Method for removing lead and cadmium in sunflower seed protein
A sunflower seed and protein technology, applied in plant protein processing, food science, etc., can solve problems such as pollution, heavy metal enrichment, food safety impact, etc., and achieve high economic benefits, mild operating conditions, and high safety effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) Take 100 kg of sunflower seed protein powder, add 980 kg of drinking water, and mix well; (2) Adsorption reaction: Slowly add 3.0 mol / L sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the slurry to 9.6. After the protein is completely dissolved, add 3.2 Kilograms of insoluble dietary fiber (the mass ratio of cellulose and lignin is 3:2, and the average particle size is 980 mesh), mixed well, kept at 50°C for 4.3 hours, during which the stirring speed was 4000 rpm; (3 ) Solid-liquid separation: carry out solid-liquid separation, remove insoluble solids, and replace chelation with the protein slurry; (4) replace chelation: add 320 grams of zinc gluconate to the sunflower seed protein slurry, stir for 30 minutes at 45 ° C, and the stirring speed is 3500 rpm; (5) pH adjustment: adjust the pH of the sunflower protein slurry to 6.5 within 10 minutes; (6) Sterilization, dehydration and drying: the slurry is sterilized, then dehydrated and dried to obtain sunflower protein product.
Embodiment 2
[0019] (1) Take 100 kg of sunflower seed protein powder, add 980 kg of drinking water, and mix well; (2) Adsorption reaction: Slowly add 3.0 mol / L sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the slurry to 9.6. After the protein is completely dissolved, add 3.2 Kilograms of insoluble dietary fiber (the mass ratio of cellulose and lignin is 3:2, and the average particle size is 980 mesh), mixed well, kept at 50°C for 4.3 hours, during which the stirring speed was 4000 rpm; (3 ) solid-liquid separation: perform solid-liquid separation to remove insoluble solids; (4) pH adjustment: adjust the pH of the sunflower seed protein slurry to 6.5 within 10 minutes; (5) sterilization, dehydration and drying: the slurry is sterilized, Then it is dehydrated and dried to obtain the sunflower seed protein product.
Embodiment 3
[0021] (1) Take 100 kg of sunflower seed protein powder, add 980 kg of drinking water, and mix well; (2) Adsorption reaction: Slowly add 3.0 mol / L sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the slurry to 9.6. Keep at ℃ for 4.3 hours, stirring continuously during the period, the stirring speed is 4000 rpm; (3) pH adjustment: adjust the pH of the sunflower seed protein slurry to 6.5 within 10 minutes; (4) Sterilization, dehydration and drying: the slurry is carried out Sterilize, then dehydrate and dry to obtain sunflower seed protein products.
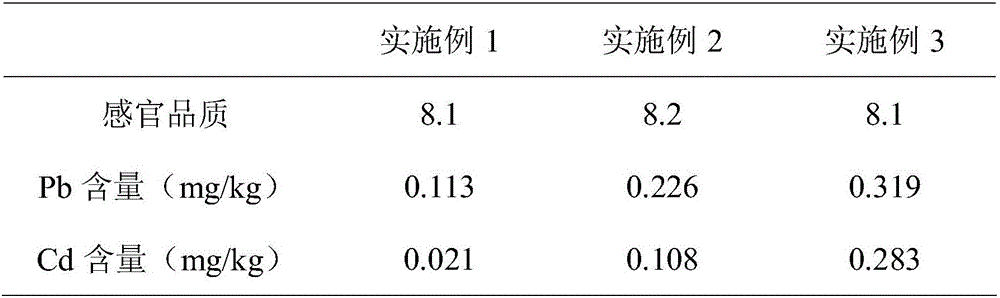
[0022] Effect analysis of different embodiments:
[0023]
[0024] Note: The higher the score of sensory quality, the better the taste
[0025] Compared with Examples 2 and 3, the contents of lead and cadmium in Example 1 processed by the present invention were reduced to 0.113 mg / kg and 0.021 mg / kg respectively; unanimous.
[0026] After the present invention adopts insoluble dietary fiber with a particle diameter of 980 meshes for ads...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com