Clostridium beijerinckii for producing butanol from xylose and its application
A technology for the production of butanol by Clostridium beijerinckii, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the utilization rate of cellulose substrates, losing the ability to produce butanol, and weak xylose utilization ability , to achieve breakthroughs in low substrate utilization, high-efficiency production, and solve the effect of low substrate utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] The breeding steps of high-yield butanol strain (Clostridium beijerinckii) 51543 are as follows:
[0018] (1) Collection of soil samples: Use a small shovel to dig off the soil surface, collect about 20g of soil at about 10cm from the surface, then put the collected soil samples in disposable gloves and seal them, and use toilet paper before and after each soil sample collection Wipe the small shovel clean and collect a total of 100 soil samples (32 of which were taken from the surrounding areas of Tianjin and 68 from all over China).
[0019] (2) Enrichment of strains: At room temperature, weigh about 1g from 100 parts of soil and inoculate them into 100 parts of 10ml screw-lock test tubes containing 10ml of xylose medium (xylose medium (1L): Yeast powder 5g, CaCO 3 3g, superphosphate 0.7g, (NH 4 )2SO 4 3g xylose, 30g xylose, natural pH, 121°C for 21min), mix upside down, heat shock at 80°C for 10min, cool to room temperature with running water, and incubate in a 30...
Embodiment 2
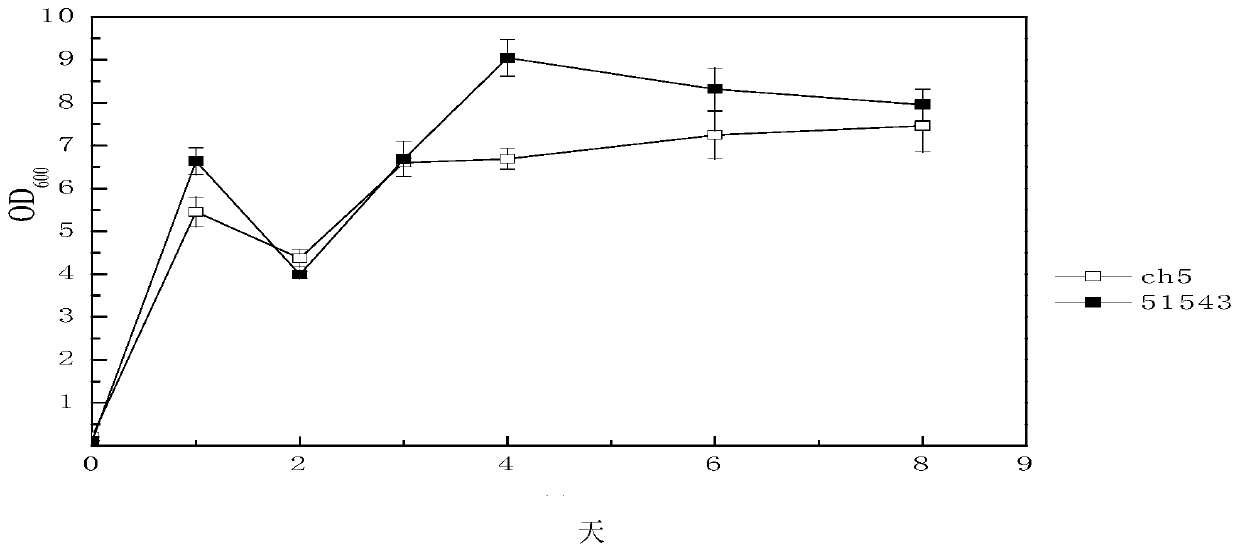
[0058] Comparison of the growth of the 51543 strain with the original strain under static conditions
[0059] 1. Test materials: 51543 strain; original strain (Clostridium beijerinckii) CH5.
[0060] 2. Experimental method:
[0061] Seed medium (g / l): yeast powder 5, CaCO 3 3. Superphosphate 0.7, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 3. Natural pH, sterilized at 121°C for 21 minutes, adding xylose to make the final concentration reach 30g / l before inoculation. Separate sterilization: xylose mother liquor 200g / l, sterilized at 110°C for 18min.
[0062] Fermentation medium (g / l): beef extract 2, yeast powder 2, tryptone 6, ammonium acetate 3, K 2 HPO 4 0.5, pH 6.5, sterilized at 121°C for 21 minutes, added before fermentation to make the final concentration of xylose 40g / l. Separate sterilization: xylose mother liquor 200g / l, sterilized at 110°C for 18min, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.01 filter sterilized.
[0063] Inoculate 500ul of the 51543 strain and the starting strain (store...
Embodiment 3
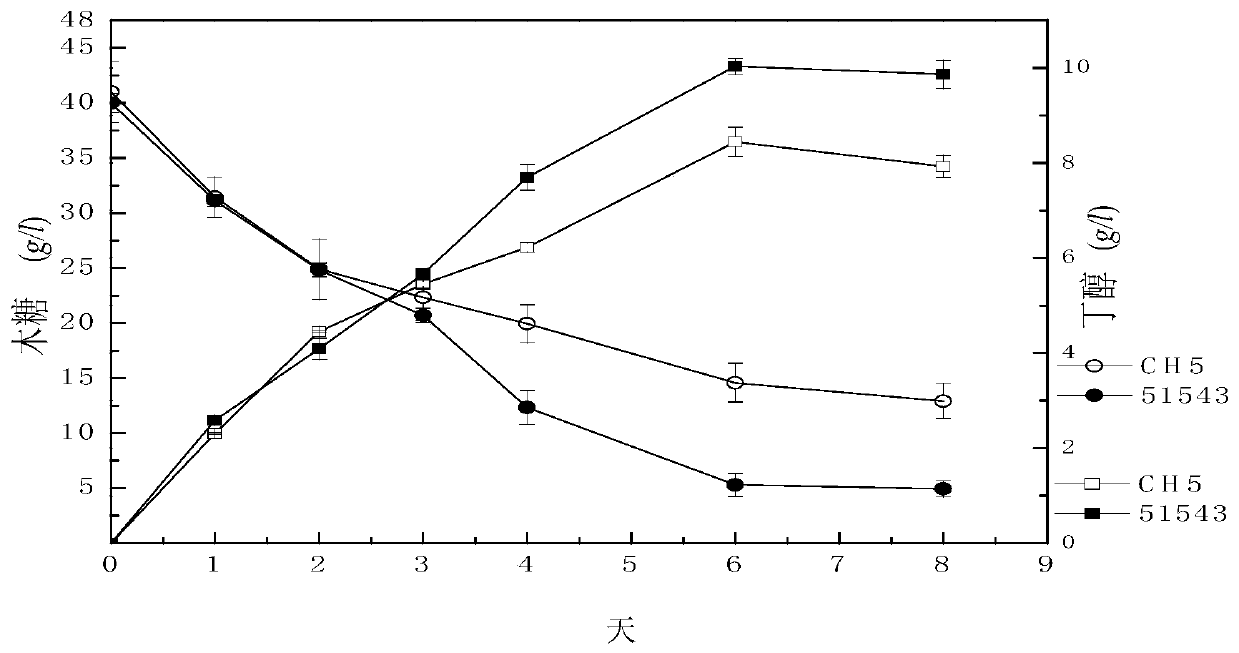
[0069] Comparison of the fermentation curves of the 51543 strain with the original CH5 strain under static conditions
[0070] 1. Experimental material: same as embodiment 2
[0071] 2. Experimental method: seed culture medium, fermentation medium are the same as embodiment 2
[0072] Inoculate 500ul of the 51543 strain and the starting strain (stored in a glycerol tube at -20°C) into 10ml seed medium, heat shock at 80°C for 10min, cool with running water and then culture at a constant temperature of 30°C for 16h, the OD is about 2. Inoculate in TYA medium with 5% inoculum amount, incubate at 30°C for 16 hours, OD is 2. Inoculate in a 250ml screw-lock conical flask containing 150ml with initial cell concentration OD600=0.1, and inoculate at 30°C Cultivate and measure the concentration of xylose, butanol, isopropanol, ethanol, butyric acid, and acetic acid in the bacteria.
[0073] 3. Analytical method: xylose concentration, butanol concentration, isopropanol concentration, e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com