A single-stranded DNA aptamer that specifically binds (1,3)-β-d-glucan in Candida albicans
A technology of Candida albicans and dextran, which is applied in the fields of molecular microbiology and infection immunity, can solve the problems of difficult antibody preparation and detection, and achieve good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: the selection of material
[0033] Reagents and instruments:
[0034] Candida albicans ATCC10231 was purchased from Wuhan University Culture Collection Center; Candida albicans culture medium was purchased from Qingdao Haibo Biotechnology Company; pUC19 plasmid and DH5α strains were frozen in our laboratory; main reagents for cloning construction BamH I, EcoR I. T4 DNA ligase was purchased from Fermentas; protein marker (Cat: SM1861) was purchased from Baoke Biological Company; DNA marker was purchased from Dongsheng Biological Company; AxyPrep plasmid DNA mini kit was purchased from AXYGEN Company; DNA gel recovery reagent The box was purchased from AxyPrep Company; PCR mix was purchased from TIANGEN Company; wavelength scanner (Beckman-Coulter); nucleic acid protein detector (German EPPENDORF Company); ultraviolet transmission instrument (Bioimaging System U.S. UVP Company); desktop centrifuge, PCR instrument (EPPENDORF, Germany); single-stranded DNA li...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: extraction method
[0040] Extraction and identification of (1,3)-β-D-glucan:
[0041] Collect the cells of Candida albicans on the solid medium, add a small amount of PBS to wash, then centrifuge and freeze-dry, take 5 grams of dried cells and add 100mL of 1M sodium hydroxide to resuspend and react in a water bath at 90°C for 3 hours; after centrifugation, wash the precipitate with pure water 3 times, and then treated with 4% acetic acid solution at 37 ° C for 3 hours, after centrifugation, the precipitate was washed 3 times with pure water, and then washed 3 times with absolute ethanol, dehydrated with ether, and dried with nitrogen to obtain the product. After identification, it was stored frozen for later use. Use (1,3)-β-glucanase to enzymatically hydrolyze it to increase its water solubility, and cut the gel to recover water-soluble (1,3)-β-D-glucan with a molecular weight of about 1.4kD and a low degree of polymerization Sugars as screening target...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Results
[0051] Extraction, purification and identification of (1,3)-β-D-glucan:
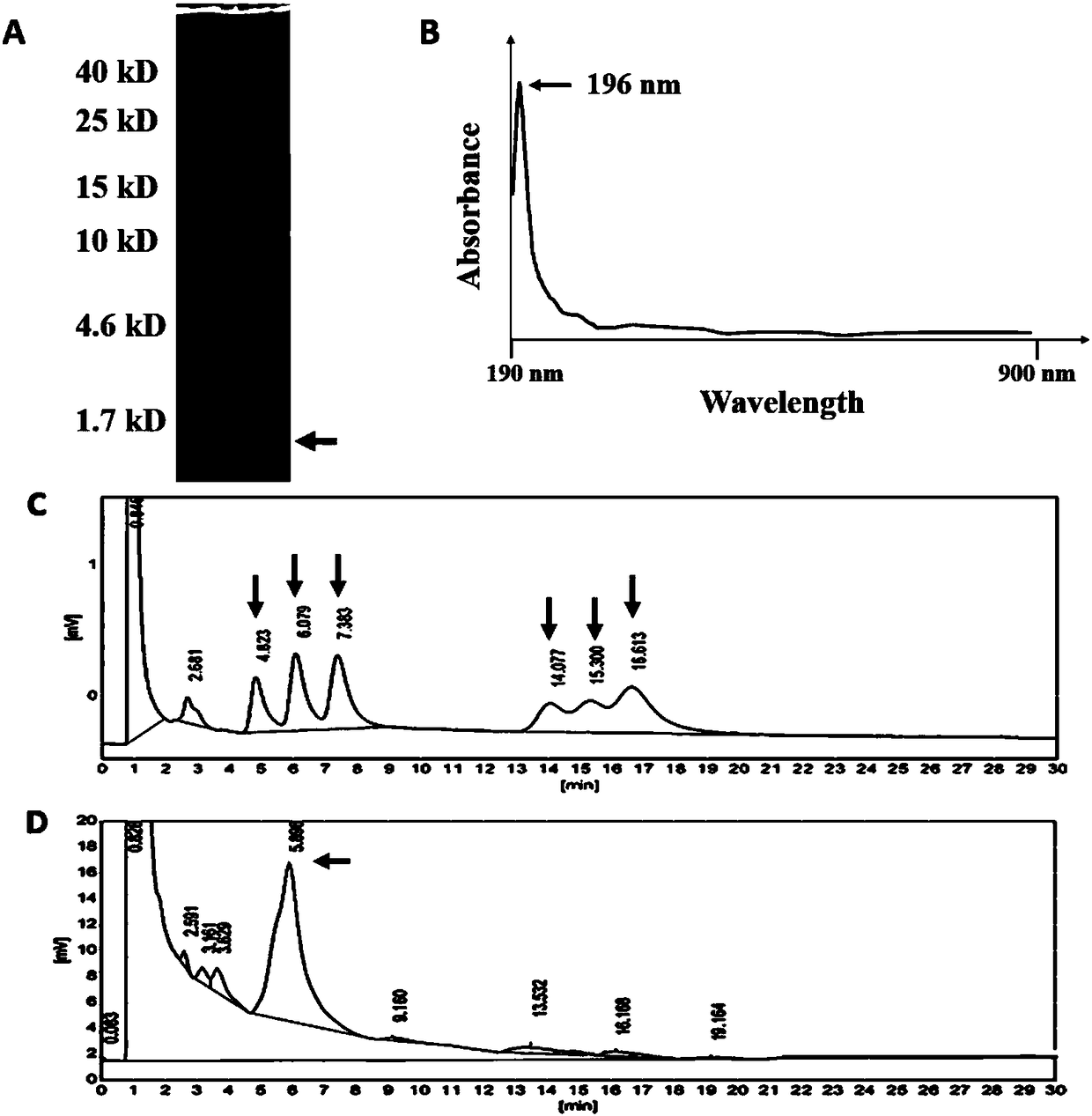
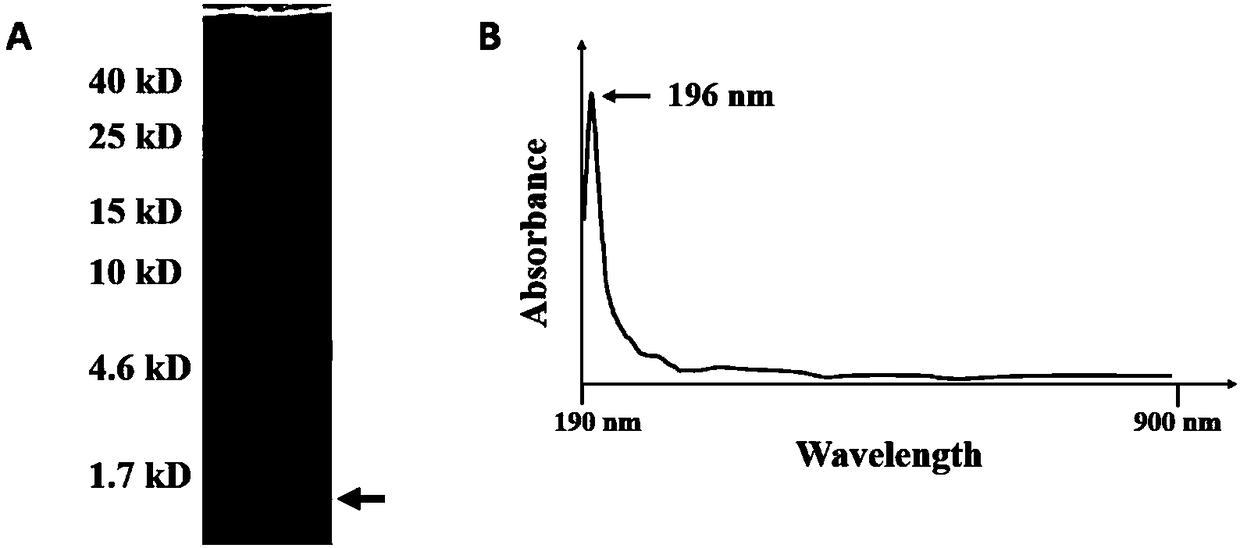
[0052] Extract (1,3)-β-D-glucan from Candida albicans, treat the supernatant with (1,3)-β-D-glucanase, perform SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and stain with glycogen , found to be mainly concentrated in three areas, figure 1 As shown in A, the arrows indicate the target substances of this study; this test mainly recovers (1,3)-β-D-glucan with a molecular weight of less than 1.7kD through gel cutting as the screening target; the recovered yield is low The degree of polymerization (1,3)-β-D-glucan was scanned at a continuous wavelength from 190nm to 900nm, and there was an obvious absorption peak at 196nm, but no obvious absorption peak at 260nm and 280nm, suggesting that the extracted substance was relatively pure carbohydrates, such as figure 1 As shown in B, the arrow shows the highest absorption peak at 196nm; figure 1 The arrows in C indicate from left to right: standard produ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com