Special primer for identifying gummy stem blight resistance of muskmelon and molecular marking method
A molecular marker, vine blight technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of inaccurate identification of vine blight resistance, heavy workload, etc., and achieve the goal of improving breeding efficiency, speeding up breeding, saving time and labor costs. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: the extraction of test material and genomic DNA
[0028] Melon material for test
[0029] All of them are melon high-generation inbred strain materials, which are the offspring of the melon material PI482398 and Baipicrisp, and the hybridization of the two. Among them, PI482398 is derived from the National Plant Seed Resource System of the United States Department of Agriculture. Melon planting resources; Baipicris is native to Xinjiang, and it is a high-quality and conventional variety that is susceptible to vine blight. Crossbreed PI482398 and Baipicria as the female parent and male parent respectively, and select and breed among the hybrid offspring to obtain high-generation inbred lines A, B, C, D, E, F, G with different resistance to vine blight , H, used together with PI482398 and Baipicui to detect the resistance of muskmelon materials to vine blight by molecular markers.
[0030] Extraction of Genomic DNA from the Tested Melon Materials
[0031]...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Screening of molecular markers and design of special primers
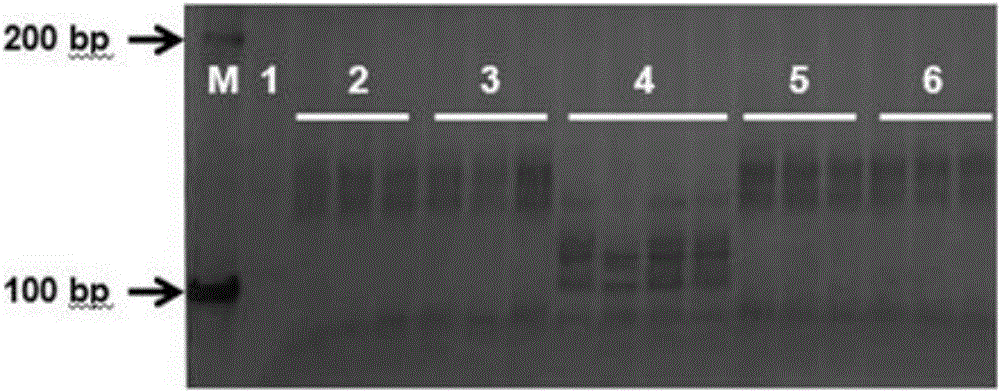
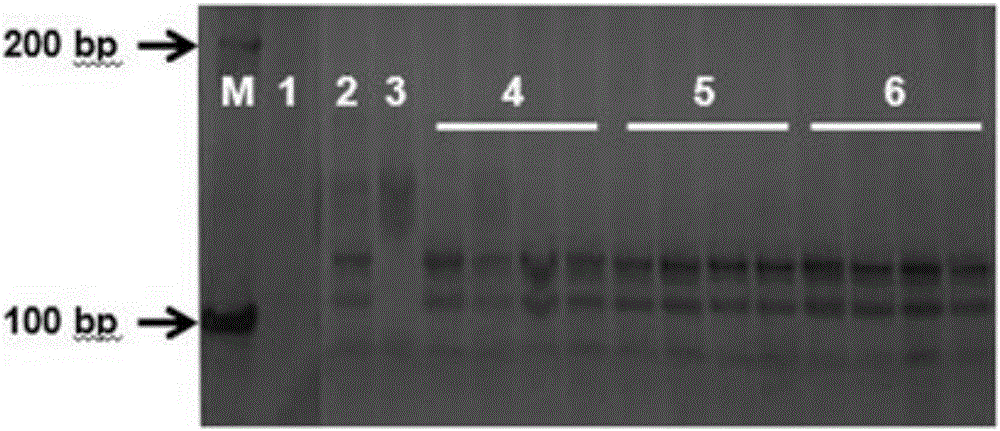
[0033] Using high-throughput sequencing technology, two muskmelon lines identified as PI482398, which are resistant to creeping blight and Baipicriu, which are susceptible to creeping blight, were resequenced and compared, and the obtained SSR molecular markers were compared with those of Previously, the germplasm resources of muskmelon resistant to creeping blight and related molecular markers were compared to find markers at similar chromosomal positions. At both ends of the molecular markers, special primers were designed. The length of the primers was selected to be 20-26 bp, and the annealing temperature was 58-60 °C, the GC content is between 40% and 60%.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: PCR amplification obtains target fragment
[0035] Using the genomic DNA of the sample to be tested extracted in Example 1 as a template and the molecular marker-specific primers designed in Example 2 as primers, perform PCR amplification to obtain the target fragment of the molecular marker. The reaction system of PCR amplification adopts the reaction system of 10 μ L, and the composition of described mixed solution is as follows:
[0036]
[0037] The reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, denaturation at 57°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s, 35 cycles; final extension at 72°C for 5 min; storage at 4°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com