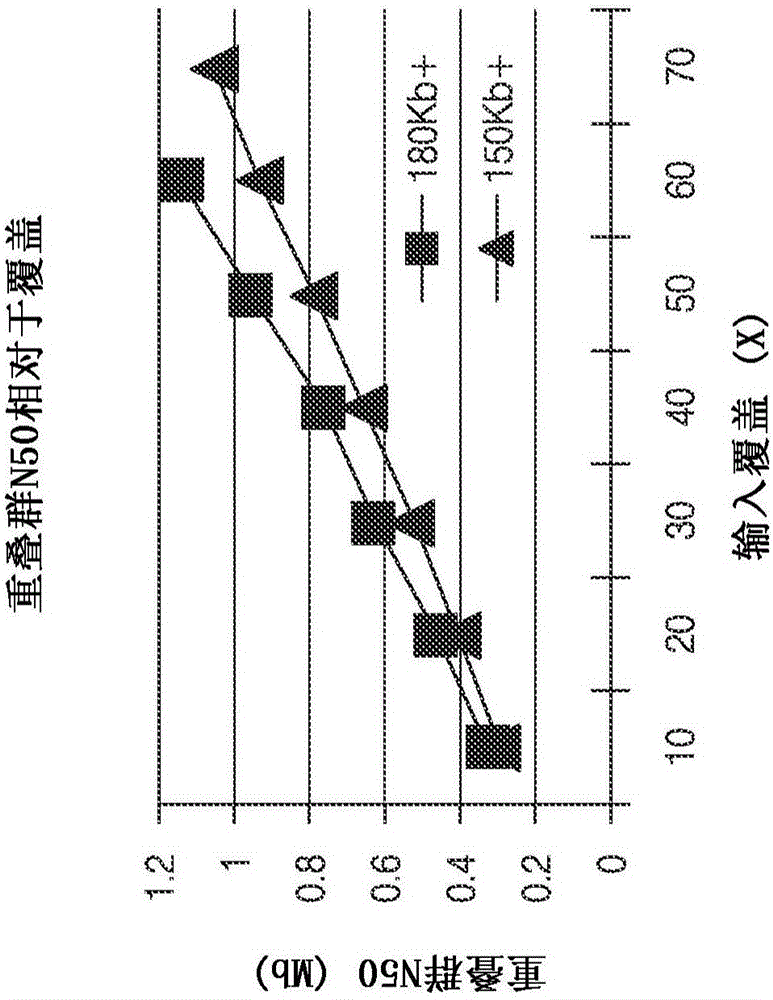
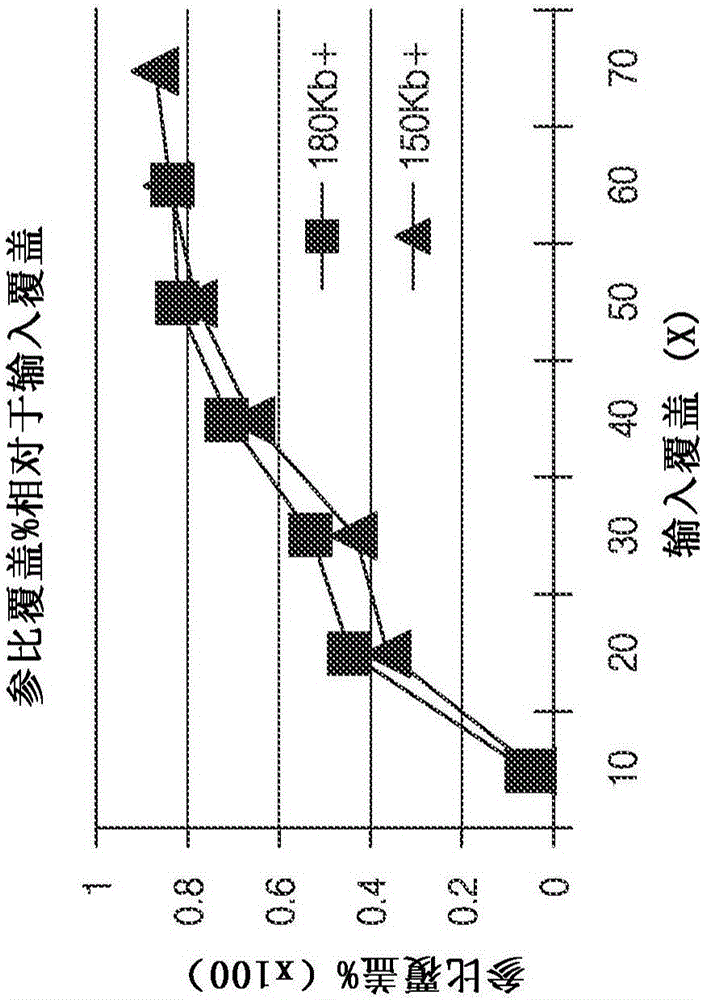
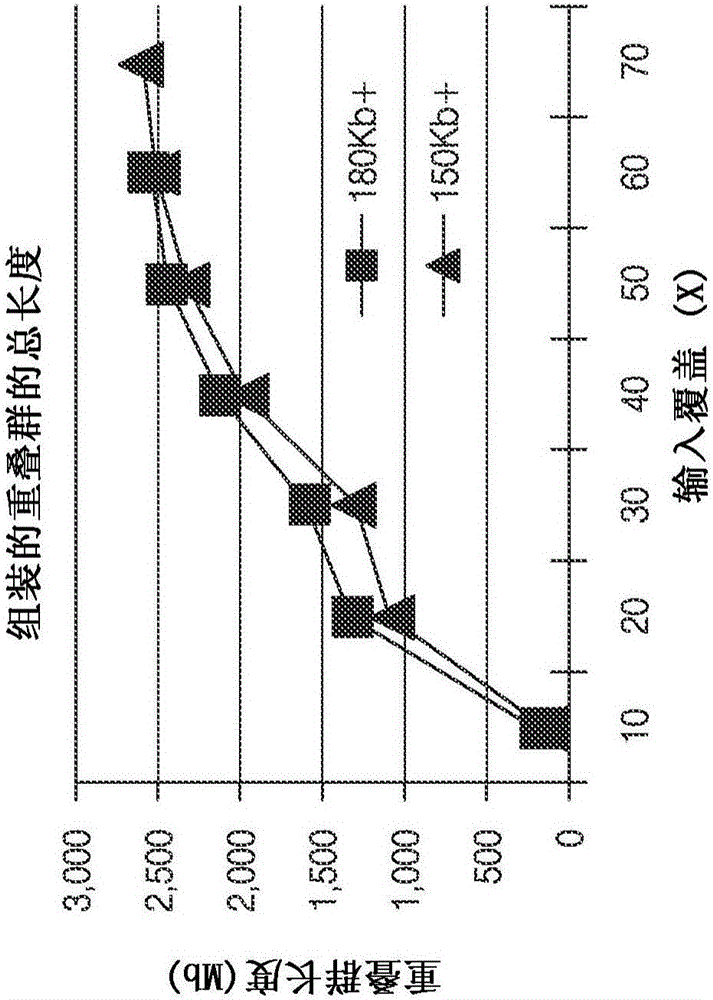
Improved methods of determining nucleic acid structural information
A technology for nucleic acid and nucleic acid molecules, applied in the field of nano, genome assembly and sample analysis based on single-molecule visualization and analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Example 1-Labeling with fluorescent SAM
[0131] The human DNA containing megabases is treated with a methyltransferase (MTase) selected from Table 1 in the presence of a modified S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) containing a fluorophore or multiple fluorophores. After covalently transferring the fluorophore-SAM complex to the methyltransferase target site, the labeled DNA was stained with yoyo I for processing on the Irys system (BioNanoGenomics). Briefly, the DNA is linearized in the overall parallel nanochannel to achieve ~80% stretch, excited with a laser suitable for the detection of the skeleton and the marker, and optical imaging is performed to show the pattern of the marker on the DNA molecule . Adjust MTase labeling conditions to achieve reference genome> 40% of the drawing and <20% error rate. Query molecules ≥ 150Kb to overlap and map to generate a genome map.
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2-Mark with click (alkynes-azide-Cu-ligand)
[0133] The human DNA containing megabases was treated with a methyltransferase selected from Table 1 in the presence of a modified S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) containing an alkyne transfer moiety. After the alkyne group is covalently transferred to the methyltransferase target site, a copper-catalyzed coupling reaction is used to fluorescently label the alkyne label site in the presence of a copper coordination ligand (such as BTTAA, BTTES), To prevent copper-induced DNA fragmentation. As described in Example 1, the labeled DNA was stained with yoyo I for processing on the Irys system.
Embodiment 3
[0134] Example 3-Mark with a click (azide-DBCO)
[0135] The human DNA containing megabases was treated with a methyltransferase selected from Table 1 in the presence of a modified S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) containing an azide transfer moiety. After covalently transferring the azide group to the methyltransferase target site, a DBCO-fluorophore conjugate is used to fluorescently label the azide labeling site (copper-free click chemistry). As described in Example 1, the labeled DNA was stained with yoyo I for processing on the Irys system. Examples of DBCO-fluorophore conjugates include coupling DBCO directly to a fluorophore, or coupling DBCO to a moiety that has been coupled to multiple fluorophores (for example, a DBCO oligomer containing multiple fluorophores) Or dendrimer).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com