Production method of forage-use mannose oligomer
A technology of a mannose oligosaccharide and a production method is applied in the field of production of mannose oligosaccharides for feed, and can solve the problems of difficulty in releasing mannose, waste, restricting the utilization of raw materials, etc. The effect of improving the comprehensive utilization value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
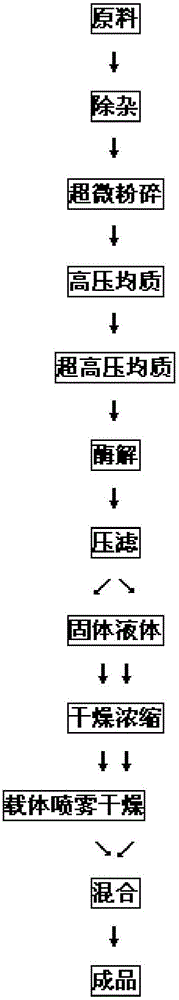
[0023] For the processing of palm kernel meal, see the flow chart of the steps figure 1 .
[0024] 1) Take 1kg of palm kernel meal and pass through sieving, winnowing, and permanent magnetization, remove the impurities therein, and pulverize it to about 125 mesh through an ultrafine pulverizer.
[0025] 2) After adding 5 times of water to the ultra-finely pulverized palm kernel meal, stir evenly, enter the high-pressure homogenizer, and process it at 1000bar,
[0026] 3) Add 1 times water to the material after high-pressure homogenization, stir evenly, enter the ultra-high pressure homogenizer, and process it at 1800bar,
[0027] 4) Heating the two homogenized materials to 63°C, adjusting the pH to 3.8 with 10% calcium hydroxide solution or 10% sulfuric acid solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing at constant temperature for 20 hours under stirring.
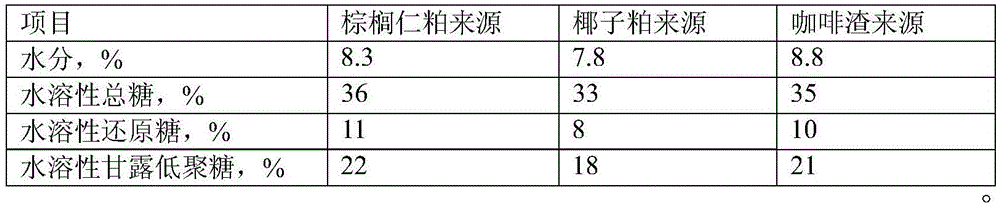
[0028] 5) After enzymatic hydrolysis, solid-liquid separation was performed, and the solid was directly dried to obtain a dry...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Processing of coconut meal
[0033] 1) Take 500g of coconut meal and pass through sieving, winnowing, and passing through permanent magnetism, remove impurities therein, and pulverize it to about 150 mesh through an ultrafine pulverizer.
[0034] 2) After adding 4 times of water to the ultra-finely pulverized coconut meal, stir evenly, enter the high-pressure homogenizer, and process at 1000bar.
[0035] 3) Add 1 times water to the material after high-pressure homogenization, stir evenly, enter the ultra-high pressure homogenizer, and process at 1800bar.
[0036] 4) Heating the two homogeneously treated materials to 60°C, adjusting the pH to 3.5 with 10% calcium hydroxide solution or 10% sulfuric acid solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing at constant temperature for 20 hours under stirring.
[0037] 5) After the enzymatic hydrolysis, solid-liquid separation was performed, and the solid was directly dried to obtain a dry residue weighing 0.34 kg.
[0038] 6) After th...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Processing of coffee grounds
[0042] 1) Take 1kg of coffee grounds and pass through sieving, winnowing, and permanent magnetization to remove impurities and crush them to about 100 meshes with a superfine pulverizer.
[0043] 2) After adding 5 times of water to the ultra-finely pulverized coffee grounds, stir evenly, enter the high-pressure homogenizer, and process at 1000bar.
[0044] 3) Add 1 times water to the material after high-pressure homogenization, stir evenly, enter the ultra-high pressure homogenizer, and process at 1800bar.
[0045] 4) Heating the two homogeneously treated materials to 65° C., adjusting the pH to 4 with 10% calcium hydroxide solution or 10% sulfuric acid solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing at constant temperature for 20 hours under stirring.
[0046] 5) After the enzymatic hydrolysis, solid-liquid separation was performed, and the solid was dried directly to obtain a dry residue weighing 0.75 kg.
[0047] 6) After the solid-liquid sep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com