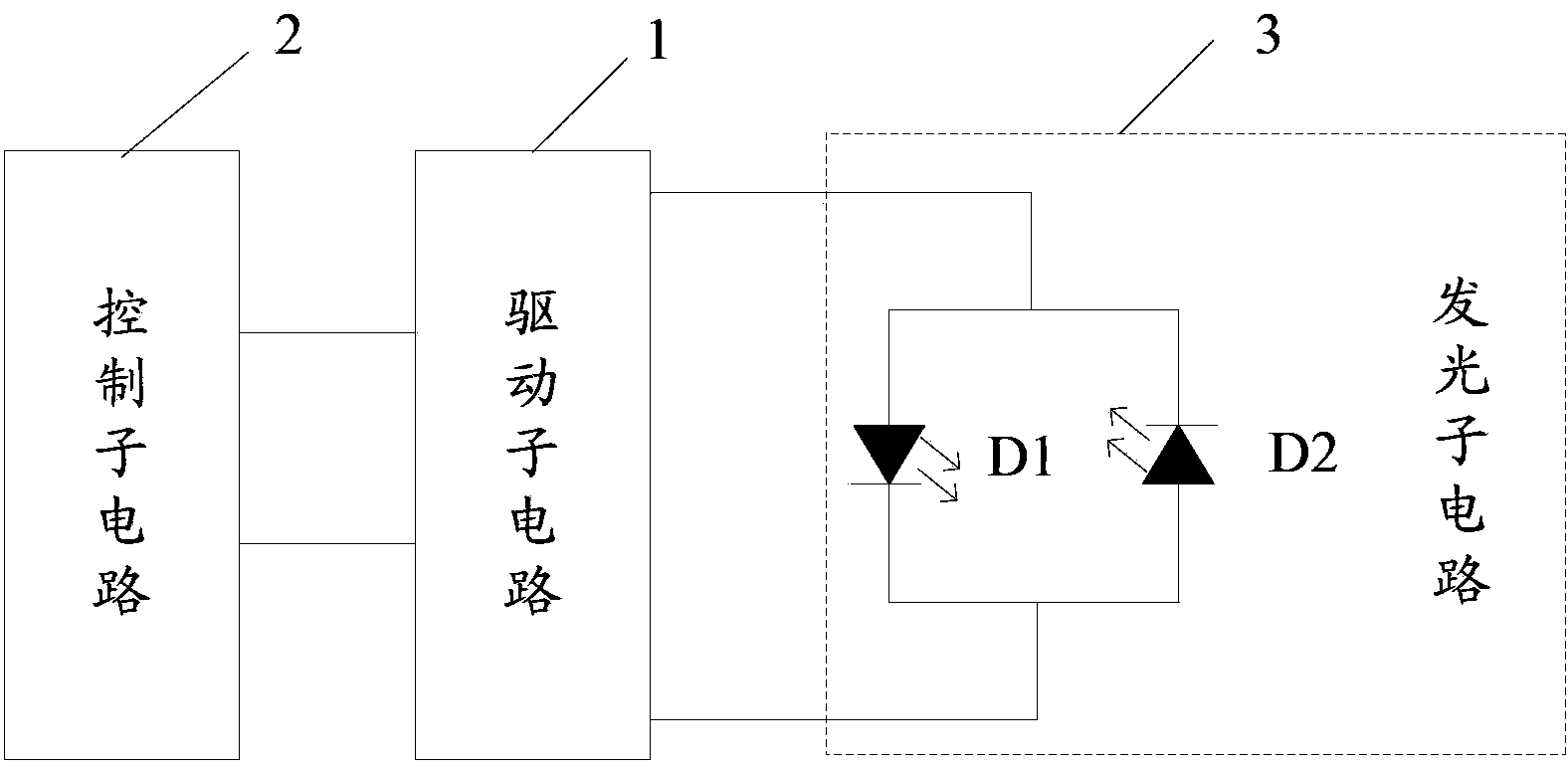
Alternating current drive OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) circuit, driving method and display device
ActiveCN103366682AEliminates the problem of uneven lighting displayImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesFrame timeDisplay device
The invention discloses an alternating current drive OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) circuit, a driving method and a display device in the technical field of display. The alternating current drive OLED circuit comprises a light emission control unit, a charging unit, a driving unit, a first storage unit, a second storage unit, a first light emitting unit, a second light emitting unit, a first voltage control unit and a second voltage control unit. Reversely connected first light emitting unit and second light emitting unit are used for alternatively emitting light in two adjacent time frames through the first light emitting unit and the second light emitting unit, only one light emitting unit emits and displays light in the same frame time, the other light emitting unit is offset reversely, and the two light emitting units are exchanged at the next frame; alternating current drive of the light emitting units is realized, and the utilization rate of energy is improved; the ageing incentive of the light emitting units is completely eliminated, the service lives of the light emitting units are greatly prolonged, the effect of internal circuit resistance on the light emitting current is eliminated, and the image display quality is perfected.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Light-emitting diode chip and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101872813AAvoid damageImprove performanceSemiconductor devicesPotassium hydroxideInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a light-emitting diode (LED) chip and a manufacturing method thereof. Materials with high heat conductivity are used as a support substrate of the LED chip, and the support substrate is sequentially provided with a bonding material layer, a reflecting layer, a transparent electrode layer, an epitaxial layer and an n-surface electrode. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: coating a transparent conducting layer on a sapphire substrate GaN epitaxial wafer by vaporization; coating the reflecting layer on the conducting layer by vaporization; spreading the bonding material layer on the reflecting layer, and bonding the sapphire substrate GaN epitaxial wafer to the substrate; removing the sapphire substrate by combining mechanical grinding, chemical mechanical polishing and wet-method corrosion; etching an n-GaN, an active layer and a p-GaN by using inductively coupled plasmas, removing the undoped GaN layer by etching with a potassium hydroxide solution, and coarsening the surface of the n-GaN; and coating the n-surface electrode to the n-GaN layer by vaporization to form an ohmic contact. The invention avoids the damage to the GaN-based LED epitaxial layer and the bonding layer caused by the stripping of the sapphire substrate by using laser, and the heat radiation efficiency is improved by using the substrate with high heat conductivity.
Owner:刘胜
Method for regulating river branch black and odorous water bodies by using graphene modified nano titanium dioxide photocatalyst fiber net
ActiveCN106698585ACause secondary pollutionReduce wastePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiberHigh density
The invention discloses a method for regulating river branch black and odorous water bodies by using a graphene modified nano titanium dioxide photocatalyst fiber net. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a reduction-oxidation graphene modified nano titanium dioxide hetero-structure composite photocatalyst; (2) preparing a water-resistant and impact-resistant aluminum-based crosslinking agent to form a homogeneous mixture with the catalyst, adding the homogeneous mixture into fiber stuff for producing a high-density polyethylene fiber net, or also preparing a high-density polyethylene fiber net provided with a nano photocatalysis film coating; (3) performing natural drying in the air, and then performing drying at a constant temperature in a drying room; and (4) arranging the graphene modified nano titanium dioxide photocatalyst high-density polyethylene fiber net on a river branch to contact with the water surface and receive illumination at the same time so as to control the river branch black and odorous water bodies. The method disclosed by the invention does not need aeration oxygenation, is energy-saving and environment-friendly, and is lower in cost and simpler in process.
Owner:钟华
Organic compound based on triazine and benzimidazole and application thereof to organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device
ActiveCN106946853APrevent free spinsImprove structural stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesRefractive indexAbsorption rate
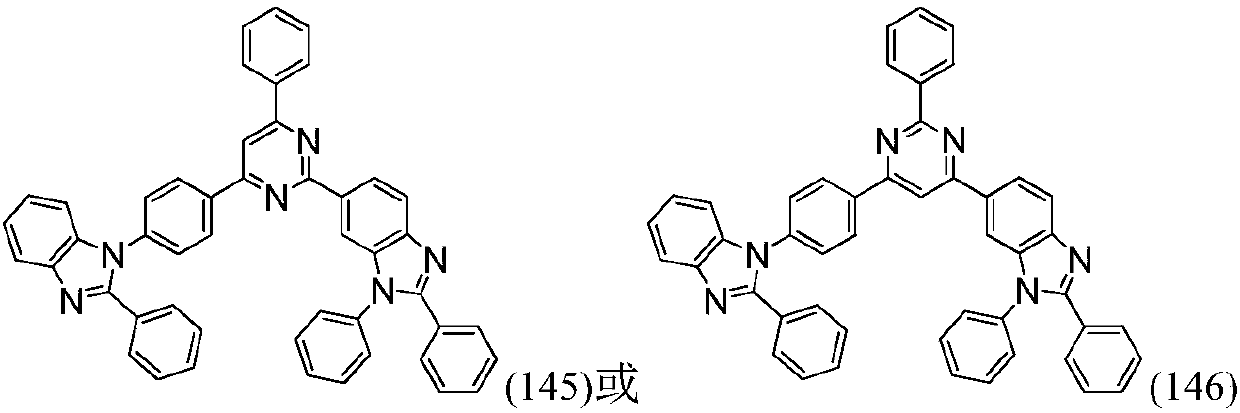
The invention relates to an organic compound based on triazine and benzimidazole and application thereof to an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device. The compound disclosed by the invention has a high vitrification temperature and high molecular thermal stability; the compound has a low absorption rate and a high refraction rate in the field of visible light, and can be applied to a CPL (Circular-Polarizing Filter) layer of the OLED device to effectively increase the light output efficiency of the OLED device; the compound also has a deep HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) energy level and a high electron mobility, can be taken as a hole-blocking / electron transport layer material of the OLED device, and can effectively block holes or prevent energy from being transported from a light-emitting layer to one side of an electron layer, so that the compound efficiency of the holes and electrons on the light-emitting layer is increased, and the light-emitting efficiency and the service life of the OLED device are increased and prolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Electron blocking layer structure of photoelectric device
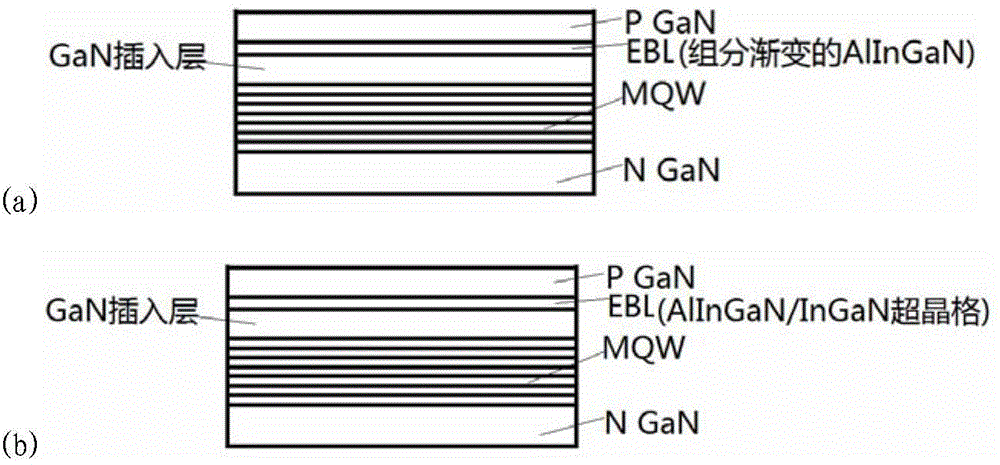
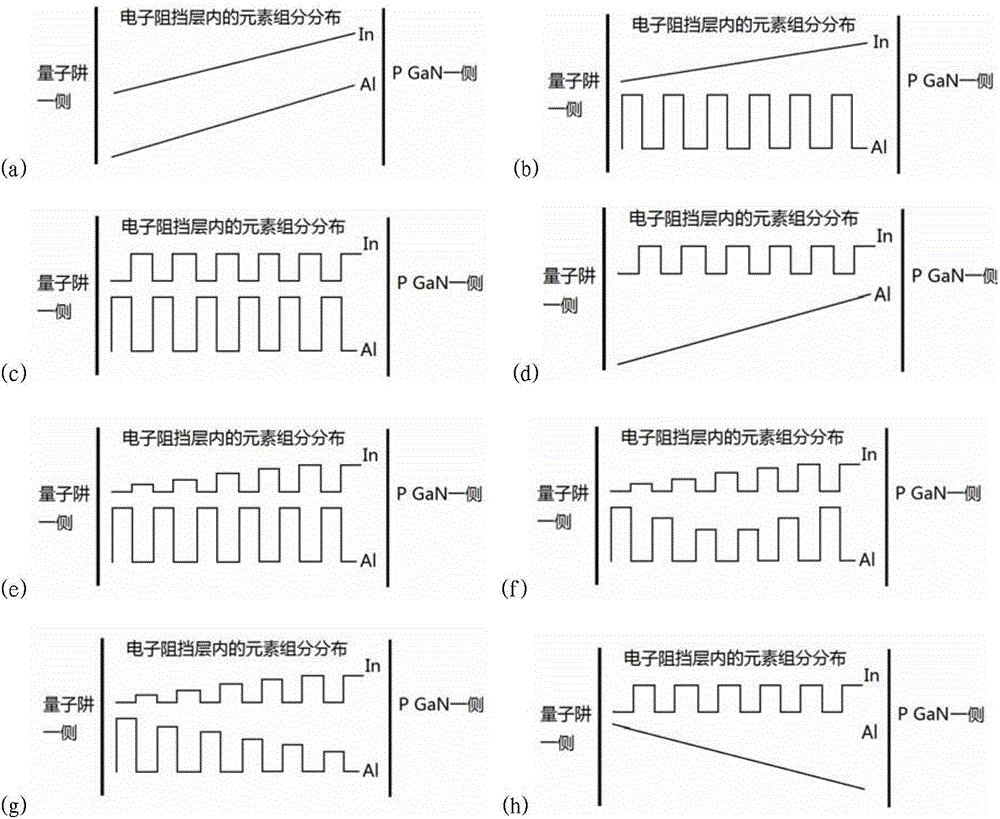
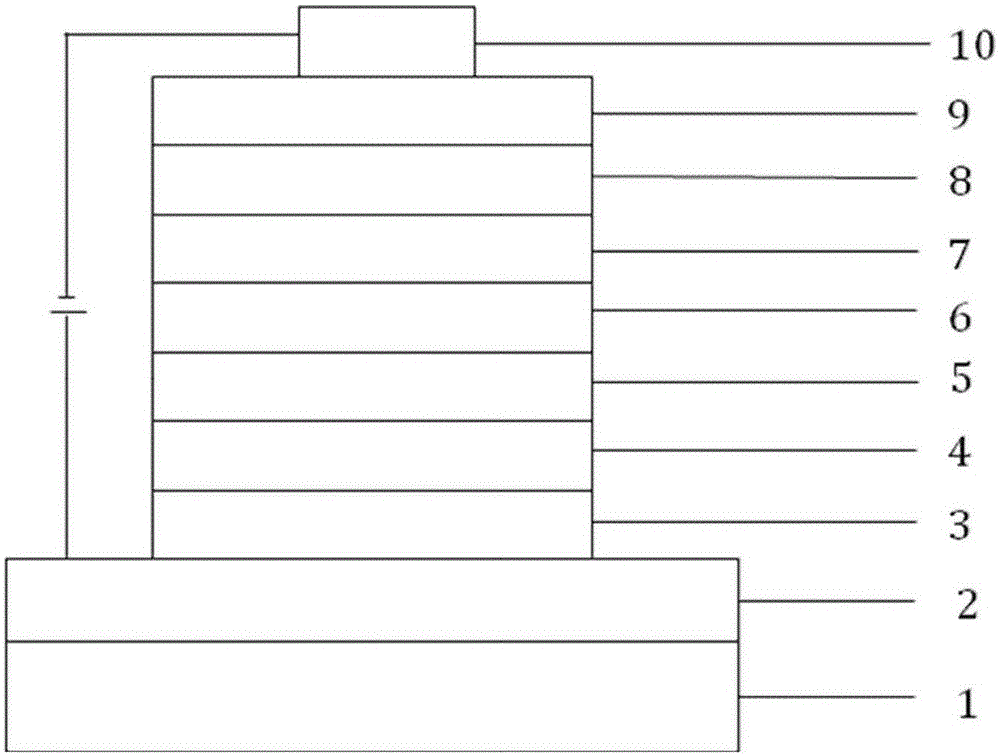
InactiveCN104659171AImprove compound efficiencyImprove electronic efficiencySemiconductor devicesBlocking layerPhotoelectric effect
The invention provides an electron blocking layer structure of a photoelectric device. The electron blocking layer structure is characterized in that structure matching between a quantum well and a P layer is achieved through adjusting a lattice structure and a band gap as much as possible; meanwhile, the formation of a polarized electric field is reduced, the formation of a negative charge area in an electron blocking layer is weakened as much as possible, and further the efficiency is improved; the electron leakage caused by energy band bending of the electron blocking layer and the increment of hole potential energy of the P layer are weakened. The electron blocking layer structure of the photoelectric device adopts AlInGaN or AlInGaN / InGaN super-lattice structure growth, wherein the In component is less than or equal to 10 percent; the Al component is less than or equal to 40 percent; the gradual distribution of the In component and the Al component exists in the electron blocking layer, and gradual change principles of the In component and the Al component are mutually independent; as for the electron blocking layer with an AlInGaN / InGaN super-lattice structure, the gradual change of the In component occurs in a super-lattice AlInGaN or a super-lattice AlInGaN / InGaN or in both the super-lattice AlInGaN and the super-lattice AlInGaN / InGaN.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Organic electroluminescent device containing triazine compound and application thereof
InactiveCN106467522AEase of escapeSmall S1-T1 state energy gap differenceOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesEnergy transferTriplet state
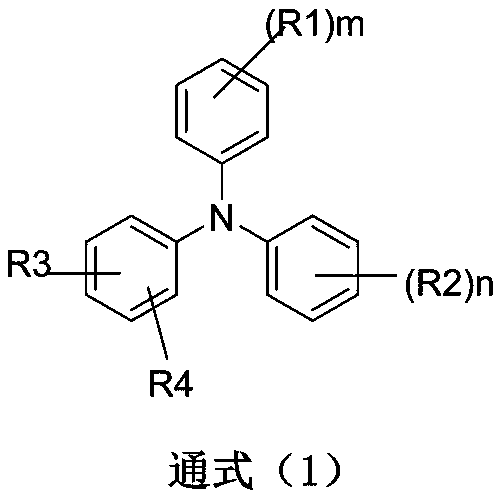
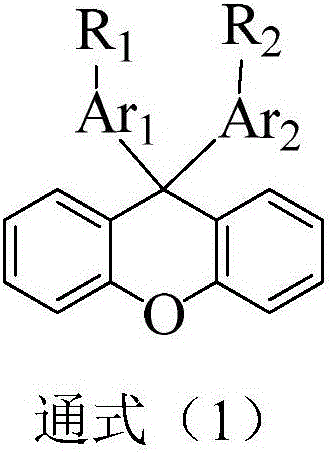
The invention discloses an organic electroluminescent device containing a triazine compound and application thereof. The device comprises a hole transport layer, a luminescent layer and an electron transfer layer. The luminescent layer material of the device contains a compound containing a triazine group. The structural formula of the compound is as shown in the general formula (1). As the triazine material has small triplet state and singlet energy difference, it is easy to realize energy transfer between host-guest materials, energy originally lost in the form of heat is easy to utilize, radiative transition efficiency of the luminescent layer is enhanced, and high efficiency of the device is easier to obtain. When a doped material is selected as a fluorescent material, luminous radiation of the doped material is easier to obtain, and long life of the material is easier to realize.
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Organic light-emitting display device
InactiveCN107146853AImprove efficiencySolution to short lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerCharge carrier
The invention provides an organic light-emitting display device. The organic light-emitting device comprises a positive electrode layer, a negative electrode layer and an organic light-emitting dielectric layer, wherein the organic light-emitting dielectric layer is arranged between the positive electrode layer and the negative electrode layer and comprises a hole injection layer, a hole transmission layer, a first hybrid layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transmission layer and an electron injection layer which are sequentially arranged, the first hybrid layer comprises a bipolar main body material and is doped with at least one of a material with an electron blocking function and a material with a hole control function, and the bipolar main body material has a function of simultaneously transmitting holes and electrons. By the organic light-emitting device, injection barriers of carriers of the holes and the electrons in the organic light-emitting device can be reduced, the injection rate of the carriers and the position of a carrier combination region are controlled, the carrier combination efficiency is improved, so that the organic light-emitting device with high efficiency and long lifetime is obtained.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent display device
InactiveCN101587941AIncrease luminous fluxLower hole injection barrierSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic layerLuminous flux
The invention discloses an organic electroluminescent display device, which comprises a glass substrate and an ITO conductive layer arranged on the upper surface of the glass substrate, wherein an anode interface modification layer, a hole transport layer, an electron transport layer, a luminescent layer, a metal cathode Mg layer and a metal cathode Al layer are sequentially arranged on the ITO conductive layer, and the anode interface modification layer is ZnO-doping PEDOT: PSS. The device takes the ZnO-doping PEDOT: PSS as the anode interface modification layer so as to reduce the hole injection barrier of a PEDOT: PSS layer and an ITO interface and improve the composite efficiency of holes and electrons, and meanwhile, the ZnO-doping PEDOT: PSS is also taken as a light scattering layer, so that crystal scattering can increase the luminous flux of the PEDOT: PSS layer, reduces the possibility that total-internal emission occurs among organic layers of a luminescent device, and improves the luminescent efficiency and brightness of organic OLED.
Owner:IRICO
Organic compound based on triazine and application thereof to organic electroluminescence device
ActiveCN109206420APrevent free spinsImprove structural stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionRefractive index
The invention relates to an organic compound based on triazine and application thereof to an OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) device. The compound has high glass transition temperature and molecular thermal stability; in the visible light field, the absorption is low; the refraction index is high; after the compound is applied to a CPL layer of the OLED device, the light taking-out efficiency of the OLED device can be effectively improved. The compound also has deep HOMO energy level and high electronic mobility and can be used as a hole blocking / electronic transmission layer material of the OLED device; holes or energy can be effectively blocked from being transmitted from the luminescent layer to one side of the electronic layer, so that the compounding efficiency of holes and electrons in the luminous layer is improved; further, the luminous efficiency of the OLED device is improved; the service life of the OLED device is prolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Organic light emitting diode
InactiveCN104795505AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove production efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionHole transport layer
The invention discloses an organic light emitting diode which is used for increasing the light emitting efficiency of the organic light emitting diode. The organic light emitting diode comprises an upper substrate, a lower substrate, an electronic transmission layer, a hole transmission layer and a light emitting layer, wherein the electronic transmission layer and / or the hole transmission layer are perovskite-organic inorganic hybrid layers.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
Dimethylanthracene-containing organic compound and application thereof
ActiveCN106467486ADestroy crystallinityInhibit aggregationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceThermal stability
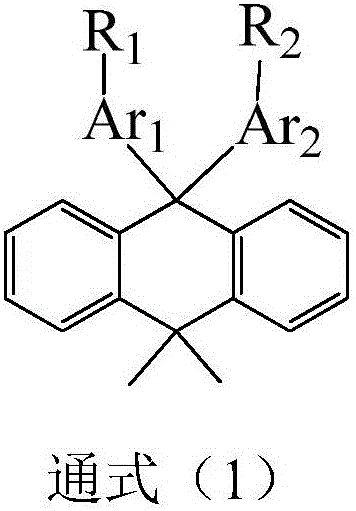
The invention discloses a dimethylanthracene-containing compound and an application of the dimethylanthracene-containing compound on an organic electroluminescent device. A structural general formula of the organic compound is shown as a general formula (1). The compound has high glass transition temperature and molecular thermal stability, and appropriate HOMO and LUMO energy level and high Eg, by optimizing a device structure, the photoelectric property of the OLED device and the life of the OLED device are effectively increased.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Organic light emission diode device containing xanthone compound and application thereof
ActiveCN107068910AEase of escapeSmall S1-T1 state energy gap differenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEnergy transferTransport layer
The invention discloses an organic light emission diode device containing a xanthone compound and an application thereof. The device comprises a hole transport layer, a light emission layer and an electron transport layer. The material of the light emission layer of the device comprises a compound with xanthone as a core group, and the structural formula of the compound is shown in the general formula (1). According to the material with xanthone as the core group, due to a small triplet and singlet energy difference, energy transfer between host and guest materials can be realized easily, energy that is originally lost in a heat form is easily available, and the high efficiency of the device can be acquired more easily. Further, when a fluorescent material is selected as a doped material, light emission radiation of the doped material is acquired more easily, and a long service life of the material can be acquired more easily.
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Azaxanthone compound and applications of azaxanthone compound in OLED light emitting devices
ActiveCN107245079ABreak symmetryDestroy crystallinityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyHost material
The invention discloses an azaxanthone compound and applications of the azaxanthone compound in organic electroluminescent devices. According to the present invention, the azaxanthone compound uses azaxanthone as the core, the molecules are not easily crystallized and are not easily aggregated, and the azaxanthone compound has good film forming property; and with the application of the azaxanthone compound as the light emitting layer main material of the OLED light emitting device, the current efficiency, the power efficiency and the external quantum efficiency of the device are greatly improved, and the service life of the device can be remarkably improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
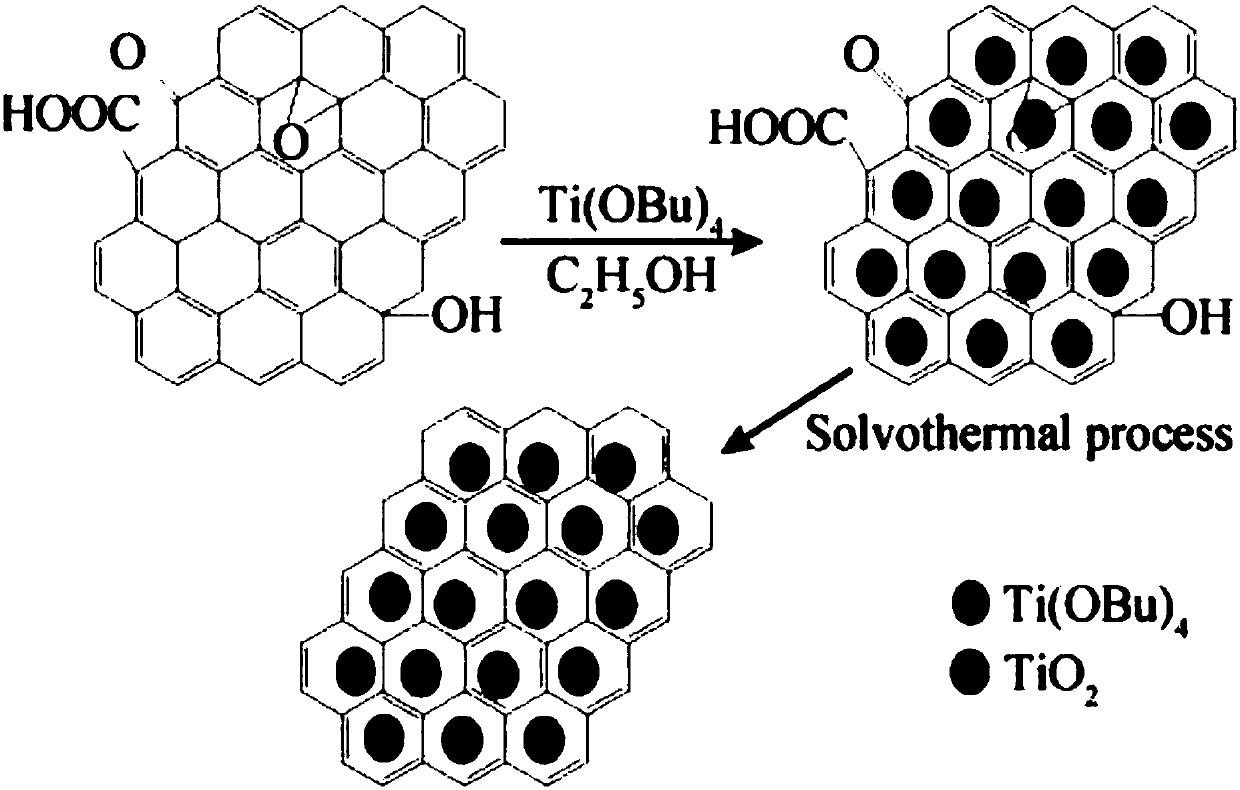
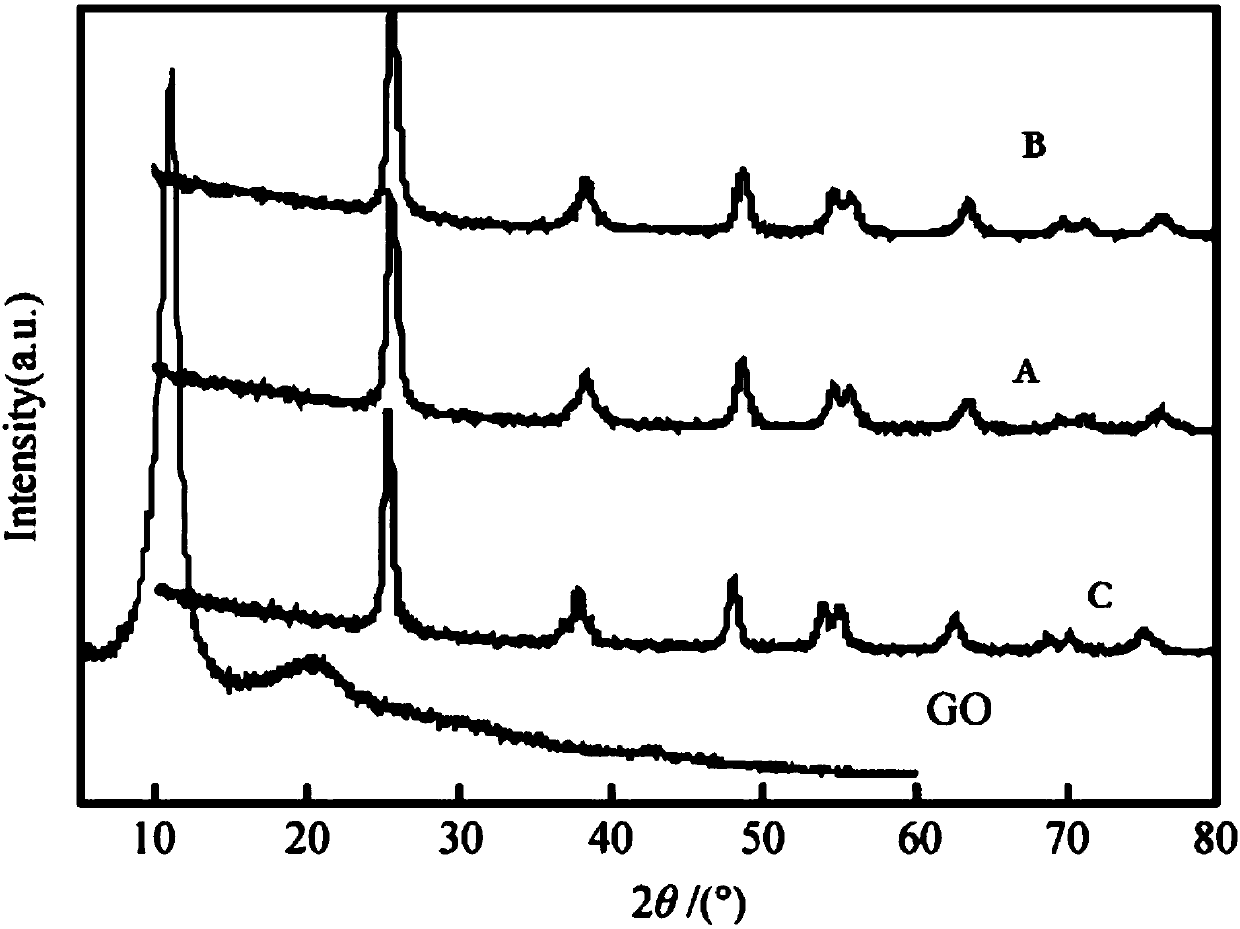
g-CNQDs/GO composite photocatalysis material preparation method
ActiveCN106111176ALarge specific surface areaEasy to separateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsOrganic dyeOxide composite
The present invention provides a g-CNQDs / GO composite photocatalysis material preparation method. The concrete scheme of the method comprises that graphite powder, urea and concentrated nitric acid are used as main raw materials, an electrostatic coupling method is used, and four steps such as oxidation of graphene, oxidation of graphite phase carbon nitride quantum dots, oxidation of protonated graphite phase carbon nitride quantum dots, and g-CNQDs / GO compounding are performed to prepare the graphite phase carbon nitride quantum dot / graphene oxide composite photocatalysis material. According to the present invention, the photocatalytic property test on the prepared composite photocatalysis material is performed with visible light ([lambda] is more than 420 nm), and the results of the degradation on rhodamine B, methyl orange and other organic dyes show that the composite photocatalyis material has the excellent photocatalytic performance under the visible light.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method of rolling composite plate and strip by slanting corrugating roll
ActiveCN105798062AImprove bindingHigh composite strengthRollsMetal rolling arrangementsComposite strengthAxial force
The invention discloses a method of rolling composite plate and strip by a slanting corrugating roll. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that a composite slab which is composed of a basal plate and a multilayer plate is rolled by a composite roughing mill with the slanting corrugating roll to prepare a semi-finished slanting corrugated composite plate, and then the semi-finished slanting corrugated composite plate is rolled by a composite finishing mill with a flat roll until the needed thickness to obtain a composite plate, wherein an axial included angle between slanting corrugation and the roll is 10-80 degrees. According to the method, the problems that instant impact is generated during rolling of a transverse corrugating roll, and the plate and strip are in deviation due to the axial force during rolling of a longitudinal corrugating roll are solved, and meanwhile, the combination area of the composite plates after being roughly milled is increased, so that the binding force between the basal plate and the multilayer plate is improved, and the composite strength and the composite efficiency of the composite plate are greatly improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Quantum dot electroluminescent device, display apparatus comprising the deivce and illumination apparatus comprising the device
ActiveCN105449112AImprove luminous efficiencyBrightness Half-Life Life ExtendedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityQuantum dot
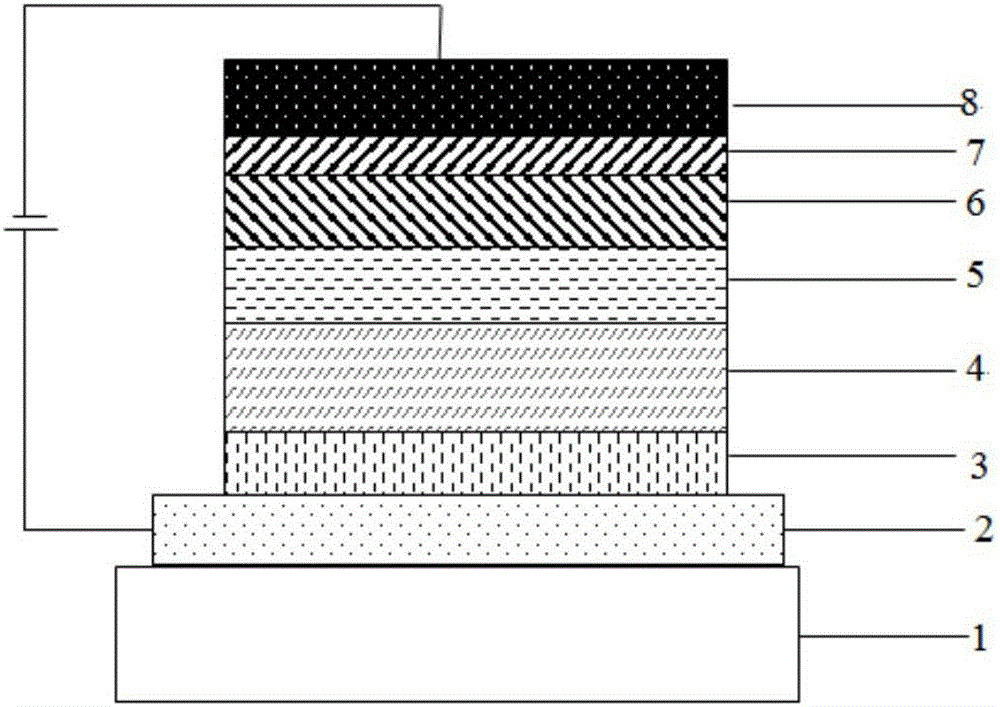
The invention provides a quantum dot electroluminescent device, a display apparatus comprising the device and an illumination apparatus comprising the device. The quantum dot electroluminescent device comprises a first electrode, a first function layer, a first charge adjusting layer, a quantum dot luminescent layer, a second charge adjusting layer, a second function layer and a second electrode which are successively arranged, wherein materials of the first charge adjusting layer and the second charge adjusting layer are respectively independently selected from insulation materials with energy gaps Eg greater than and equal to 5eV, and the thickness of the first charge adjusting layer and the thickness of the second charge adjusting layer both range from 1 to 30nm. The luminescence efficiency of the device is quite high, and the half-period life of the brightness of the device is quite long.
Owner:NANJING TECH CORP LTD
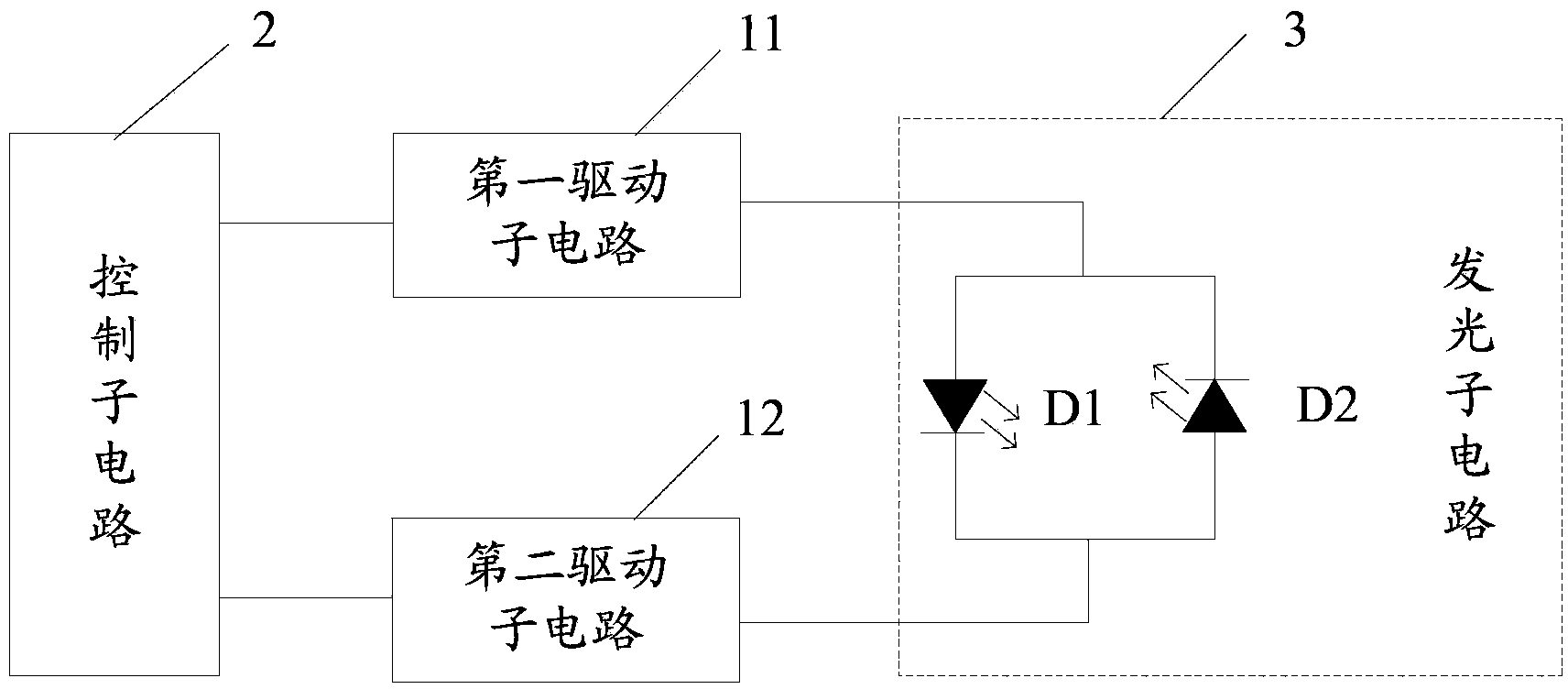
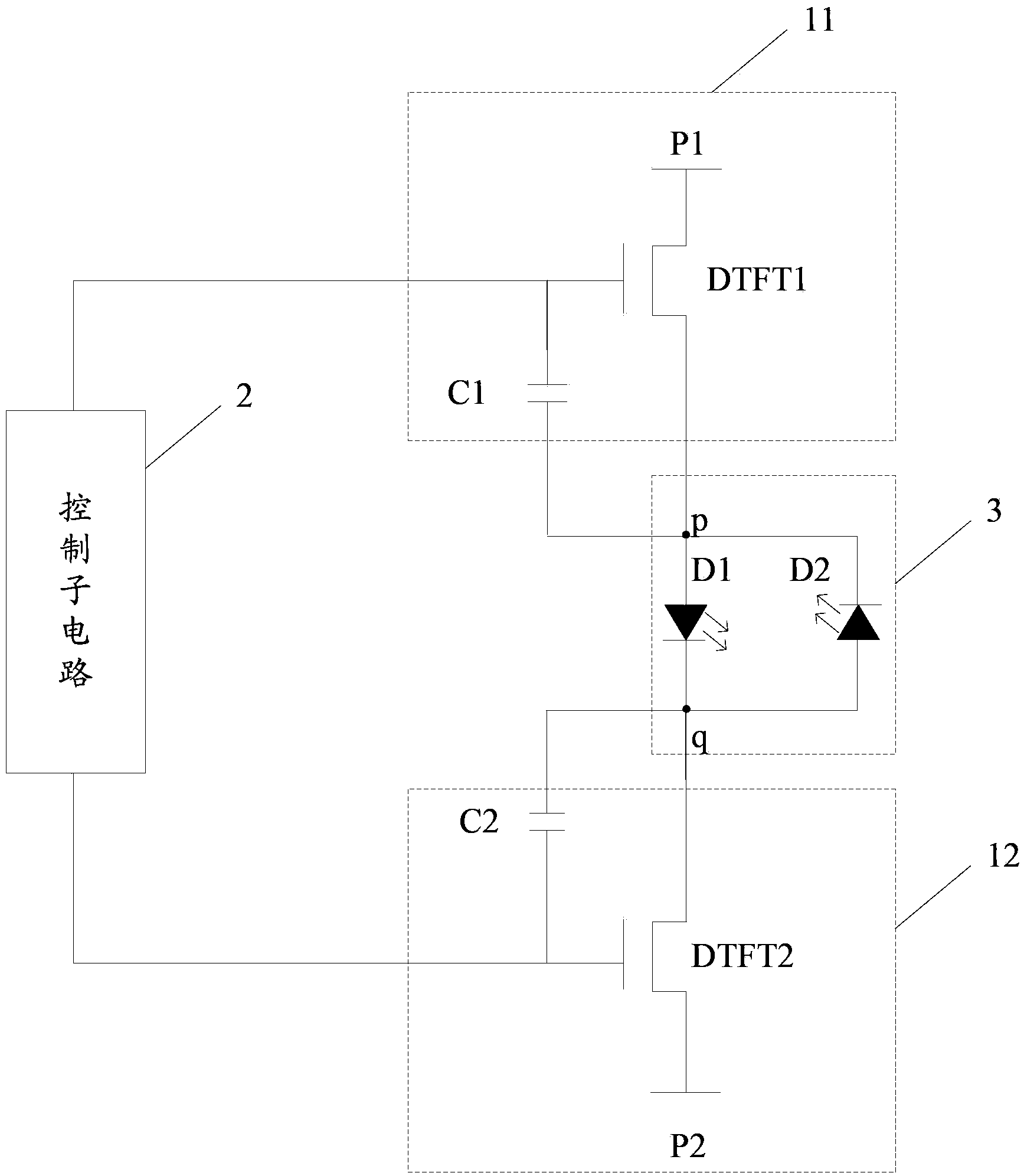
Pixel circuit and driving method, array substrate and display device thereof
ActiveCN103413519AEliminate built-in electric fieldImprove compound efficiencyStatic indicating devicesElectric fieldAge problems
The invention discloses a pixel circuit and a driving method, an array substrate and a display device of the pixel circuit to resolve the problem of ageing of an organic light-emitting component. The pixel circuit comprises a driving sub-circuit, a control sub-circuit and a light-emitting sub-circuit, wherein the light-emitting sub-circuit comprises a first organic light-emitting element and a second organic light-emitting element; the first organic light-emitting element and the second organic light-emitting element are connected with the driving sub-circuit; the control sub-circuit is connected with the driving sub-circuit and is used for controlling the driving sub-circuit to drive one of the first organic light-emitting element and the second organic light-emitting element to emit light in the forward direction in a bias mode in the same display stage and to drive the other of the first organic light-emitting element and the second organic light-emitting element to emit light in the reverse direction in a bias mode, and a bias state is switched in adjacent display stages. According to the pixel circuit and the driving method, the array substrate and the display device of the pixel circuit, built-in electric fields formed inside the organic light-emitting elements can be eliminated, current carrier recombination efficiency is enhanced, and the ageing problem of the organic light-emitting elements is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Gallium nitride base light-emitting diode with composite potential barrier
ActiveCN103151435AReduce the built-in electric fieldEliminate mismatchSemiconductor devicesPotential wellIndium
The invention discloses a gallium nitride base light-emitting diode with a composite potential barrier. The gallium nitride base light-emitting diode comprises a sapphire substrate, a buffering layer, an n-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer, a multiple quantum well active area, a p-type algan epitaxial layer and a p-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer, wherein the sapphire substrate, the buffering layer, the n-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer, the multiple quantum well active area, the p-type algan epitaxial layer and the p-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer are arranged sequentially from bottom to top. A p-type metal electrode is arranged on the upper surface of the p-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer. An n-type electrode is arranged on a lower platform surface of the n-type gallium nitride epitaxial layer. The multiple quantum well active area comprises 5-20 indium gallium nitride potential well layers which are arranged at intervals from bottom to top. A first kind composite potential barrier layer is arranged between every two indium gallium nitride potential barrier layers. A second kind composite potential well layer is arranged on the upper surface of an indium gallium nitride potential well layer at the top layer. According to the composite potential barrier, at the contact position of an aluminum, gallium and indium nitride layer and an InGaN potential well layer, a built-in electric field which is produced due to a polarization effect can be decreased through adjustment of aluminum (Al) and indium (In). On a contact interface between an AlInGaN layer and a GaN layer, a ratio between the Al and the In is adjusted to be 0.83:0.17, and lattices of the Al and the In are enabled to be matched.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Organic compound based on pyridine and benzimidazole and application thereof in organic light emitting diodes (OLED)
ActiveCN107417668APrevent free spinsImprove structural stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesHeat stabilityRefractive index
The invention relates to an organic compound taking pyridine and benzimidazole as a core and application thereof in organic light emitting diode (OLED) devices. The compound disclosed by the invention has higher glass transition temperature and molecular heat stability; the compound has low absorption and high refractive index in the field of visible light; after being applied to CPL layers of the OLED devices, the compound can effectively improve light extraction efficiency of the OLED devices. The compound disclosed by the invention further has a deep HOMO energy level and high electronic mobility, can serve as a cavity blocking / electron transfer layer material of the OLED devices and can effectively prevent cavities or energy from being transmitted to one side of an electronic layer from a luminescent layer; thus, composition efficiency of the cavities and the electrons in the luminescent layer is improved, and further luminous efficiency and service life of the OLED devices are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Light emitting diode epitaxy and growing method of light emitting diode electronic barrier layer
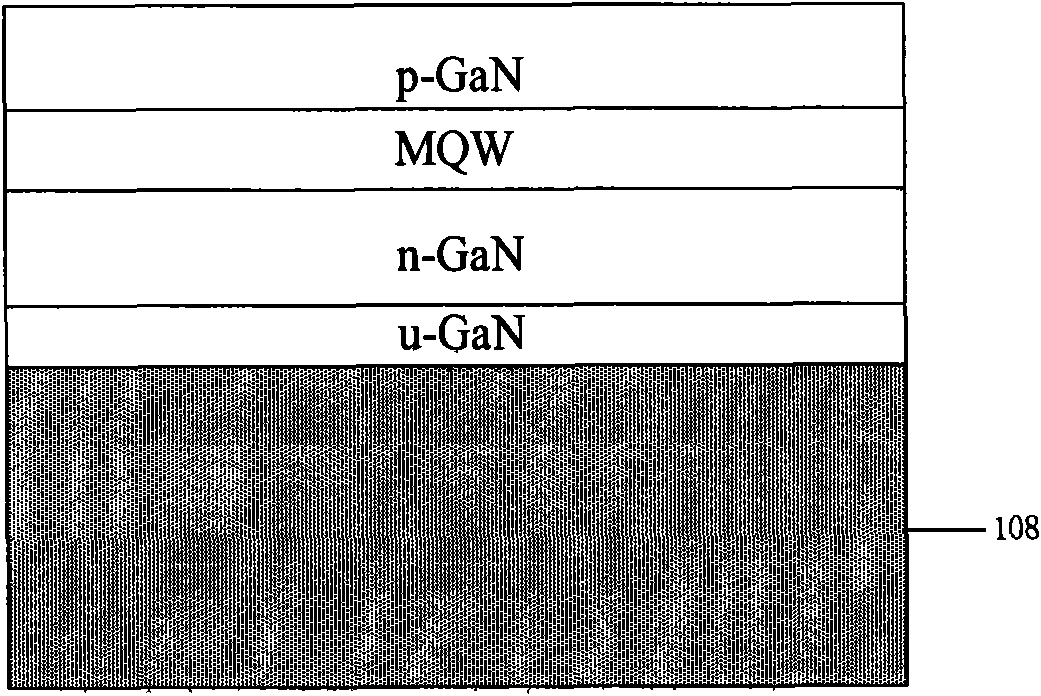
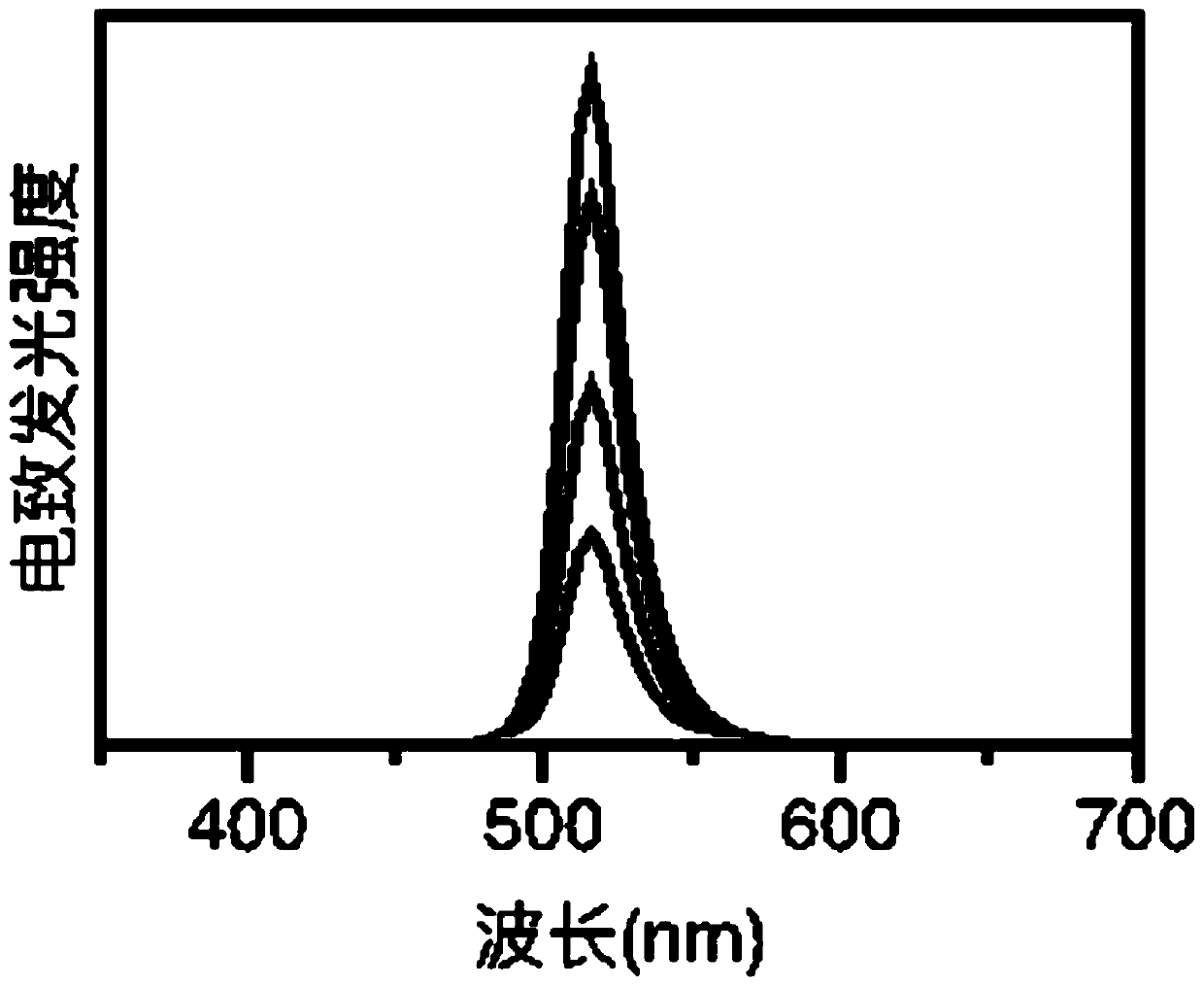
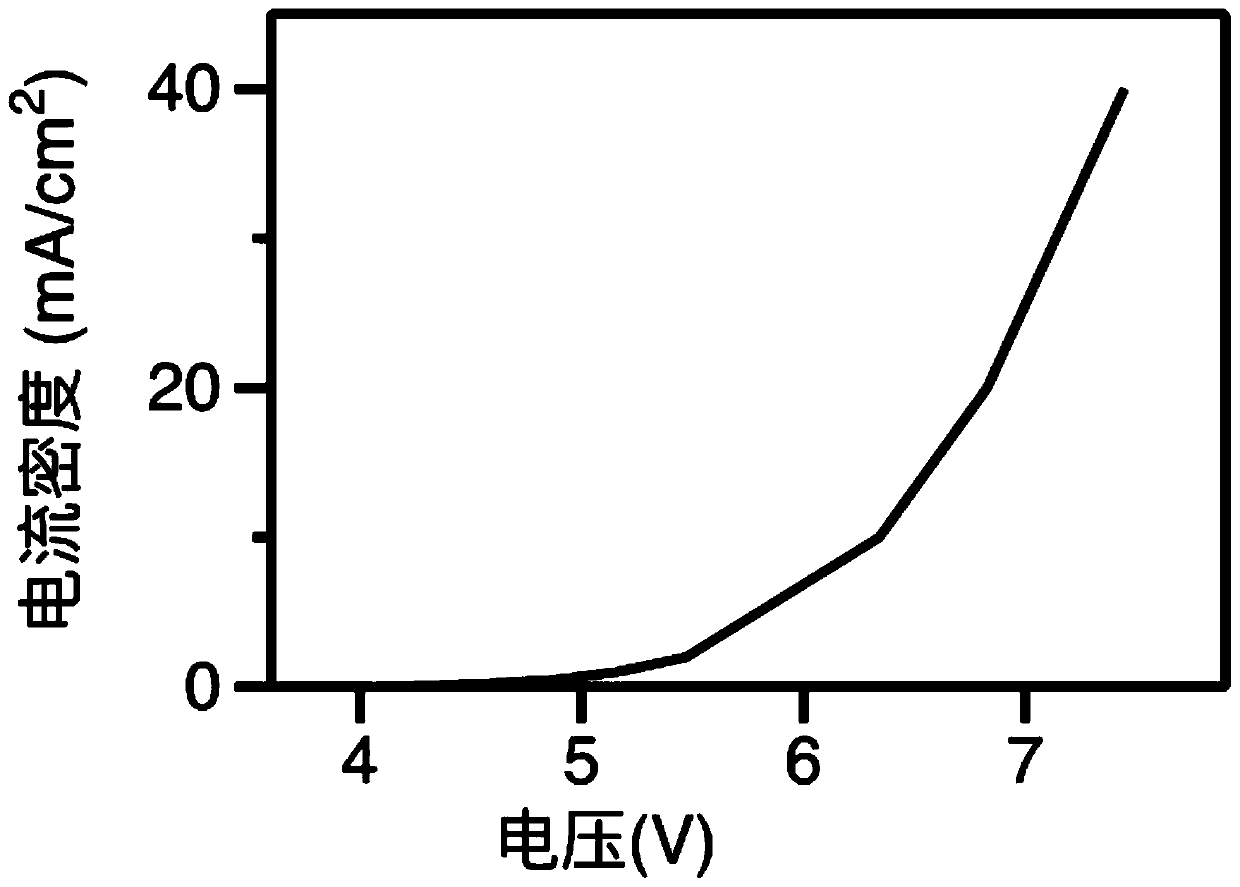
InactiveCN104201263AAvoid accessImprove compound efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum wellInterface layer
Owner:EPITOP PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
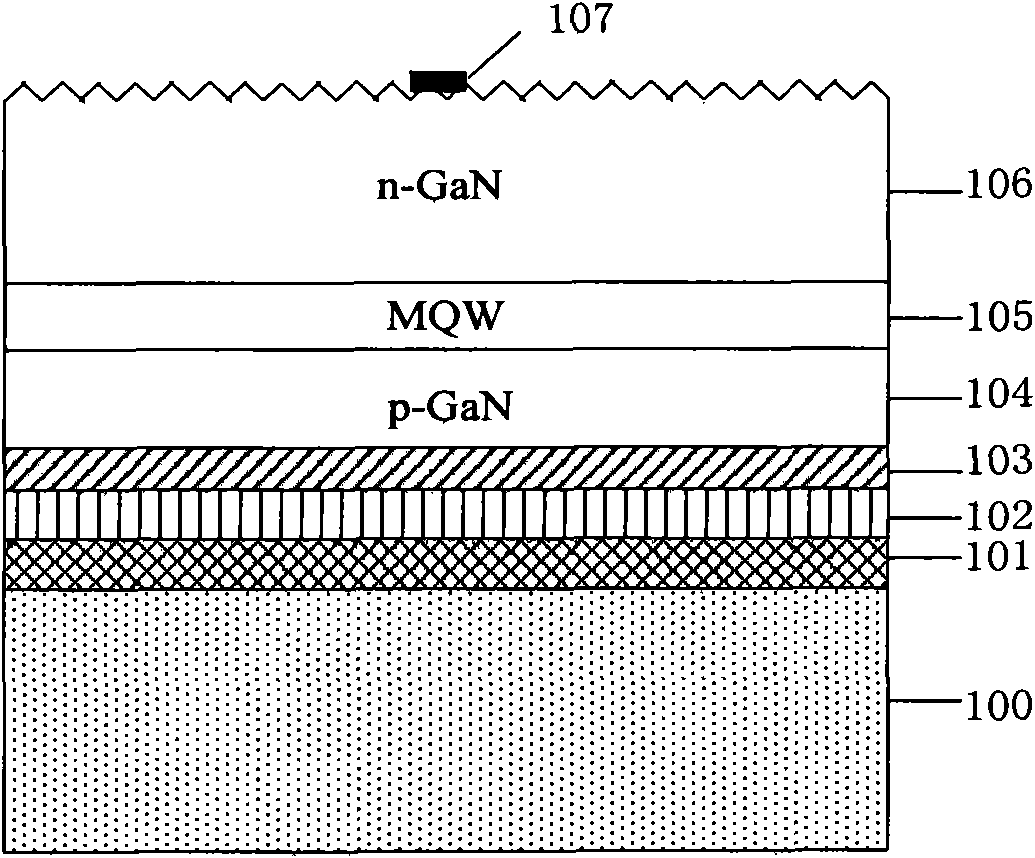
GaN-based III-V compound semiconductor LED (light emitting diode) epitaxial wafer and production method thereof
ActiveCN104409586AImprove antistatic performanceQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyContact layer
This application discloses a GaN-based III-V compound semiconductor LED (light emitting diode) epitaxial wafer and a production method thereof. The GaN-based III-V compound semiconductor LED epitaxial wafer structurally comprises a substrate, a low temperature GaN buffer layer, a first high temperature non-doped GaN layer and a second high temperature non-doped GaN layer, wherein an AlGaN / GaN superlattice layer is formed on the second high temperature non-doped GaN layer, a high temperature N type GaN layer is formed on the AlGaN / GaN superlattice layer, a stress release layer, an MQW protection layer, a P type electron barrier layer and a high temperature P type GaN layer are formed on the high temperature N type GaN layer, a contact layer is formed on the high temperature P type GaN layer, SiN mask / N type GaN layers are periodically inserted into the high temperature N type GaN layer, and the number of periods of the SiN mask / N type GaN layers ranges from 5 to 20. The GaN-based III-V compound semiconductor LED epitaxial wafer has the advantages of signally improving antistatic ability, effectively enhancing recombination efficiency of current carriers, and improving internal quantum efficiency of an LED.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
Compound with triarylamine structure as core and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110577511AImprove efficiencyImprove thermal stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesThermal stabilityGlass transition
The invention discloses a compound taking a triarylamine structure as a core as well as a preparation method and application of the compound. The structure of the compound is shown as a general formula (1). The compound provided by the invention has relatively high glass transition temperature and molecular thermal stability, proper HOMO and LUMO energy levels and relatively high mobility, and caneffectively improve the photoelectric property of an OLED device and prolong the service life of the OLED device by optimizing the structure of the device.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
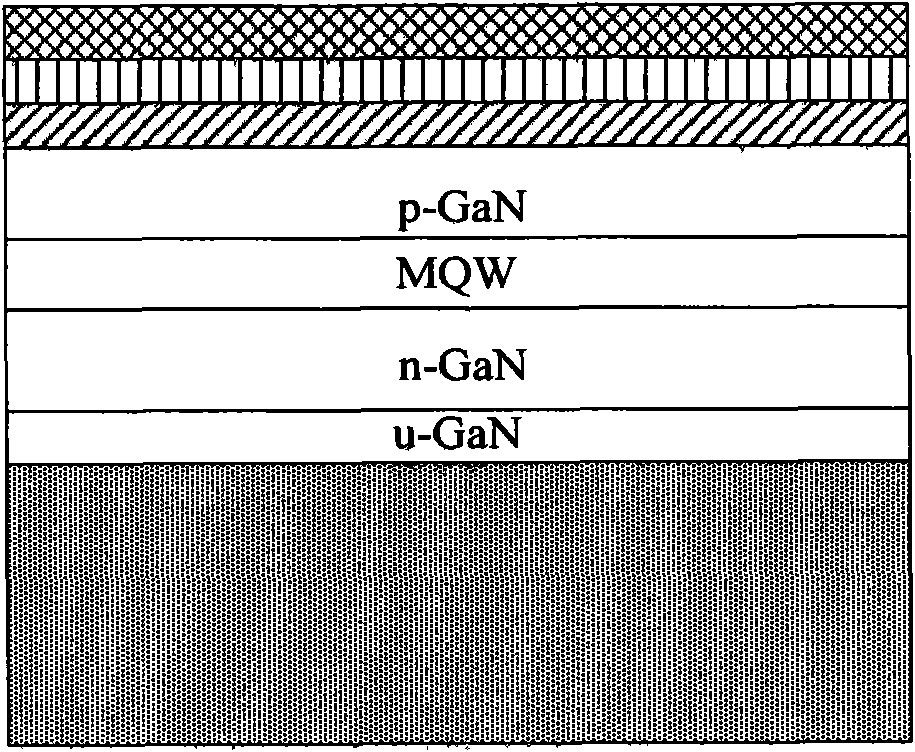
P-type epitaxial layer of LED, manufacturing method thereof and LED epitaxial wafer comprising thereof
ActiveCN104064643AImprove luminous efficiencyAvoid damageSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellProtection layer
The invention discloses a P-type epitaxial layer of an LED, a manufacturing method thereof and an LED epitaxial wafer comprising thereof. The P-type epitaxial layer comprises a quantum well protection layer which is arranged on a quantum well layer of the LED, wherein the quantum well protection layer is formed by AlGaN / InGaN superlattice; a low-temperature P-type GaN layer which is arranged on the quantum well protection layer; a low-temperature electron barrier layer which is arranged on the low-temperature P-type GaN layer and is formed by P-type AlInGaN; a high-temperature electron barrier layer which is arranged on the low-temperature electron barrier layer and is formed by P-type AlGaN / P-type InGaN superlattice; and a high-temperature P-type GaN layer which is arranged on the high-temperature electron barrier layer. The high temperature growth process of the P-type epitaxial layer causes less damage to the quantum well layer, and nonradiative recombination happening between the electrons entering the P-type epitaxial layer from the quantum well layer and holes in the P-type epitaxial layer is allowed to be reduced, thereby improving the luminous efficiency of the LED.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
Perovskite LED device based on surface ligand control and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110867532ALong luminous lifeImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive agentSurface-active agents
The invention relates to a method for preparing a perovskite LED device based on surface ligand control, including the following steps: applying an organic solution of a hole injection layer materialto the surface of a conductive substrate, and forming a hole injection layer after annealing; dissolving cesium bromide, lead bromide and phenethylamine bromide in an organic solvent under the effectof a 3-(decyl dimethyl ammonium) propane-1-sulfonic acid inner salt surfactant to obtain a perovskite precursor solution, applying the perovskite precursor solution to the surface of the hole injection layer and obtaining a perovskite film after annealing; treating the surface of the perovskite film with an alkylamine organic solution to form a light-emitting layer; and successively preparing an electron transport layer, an electron injection layer and a metal cathode electrode on the surface of the light-emitting layer. The method of the invention is simple and convenient, has a wide range ofmaterials and good repeatability, and can achieve the device performance. Through surface ligand exchange, the flatness and uniformity of the perovskite film are improved, the formation of defects iseffectively suppressed, and the overall performance of the device is significantly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for designing quantum barrier used for enhancing light emitting diode (LED) brightness
InactiveCN103346217AImprove luminous efficiencyPromote migrationSemiconductor devicesLuminous intensityContact layer
The invention discloses a method for designing a quantum barrier used for enhancing light emitting diode (LED) brightness. An epitaxial slice structure of an LED comprises a substrate layer, a low-temperature GaN buffer layer, a non-doped high-temperature GaN buffer layer, a Si doped n-type GaN layer, a luminescent layer multiple quantum well, a low-temperature p-type GaN layer, a p-type AlGaN electronic barrier layer, a high-temperature p-type GaN layer and a p-type GaN contact layer in sequence from bottom to top. The luminescent layer multiple quantum well comprises a low-temperature shallow quantum well and a low-temperature multiple quantum well luminescent layer from bottom to top, wherein the multiple quantum well luminescent layer is divided into three parts, namely a first quantum well barrier layer, a second quantum well barrier layer and a third quantum well barrier layer. The first quantum well barrier layer grows in the mode that aluminum components are not doped; the second quantum well barrier layer grows in the mode that 10% of the aluminum components are doped, and the total thickness is kept unchanged; the third quantum well barrier layer grows in the mode that 5%-8% of the aluminum components are doped, and the total thickness is also kept unchanged. By means of the method, GaN series light emitting diodes with high luminous intensity can be obtained.
Owner:合肥彩虹蓝光科技有限公司
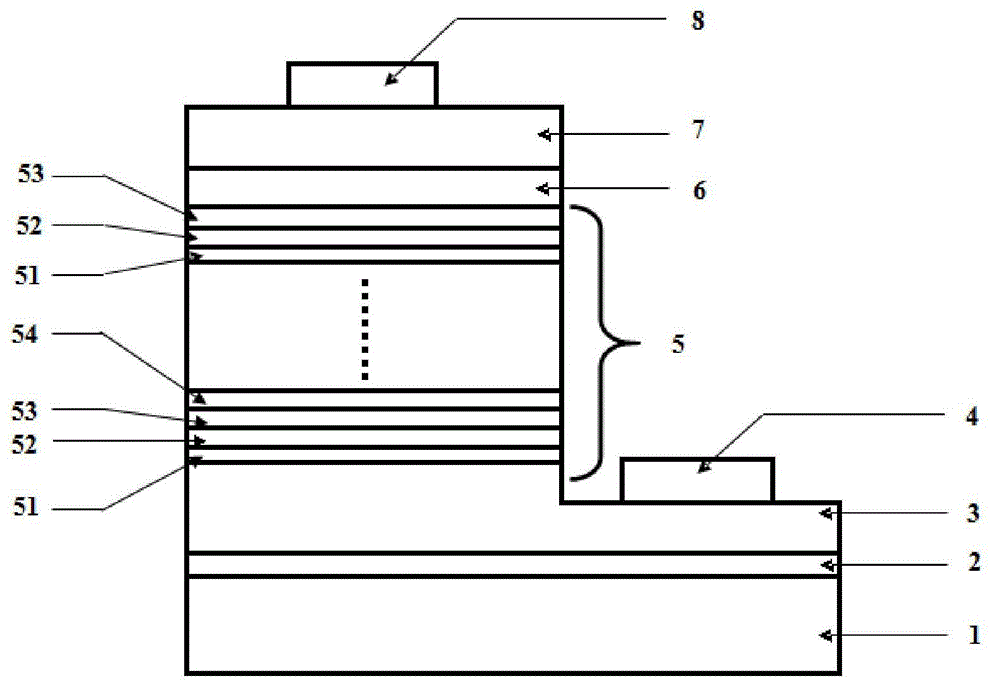
Light-emitting diode with composite polar face electron blocking layer
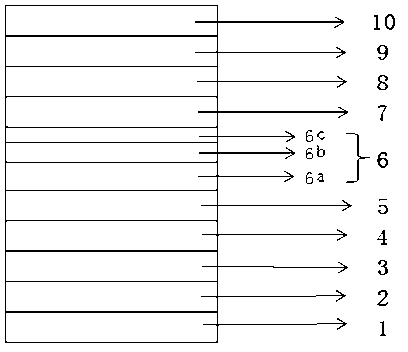
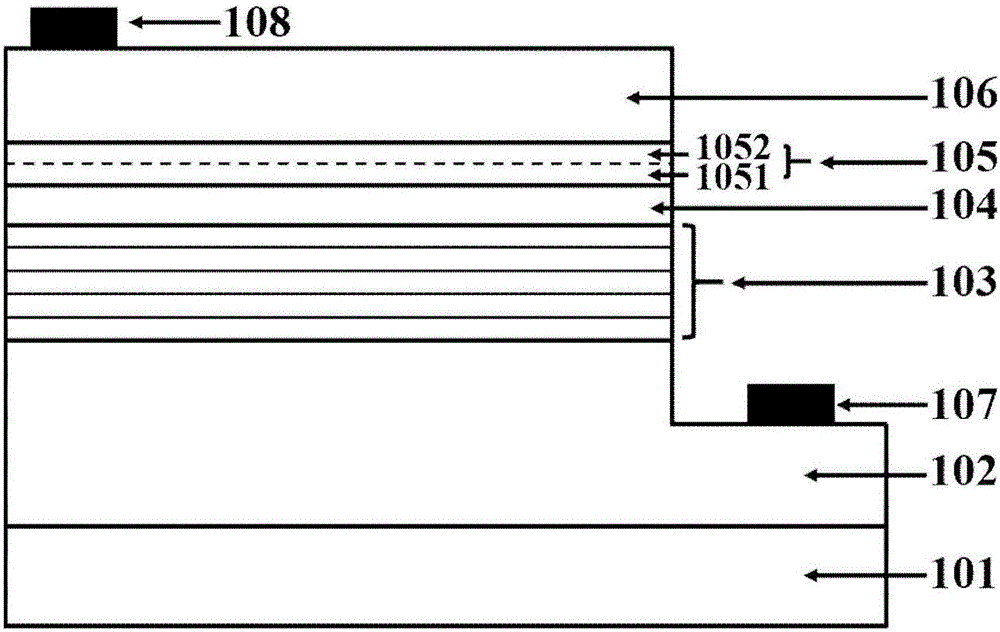
ActiveCN105870283AReduce leakage currentIncrease chanceSemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumElectron blocking layer
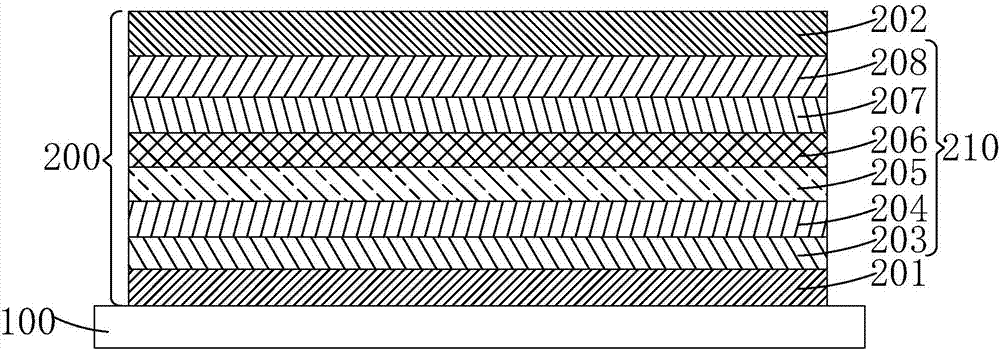
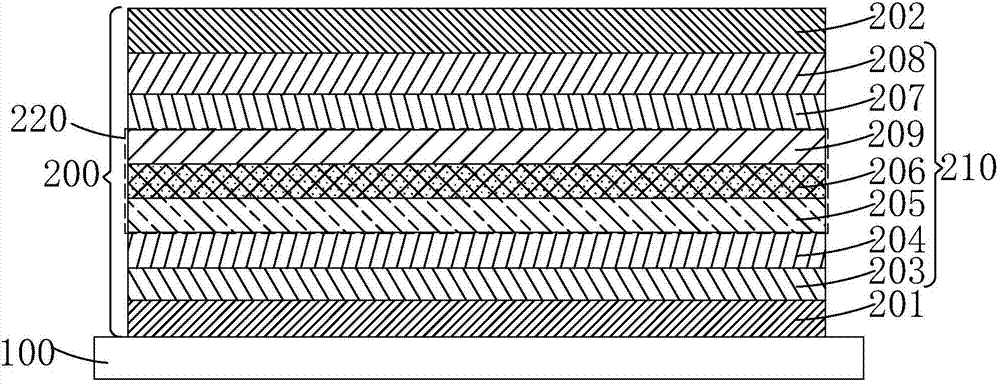
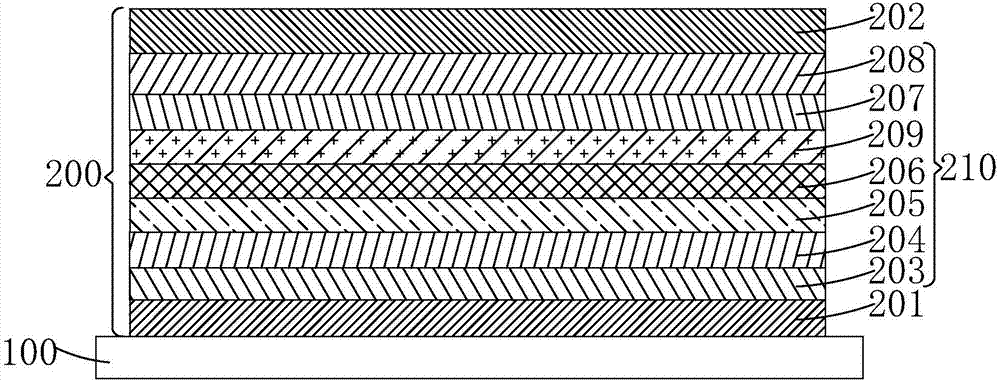
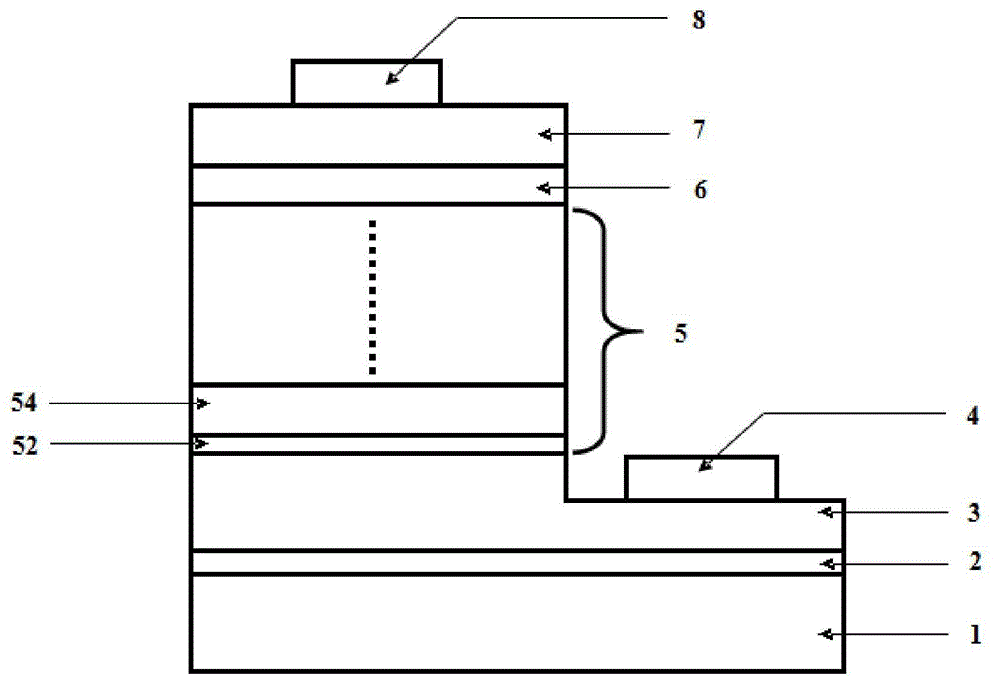
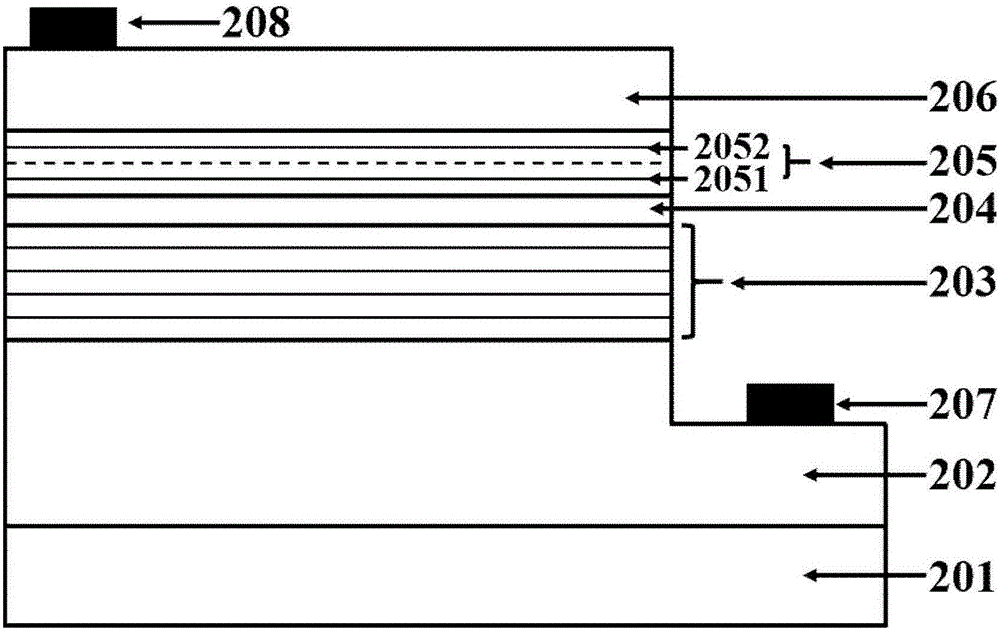
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode with a composite polar face electron blocking layer. The light-emitting diode comprises a substrate (101), a metal polar face n-type nitride layer (102), a metal polar face multiple quantum well layer (103), a metal polar face p-type nitride layer (104), a composite polar face p-type electron blocking layer (105) composed of a metal polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1051) and a nitrogen polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1052), a nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer (106), an n electrode (7) arranged on the metal polar face n-type nitride layer and a p electrode (8) arranged on the nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer, and the layers and the electrodes are arranged sequentially from bottom to top. A high electronic barrier is formed on a conduction band by the composite polar face electron blocking layer and blocks electrons from crossing a multiple quantum well active region to enter a p-type region, leakage currents can be reduced, and the probability of radiative recombination of the electrons and holes is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Organic compound containing xanthene and application thereof
ActiveCN106467526ADestroy crystallinityInhibit aggregationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesVitrificationThermal stability
The invention discloses an organic compound containing xanthene and an application thereof. A structural general formula of the organic compound is shown as a general formula (1). The vitrification temperature of the organic compound is high, the molecular thermal stability is strong, the organic compound has appropriate HOMO and LUMO energy level and high Eg, and the photoelectric property of an OLED device and life of the OLED device are effectively increased through optimization of a device structure.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Epitaxial wafer of light emitting diode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109360876AImprove compound efficiencyImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum wellElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses an epitaxial wafer of a light emitting diode and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of the light emitting diode manufacture. A combined inserting layer installed between an electron blocking layer and an InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well layer can be cooperated with the last one GaN quantum barrier layer doped with an Al element in the InGaN / GaN multi-quantumwell layer. The last one GaN quantum barrier layer doped with the Al element can play a partial effect of blocking an electron, the electron is blocked in the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well layer, andan AlN layer and an InGaN layer with higher potential barriers in the combined inserting layer can also play the effect of blocking the electron. In addition, because a magnesium element is doped in the AlN layer and the InGaN layer, the AlN layer and the InGaN layer can be used as a hole source, the electron can be blocked in the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well layer, and more holes can enter the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well layer and are combined with the electrons so as to illuminate, and combination efficiency of the electrons and holes in the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well layer is improved, so luminous efficiency of the light emitting diode is improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Organic compound based on azabenzene and application thereof in OLED
ActiveCN110229145APrevent free spinsImprove structural stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesRefractive indexHigh electron
The invention relates to an organic compound based on azabenzene and an application thereof in an OLED device. The compound has relatively high glass transition temperature and molecular thermal stability; the compound has low absorption and high refractive index in the visible light field, and light extraction efficiency of the OLED device can be effectively improved after the compound is appliedin a CPL layer of the OLED device; and the compound also has deep HOMO energy level and high electron mobility, and can be used as a hole blocking / electron transport layer material of the OLED device, transmission of holes or energy from a luminescent layer to the side of an electron layer can be effectively blocked, and thus composite efficiency of holes and electrons in the luminescent layer isimproved, and luminescent efficiency and service life of the OLED device are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Shallow quantum well growth method for increasing light emitting efficiency of GaN-based LED (Light-Emitting Diode)
InactiveCN102903808AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce defect densitySemiconductor devicesContact layerGallium nitride
The invention relates to a shallow quantum well growth method for increasing the light emitting efficiency of a GaN-based LED (Light-Emitting Diode). The epitaxial wafer structure of the LED sequentially comprises a substrate layer, a low-temperature GaN buffer layer, an undoped high-temperature GaN buffer layer, a Si doped n type GaN layer, a luminous-layer multiple-quantum well, a low-temperature p type GaN layer, a p type AlGaN electron blocking layer, a high-temperature p type GaN layer and a p type GaN contact layer from bottom to top. The luminous-layer multiple-quantum well sequentially comprises a low-temperature shallow quantum well and a low-temperature multiple-quantum well luminous layer structure from bottom to top, wherein the low-temperature shallow quantum well is composed of three parts of shallow quantum wells. According to the method, a quantum-well-structure gallium nitride base material with high crystallization quality and high luminous efficiency can be effectively obtained, and a gallium nitride system LED with high luminescent intensity is obtained.
Owner:合肥彩虹蓝光科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com