Thin-film device based on GeSbTe phase-change material
A phase change material and thin film device technology, applied in the field of phase change storage, can solve the problems of poor thermal stability, poor crystallization speed, and short data storage life, improve thermal stability, avoid quality defects, and improve thermal stability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
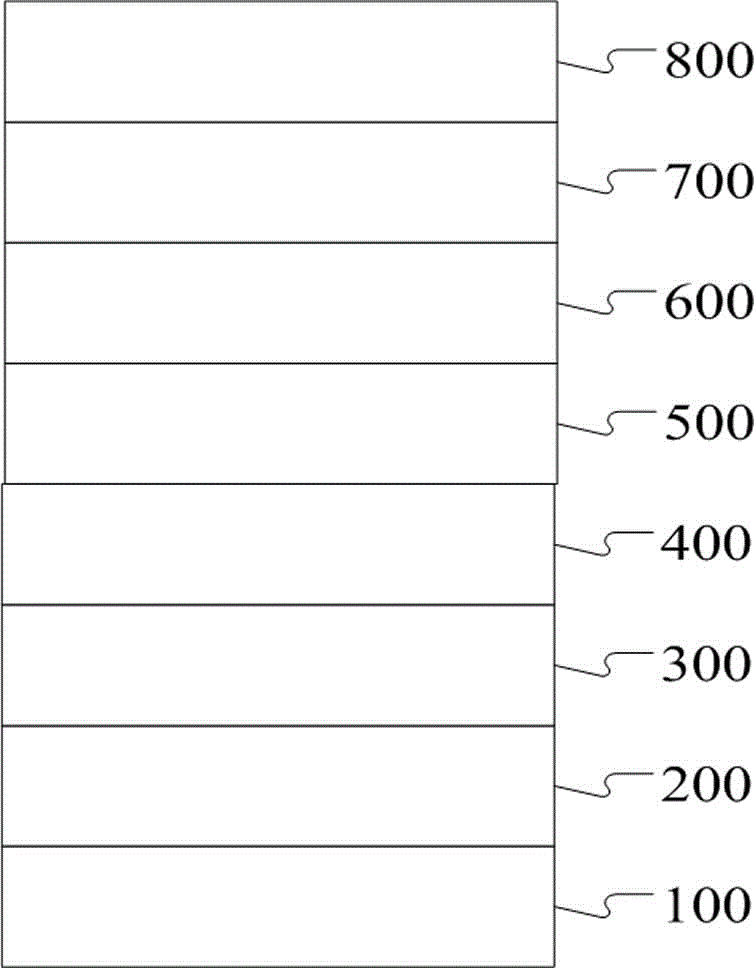
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a thin film device based on a GeSbTe phase change material comprising a substrate layer 100, a lower electrode layer 200, a first GeSbTe material layer 300, a molybdenum disulfide layer 400, a second GeSbTe material layer 500, and graphene Layer 600, upper electrode layer 700 and protective layer 800, the lower electrode layer 200, the first GeSbTe material layer 300, molybdenum disulfide layer 400, the second GeSbTe material layer 500, graphene layer 600, upper electrode layer 700, protective Layers 800 are sequentially deposited and superimposed on the substrate layer 100, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 is an ion-doped GeSbTe phase change material layer, and the second GeSbTe material layer 500 is a pure phase GeSbTe phase change material.
[0032] In this embodiment, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 is Ti 3+ Doped GeSbTe phase change material; the substrate layer 100 is a glass sheet; the protective la...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a thin film device based on a GeSbTe phase change material comprising a substrate layer 100, a lower electrode layer 200, a first GeSbTe material layer 300, a molybdenum disulfide layer 400, a second GeSbTe material layer 500, and graphene Layer 600, upper electrode layer 700 and protective layer 800, the lower electrode layer 200, the first GeSbTe material layer 300, molybdenum disulfide layer 400, the second GeSbTe material layer 500, graphene layer 600, upper electrode layer 700, protective Layers 800 are sequentially deposited and superimposed on the substrate layer 100, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 is an ion-doped GeSbTe phase change material layer, and the second GeSbTe material layer 500 is a pure phase GeSbTe phase change material.
[0036] In this embodiment, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 is Ni 2+ Doped GeSbTe phase change material; the substrate layer 100 is a silicon wafer; the protectiv...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a thin film device based on a GeSbTe phase change material comprising a substrate layer 100, a lower electrode layer 200, a first GeSbTe material layer 300, a molybdenum disulfide layer 400, a second GeSbTe material layer 500, and graphene Layer 600, upper electrode layer 700 and protective layer 800, the lower electrode layer 200, the first GeSbTe material layer 300, molybdenum disulfide layer 400, the second GeSbTe material layer 500, graphene layer 600, upper electrode layer 700, protective Layers 800 are sequentially deposited and superimposed on the substrate layer 100, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 is an ion-doped GeSbTe phase change material layer, and the second GeSbTe material layer 500 is a pure phase GeSbTe phase change material.
[0040] In this embodiment, the first GeSbTe material layer 300 includes Al 3+ Doped GeSbTe phase change material; the substrate layer 100 is a carbonate sheet; the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com