Element-doped SiOx negative electrode composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and element doping technology, which is applied in the application field of high specific capacity lithium-ion battery anode materials, can solve problems such as difficult control of sintering temperature, and achieve good dispersion, excellent cycle performance, and excellent cycle performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Disperse silicon oxide powder in ethanol and perform ball milling until the median particle size is 3 μm, then add phosphoric acid, the weight is 5% of the mass of silicon oxide, and further mix and grind to obtain a uniformly mixed slurry; The slurry was dried to obtain powder A, and powder A was sintered at 1200°C in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere, the heating rate was 5°C / min, and sintered for 6h to obtain solid powder B. Mix powder B:artificial graphite=1:2 mass ratio, add PVP as a polymer additive, mix with a weight average molecular weight of 300,000, carry out ball milling under the condition of solvent dispersion and pulverize to a suitable particle size; the resulting slurry Drying treatment afforded C as a solid powder. Powder C is carbonized at high temperature in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere to obtain phosphorus-doped SiO x Negative material.
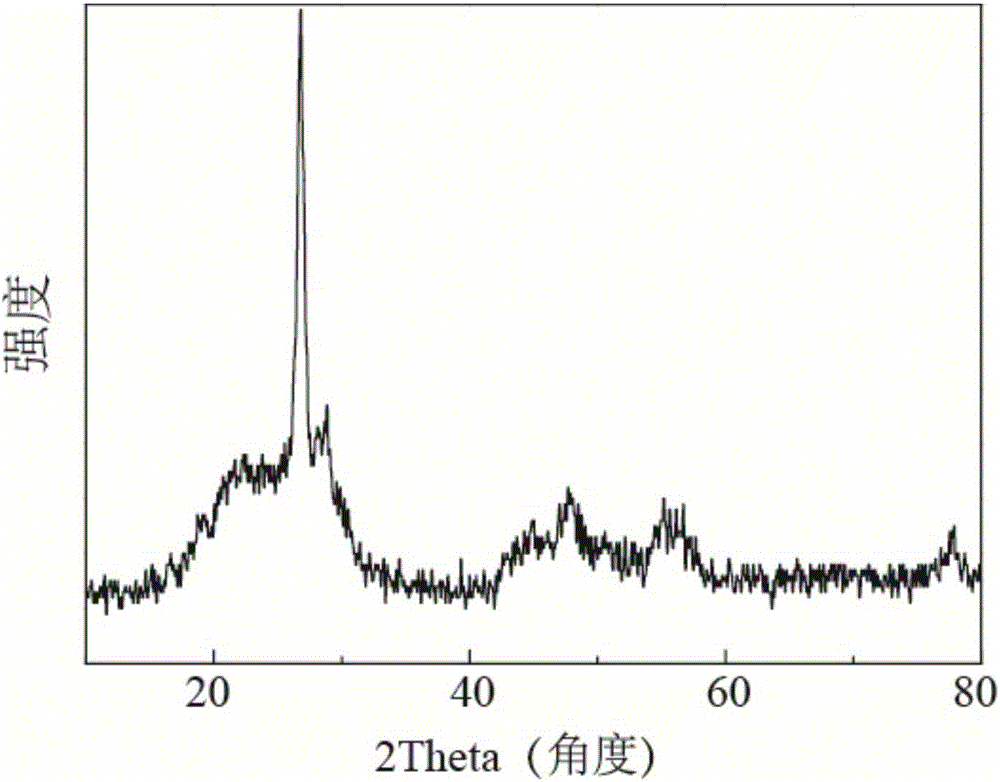
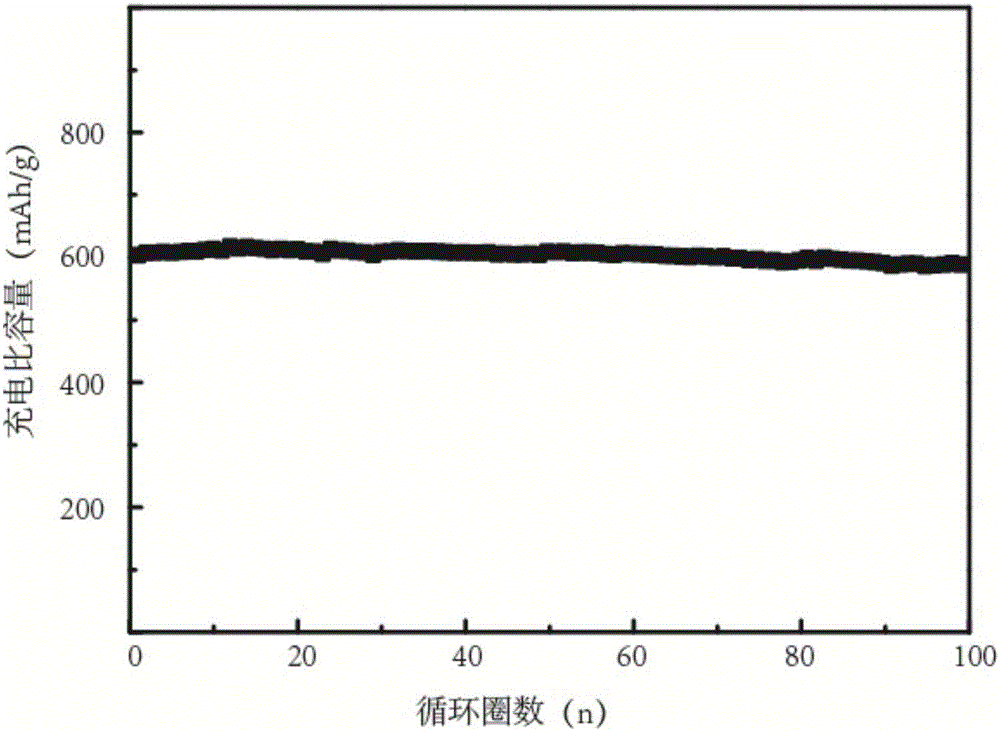
[0035] element doped SiO x Characterization of anode materials:
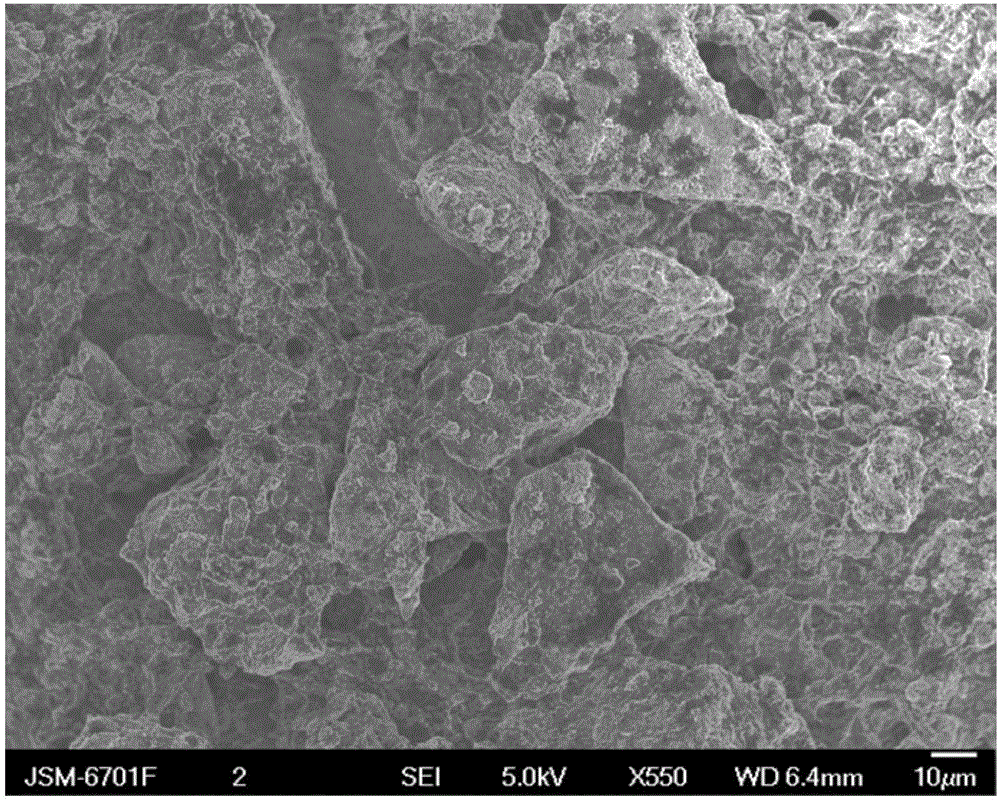
[0036] The particle size and particle...
Embodiment 2
[0040] After dispersing the silica powder in ethanol, ball milling is carried out until the median particle size is 3 μm, then phosphorus pentoxide is added, the weight is 5% of the mass of silicon oxide, further mixed and crushed to obtain a uniformly mixed slurry; The obtained slurry was dried to obtain powder A, and powder A was sintered at 400°C in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C / min for 6h to obtain solid powder B. Mix powder B:artificial graphite=1:2 mass ratio, add PVP as a polymer additive, mix with a weight average molecular weight of 300,000, carry out ball milling under the condition of solvent dispersion and pulverize to a suitable particle size; the resulting slurry Drying treatment afforded C as a solid powder. Powder C is carbonized at high temperature in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere to obtain SiO doped with element phosphorus x Negative material.
[0041] element doped SiO x The characterization of the negative electrode mater...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Disperse silicon oxide powder in ethanol and perform ball milling until the median particle size is 3 μm, then add boron oxide with a weight of 5% of the mass of silicon oxide, and further mix and grind to obtain a uniformly mixed slurry; The slurry was dried to obtain powder A, and powder A was sintered at 500°C in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C / min for 6h to obtain solid powder B. Mix powder B:artificial graphite=1:2 mass ratio, add PVP as a polymer additive, mix with a weight average molecular weight of 350,000, carry out ball milling and mixing under the condition of solvent dispersion and pulverize to a suitable particle size; the obtained slurry Drying treatment afforded C as a solid powder. Powder C is carbonized at high temperature in an inert pure nitrogen atmosphere to obtain boron-doped SiO x Negative material.
[0046] element doped SiO x The characterization of the negative electrode material is the same as in Example 1.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com