Method for removing heavy metals in soil through combination of bioleaching and Fenton reaction
A biological leaching and heavy metal technology, applied in the restoration of contaminated soil, etc., can solve the problem of high treatment costs, achieve the effect of small secondary pollution, efficient removal, and low operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
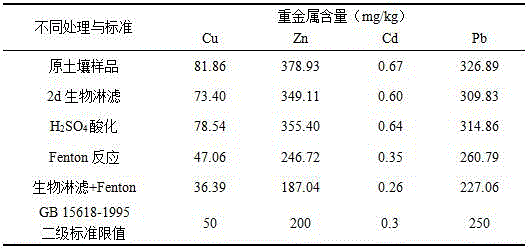
[0036] The contaminated soil samples for the test were taken from the 0-20 cm surface soil of the farmland surrounding the Fankou lead-zinc mine in Shaoguan City, Guangdong Province. Crush the large samples in the soil, place them in a cool and dry place to air-dry naturally, remove stones, rhizomes and other sundries, and pass through a 2mm sieve for later use. The main physical and chemical properties of the soil were tested as follows: pH 5.80±0.04, organic matter content (10.94±0.71)%, heavy metal Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd content were (81.86±3.63), (378.93±10.87), (326.89±11.15 ) and (0.67±0.05) mg·kg -1 .
[0037] Thiobacillus ferrooxidans isolated from sludge Thiobacillus ferrooxidans LX 5 , the strain was preserved and donated by the College of Resources and Environment, Nanjing Agricultural University, CGMCC NO.0727 (see invention patent ZL02112924.X). will LX 5 The strain was inoculated into the test soil solution with a solid content of 1% sterilized by radiation, and...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The preparation of the test soil sample and the inoculum of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was the same as in Example 1.
[0041] After sterilizing the test soil by radiation, prepare a soil solution with a solid content of 2% with sterile distilled water; add FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O as a substrate to Fe in soil solution 2+ The content reaches 4g•L -1 , the inoculum of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans whose inoculation quality is 10% of the mass of soil solution, at 150r·min -1 , Shaking culture at 30°C. When the pH of the solution dropped to 2.5±0.1, add H 2 o 2 up to 9g•L -1 After the final concentration was subjected to Fenton reaction for 1 day, samples were taken to detect and analyze the dissolution efficiency of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb. After detection and analysis, the dissolution rates of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb were 60.3%, 52.7%, 65.9% and 30.7%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation of the test soil sample and the inoculum of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was the same as in Example 1.
[0044] After sterilizing the test soil by radiation, prepare a soil solution with a solid content of 1% with sterile distilled water; add FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O as a substrate to Fe in soil solution 2+ The content reaches 3g•L -1 , the inoculum of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans whose inoculation quality is 10% of the mass of soil solution, at 150r·min -1 , Shaking culture at 30°C. When the pH of the solution drops to 3.0±0.1, add H 2 o 2 up to 5g•L -1 After the final concentration was subjected to Fenton reaction for 1 day, samples were taken to detect and analyze the dissolution efficiency of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb. After detection and analysis, the dissolution rates of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb were 64.5%, 54.1%, 66.5% and 29.3%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com