Method of using plasma transmission spectrograph to detect potassium oxide in compound fertilizer
A compound fertilizer and spectrometer technology, which is applied in the field of determination of potassium oxide in compound fertilizer by ion emission spectrometer, can solve problems such as interference in the determination, and achieve the effects of short time consumption, improved analysis efficiency and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
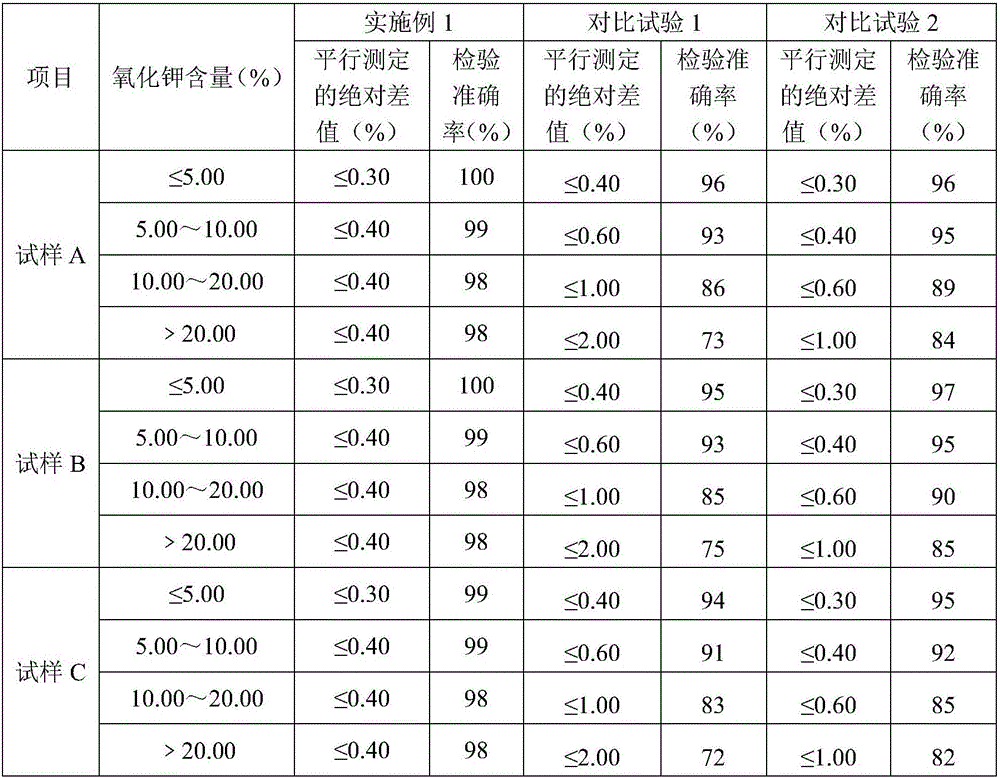
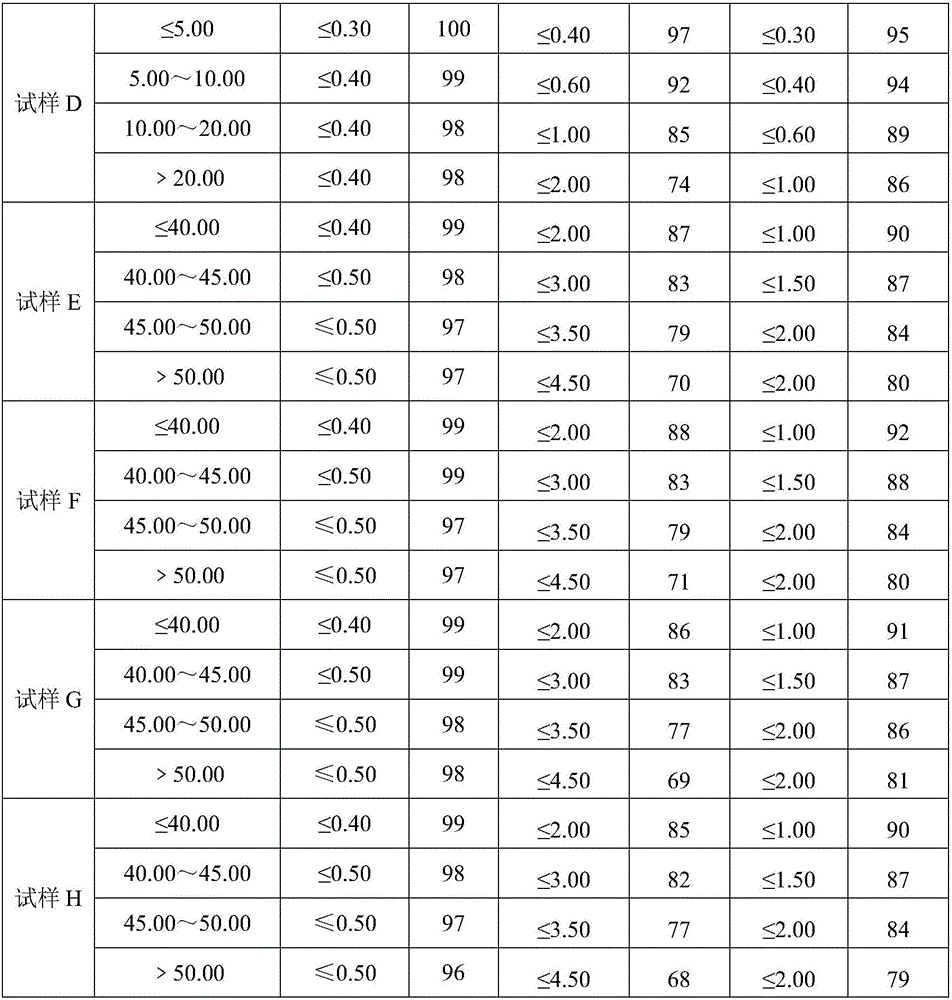
[0027] In order to enable those skilled in the art to understand the method of the present invention more clearly, the applicant has further described it experimentally in specific embodiments.
[0028] A plasma emission spectrometer method for determining potassium oxide in compound fertilizers includes the following steps:
[0029] 1) Sample processing
[0030] Divide the sample to 40-60g with a shrinking device or quartering method, crush it with a universal crusher, and pass through a 0.4mm test sieve for analysis; the sample is made of monoammonium phosphate (diammonium phosphate), nitric acid Analytical sample prepared from chlorine-based compound fertilizer produced with ammonium and potassium chloride as raw materials, named as sample A; sulfur-based compound fertilizer produced with monoammonium phosphate (diammonium phosphate), ammonium nitrate, and potassium sulfate as raw materials The prepared analysis sample is named sample B; the analysis sample prepared from the comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com