Actinoplanes spp. genetic manipulation system
A kind of acarbose, genetic manipulation technology, applied in the field of genetic manipulation system, can solve the problems of research limitation, lack of genetic manipulation system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
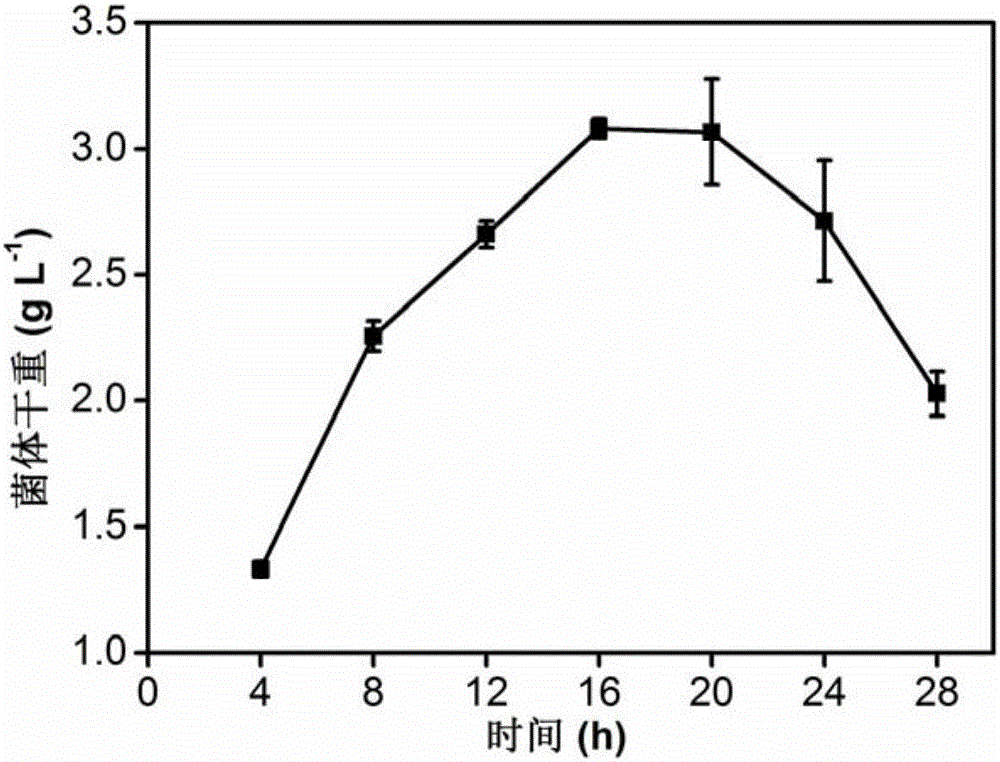
[0046] The establishment and optimization of embodiment 1 mycelia conjugation transfer system
[0047] A. Antibiotic susceptibility analysis
[0048] After activating the three strains of acarbose-producing bacteria Actinoplanes sp.SE50, SE50 / 110 and HDC preserved in the laboratory, take fresh mycelia and streak them on a plate containing different antibiotics, culture them at 30°C for 3-5 days, and observe the bacteria of growth. The results are shown in Table 1. Actinoplanes spp. is insensitive to thiostrepton (Thio), spectinomycin (Spec) and trimethoprim (TMP), but to apramycin (Apr), kanamycin (Kan), chloramphenicol Sensitivity to hormone (Cml), streptomycin (Str) and nabumexate.
[0049] Table 1 Sensitivity analysis of Actinoplanes sp. to commonly used antibiotics
[0050]
[0051] Note: "+" means sensitive; "-" means insensitive;
[0052] B. Culture of mycelium
[0053] Streak the hyphae preserved in glycerol into the activation medium, after culturing for 48 ho...
Embodiment 2
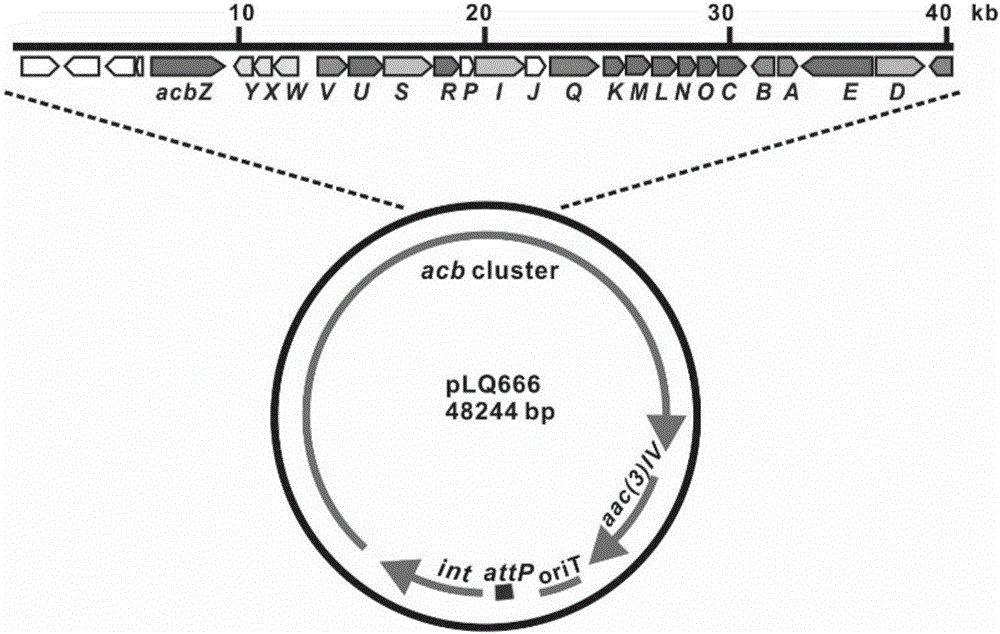
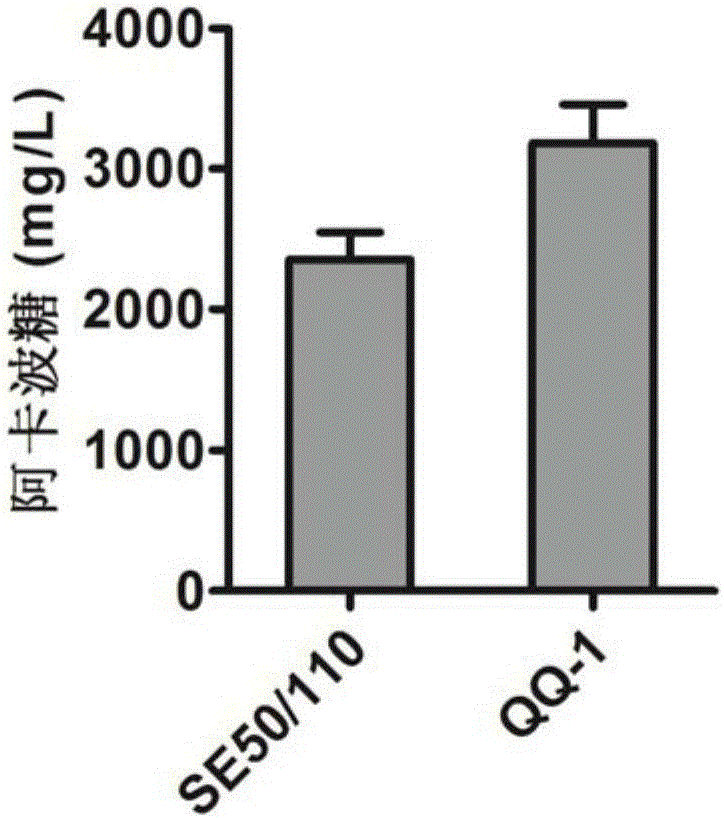
[0066] Example 2. Enhanced expression of acarbose biosynthesis gene cluster
[0067]A. Construction and screening of a fosmid plasmid containing a complete acb cluster: extract the genomic gDNA of Actinoplanes sp., blow it with a yellow pipette tip, randomly interrupt the gDNA, fill in the end, and use low melting point agar after 5' phosphorylation Sugar recovery fragments with a length of 40kb were ligated and embedded with Copycontrol pCC1FOS vector, and transfected into EPI300-TI R Plating cells, using the genes (acbM, acbZ, acbD) located in the middle and both ends of the acb cluster as selection markers, were screened to obtain the Fosmid plasmid 31F6 containing the complete acarbose biosynthesis gene cluster. The attP-int-oriT-aac(3) IV element from pSET152 was integrated into fosmid plasmid 31F6 by PCR targeting to obtain pLQ666, which was transformed into E.coli ET12567 (pUZ8002).
[0068] Conjugative transfer of B.E.coli ET12567::pLQ666 to Actinoplane spp.
[0069]...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Example 3. Construction of replicating plasmid pLQ-752
[0095] A. Replacement of thiostrepton resistance selection marker
[0096] Using apr-1278-F / R as a primer and pSET152 as a template, the apramycin resistance gene aac(3)IV and its promoter fragment were obtained by PCR amplification, with AflII and NheI restriction enzymes at both ends At the same time, using OriT-F / R as primers and pJTU1278 as a template, amplify a 986bp fragment including the oriT element, two segments containing NheI and AflII restriction sites, and insert them with NdeI after digestion and pJTU1278 digested with NheI to obtain recombinant plasmid pLQ750.
[0097] B. Insert reverse screening marker CodA(sm)
[0098] The codA(sm) gene was amplified from pWHU2573 with codA-F / R primers, both ends contained AflII restriction sites, and inserted into pLQ750 after AflII restriction to obtain recombinant plasmid pLQ752. The primer sequences are shown in Table 6, and the construction process is as f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com