Double-layer conductive thin film-based transparent broadband electromagnetic wave absorber
A technology of conductive film and wave absorber, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, antennas, etc., can solve the problem of narrow application range of wave absorber, and achieve the effect of ensuring broadband wave absorption effect, expanding application range, and high mechanical hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
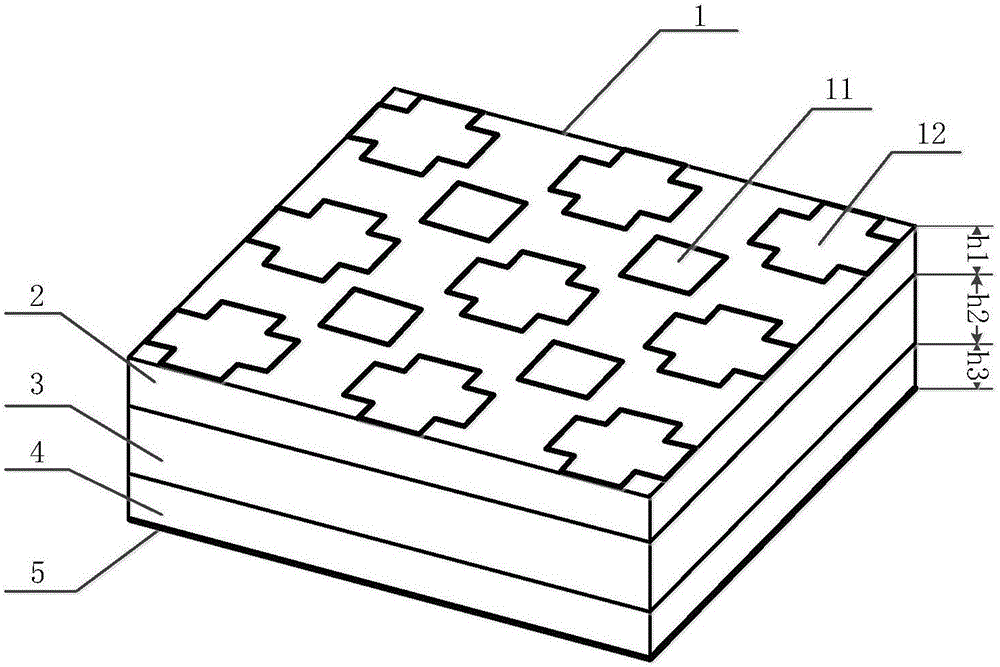
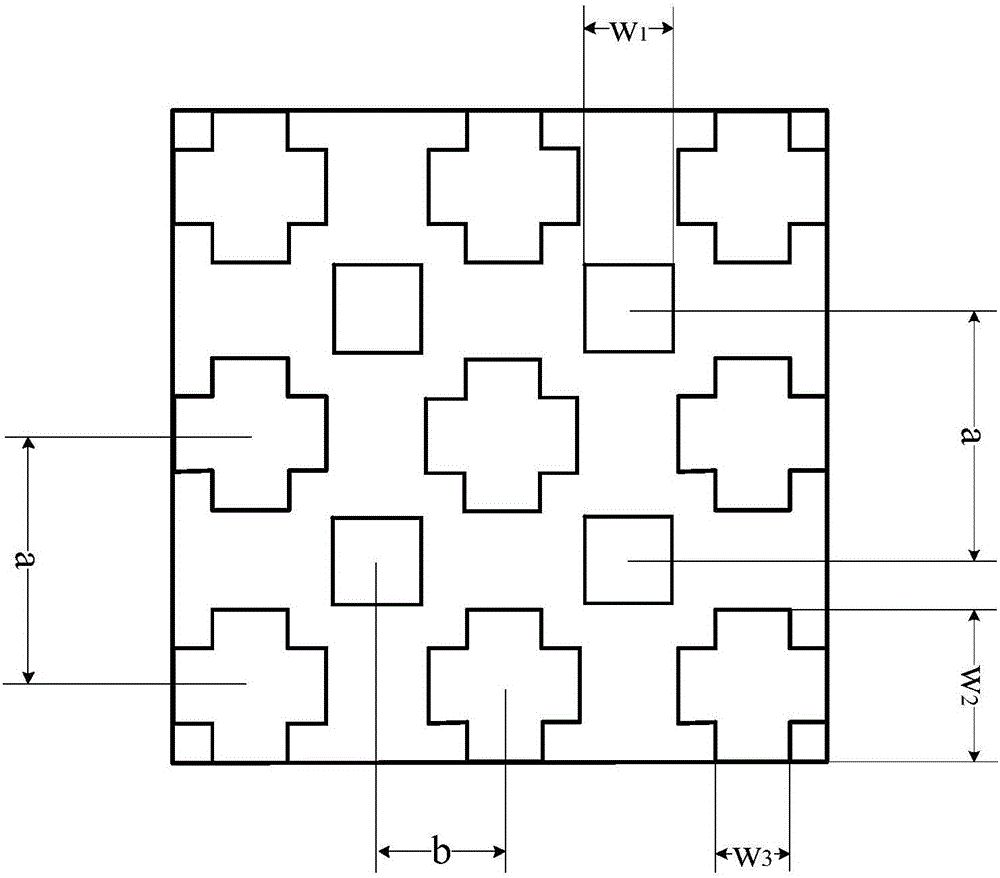
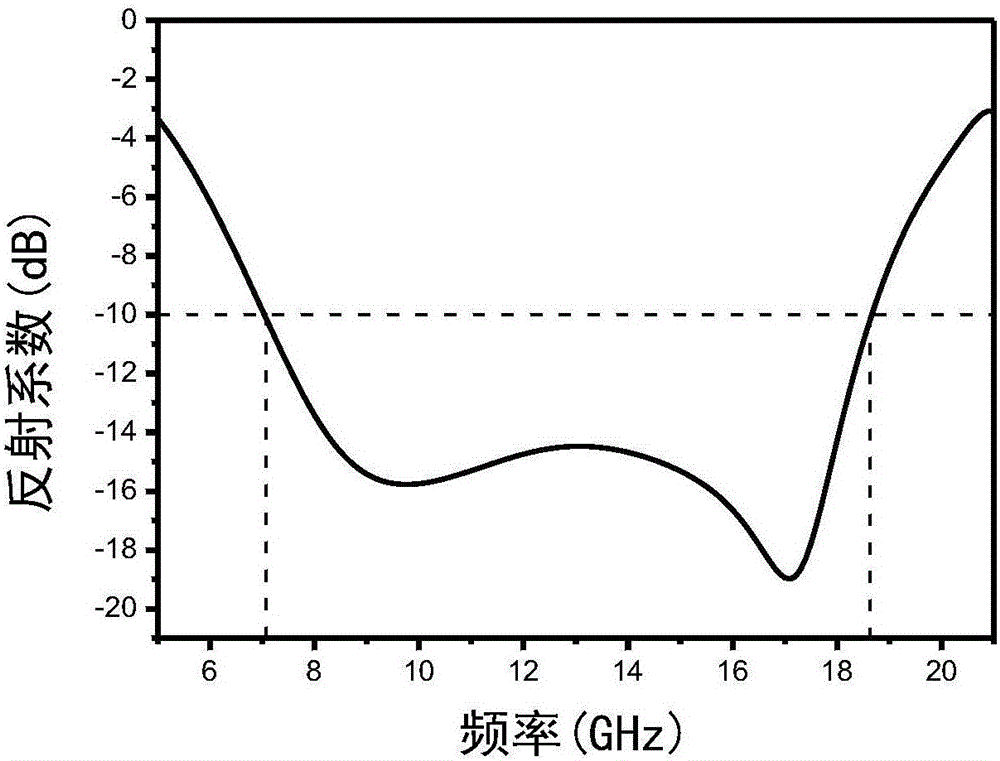
[0024] refer to figure 1 , including a conductive film 1, a first dielectric layer 2, a second dielectric layer 3, a third dielectric layer 4 and a bottom plate 5, wherein the three dielectric layers 2, 3 and 4 are arranged from top to bottom to form a stacked dielectric layer The bottom plate 5 is printed on the lower surface of the third dielectric layer 4, and the conductive film 1 is printed on the upper surface of the first dielectric layer 2, and the conductive film 1 is an array composed of m×n square transparent conductive films 11 and (m +1)×(n+1) arrays composed of cross-shaped transparent conductive films 12 are composited. In this embodiment, an array composed of 2×2 square transparent conductive films 11 and 3×3 cross-shaped transparent conductive films are used An array composed of 12, its specific structure is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0025] Both the first dielectric layer 2 and the third dielectric layer 4 adopt a relative permittivity ε r1 2.7 square p...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2 has the same structure as Embodiment 1, and the following parameters have been adjusted:
[0032] Both the first dielectric layer 2 and the third dielectric layer 4 adopt a relative permittivity ε r1 A square polymethacrylate (PMMA) dielectric plate of 4, wherein the thickness h of the first dielectric layer 2 1 =1mm, the thickness h of the third dielectric layer 4 3 =1mm; the thickness h of the second dielectric layer 3 is selected 2 2mm, relative permittivity ε r2 3.9 square quartz glass dielectric plate; square conductive film 11 and cross-shaped conductive film 12 adopt square resistance R S1 The graphene film is 100Ω / sq, and the bottom layer 5 adopts square resistance R S It is a square indium tin oxide film of 10Ω / sq, and the side length of the square conductive film 11 is W 1 is 9mm.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The structure of embodiment 3 is identical with the structure of embodiment 1, and following parameter has been adjusted:
[0035] Both the first dielectric layer 2 and the third dielectric layer 4 adopt a relative permittivity ε r1 is a square polymethacrylate (PMMA) dielectric plate of 2, wherein the thickness h of the first dielectric layer 2 1 =2.5mm, the thickness h of the third dielectric layer 4 3 =2.5mm; the thickness h of the second dielectric layer 3 is selected 2 2.5mm, relative permittivity ε r2 2.7 square polycarbonate dielectric plate; square conductive film 11 and cross-shaped conductive film 12 adopt square resistance R S1 It is a graphene film of 60Ω / sq, and the bottom plate 5 adopts square resistance R S A square indium tin oxide film of 5Ω / sq.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com