Elastin-like silk fiber porous composite material and application thereof
A porous composite material and elastin-like technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of small pore size, unfavorable cell tissue ingrowth, biological inertness and non-degradability, which are difficult to shape and limit applications, and achieve porosity. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
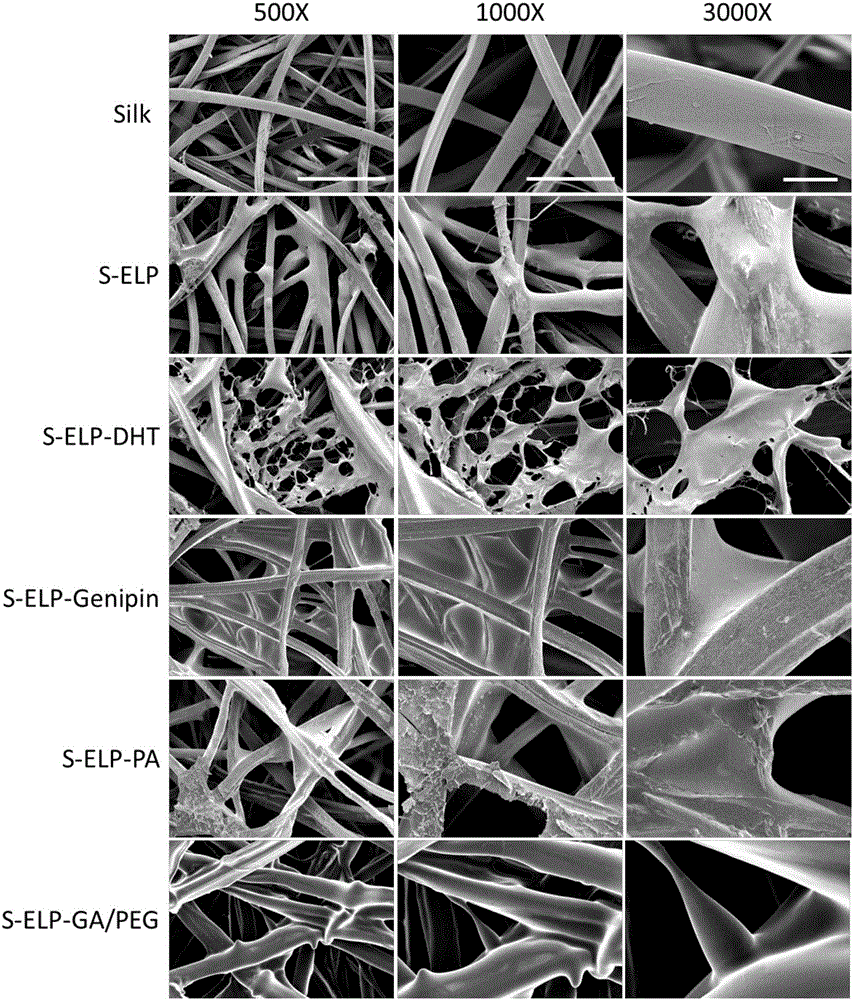
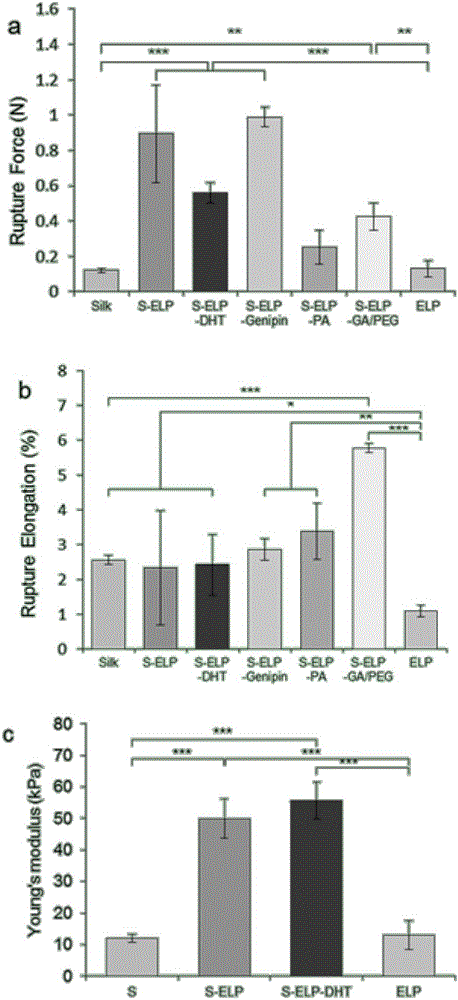
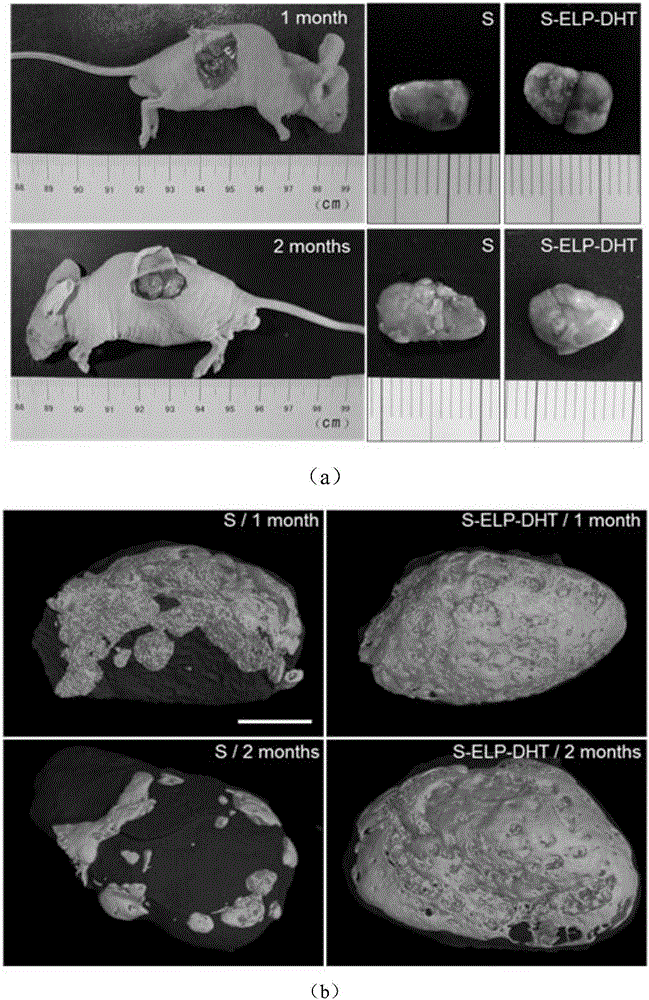
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment provides a preparation method of elastin-like silk fiber porous composite material, the specific steps are:
[0037] Cut B.mori cocoons into pieces and dry them, store them in a desiccator, use deionized water as a solvent, prepare 1.9M sodium carbonate solution, heat to 100°C, soak the dried cocoon pieces in boiling sodium carbonate solution After taking it out, ultrasonically clean it 3 times with deionized water (10 minutes / time), dialyze with deionized water to remove salt, and then dry to obtain silk fibers (or you can also cut B.mori cocoons into pieces and place them in deionized In deionized water, after boiling for 0.5 to 24 hours under the condition of higher than atmospheric pressure, the silk fibers are taken out and dried and stored);
[0038]10 mg of freeze-dried silk fibers were immersed in 1 mL of elastin-like protein solution with a mass concentration of 1% and freeze-dried to shape, which was designated as S-ELP. After that, S-ELP was c...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment provides a preparation method of elastin-like silk fiber porous composite material, the specific steps are:
[0041] Cut B.mori cocoons into pieces and dry them, store them in a desiccator, use deionized water as solvent, prepare 1M hydrochloric acid solution, heat to 100°C, soak the dried cocoon pieces in boiling hydrochloric acid solution for 24 hours , after taking it out, use deionized water to ultrasonically clean it 3 times (10 minutes / time), use deionized water to dialyze and desalinate and then dry to obtain silk fiber;
[0042] Submerge 10 mg of freeze-dried silk fiber in 1 mL of elastin-like protein solution with a mass concentration of 0.01%, freeze-dry and form it, then immerse it in a genipin solution with a mass concentration of 0.01%, and react at 4°C for 48 hours to obtain a genipin cross-linked composite material (recorded as S-ELP-Genipin), washed with deionized water for 3 times, vacuum-dried, and sealed at 4°C.
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment provides a preparation method of elastin-like silk fiber porous composite material, the specific steps are:
[0045] Cut B.mori silkworm cocoons into pieces and dry them, store them in a desiccator, use deionized water as solvent, prepare 0.01M sodium hydroxide solution, heat to 100°C, soak the dried silkworm cocoons in boiling hydroxide Sodium solution for 30 minutes, after taking it out, use deionized water to ultrasonically clean it 3 times (10 minutes / time), use deionized water to dialyze and desalinate and then dry to obtain silk fiber;
[0046] Submerge 10 mg of freeze-dried silk fiber in 1 mL of elastinoid solution (prepared with deionized water) with a mass concentration of 1% and lyophilize it, denoting it as S-ELP, and immerse the lyophilized S-ELP in 2% proanthocyanidin In the solution (prepared with deionized water), the proanthocyanidin cross-linked composite material (S-ELP-PA) was obtained after reacting at 37°C for 0.5 hours, washed with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com